|
Quinpirole
Quinpirole is a psychoactive drug and research chemical which acts as a selective D2 and D3 receptor agonist. It is used in scientific research. Quinpirole has been shown to increase locomotion and sniffing behavior in mice treated with it. At least one study has found that quinpirole induces compulsive behavior symptomatic of obsessive compulsive disorder in rats. Another study in rats show that quinpirole produces significant THC-like effects when metabolic degradation of anandamide is inhibited, supporting the hypothesis that these effects of quinpirole are mediated by cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Quinpirole may also reduce relapse in adolescent rat models of cocaine addiction. Experiments in flies found quinpirole may have neuroprotective effects against Parkinson's disease-like pathology. Moreover, in primary neuronal cultures it also reduces the rate of firing in dopaminergic neurons. See also * Quinelorane Quinelorane is a drug which acts as a dopamine agonist A do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinelorane
Quinelorane is a drug which acts as a dopamine agonist A dopamine agonist (DA) is a compound that activates dopamine receptors. There are two families of dopamine receptors, D2-like and D1-like, and they are all G protein-coupled receptors. D1- and D5-receptors belong to the D1-like family and the ... for the D2 and D3 receptor. See also * Quinpirole References Dopamine agonists Aminopyrimidines {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D2 Receptor
Dopamine receptor D2, also known as D2R, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''DRD2'' gene. After work from Paul Greengard's lab had suggested that dopamine receptors were the site of action of antipsychotic drugs, several groups, including those of Solomon Snyder and Philip Seeman used a radiolabeled antipsychotic drug to identify what is now known as the dopamine D2 receptor. The dopamine D2 receptor is the main receptor for most antipsychotic drugs. The structure of DRD2 in complex with the atypical antipsychotic risperidone has been determined. Function D2 receptors are coupled to Gi subtype of G protein. This G protein-coupled receptor inhibits adenylyl cyclase activity. In mice, regulation of D2R surface expression by the neuronal calcium sensor-1 (NCS-1) in the dentate gyrus is involved in exploration, synaptic plasticity and memory formation. Studies have shown potential roles for D2R in retrieval of fear memories in the prelimbic cortex and in discrimin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D3 Receptor
Dopamine receptor D3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DRD3'' gene. This gene encodes the D3 subtype of the dopamine receptor. The D3 subtype inhibits adenylyl cyclase through inhibitory G-proteins. This receptor is expressed in phylogenetically older regions of the brain, suggesting that this receptor plays a role in cognitive and emotional functions. It is a target for drugs which treat schizophrenia, drug addiction, and Parkinson's disease. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants that would encode different isoforms, although some variants may be subject to nonsense-mediated decay (NMD). Function Alpha-synuclein (α-Syn) aggregation via Lewy bodies inclusion, a pathogenic signature exclusively present in PD patients, is decreased by D3 agonists while DA content is elevated by inhibiting DA reuptake and breakdown. The regulation of α-Syn aggregation and clearance enhances brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) secretion, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychoactive Drug
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior. These substances may be used medically, recreationally or spiritually to a. Purposefully improve one’s perceived performance b. Alter one's consciousness (such as with entheogens for ritual, spiritual or shamanic purposes) or c. For research. Some categories of psychoactive drugs - which are believed, by some, to have therapeutic value - may be prescribed by some physicians and other healthcare practitioners. Examples of medication categories that may contain potentially beneficial psychoactive drugs include, but are not limited to: # Anesthetics # Analgesics # Anticonvulsants # Anti-Parkinson’s medications # Medications used to treat Neuropsychiatric Disorders a. Antidepressants b. Anxiolytics c. Antipsychotics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anandamide
Anandamide (ANA), also known as ''N''-arachidonoylethanolamine (AEA), is a fatty acid neurotransmitter. Anandamide was the first endocannabinoid to be discovered: it participates in the body's endocannabinoid system by binding to cannabinoid receptors, the same receptors that the psychoactive compound THC in cannabis acts on. Anandamide is found in nearly all tissues in a wide range of animals. Anandamide has also been found in plants, including small amounts in chocolate. The name 'anandamide' is taken from the Sanskrit word '' ananda'', which means "joy, bliss, delight", plus amide. Anandamide is derived from the non-oxidative metabolism of arachidonic acid, an essential omega-6 fatty acid. It is synthesized from ''N''-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine by multiple pathways. It is degraded primarily by the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) enzyme, which converts anandamide into ethanolamine and arachidonic acid. As such, inhibitors of FAAH lead to elevated anandamide leve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms become more common. The most obvious early symptoms are tremor, rigidity, slowness of movement, and difficulty with walking. Cognitive and behavioral problems may also occur with depression, anxiety, and apathy occurring in many people with PD. Parkinson's disease dementia becomes common in the advanced stages of the disease. Those with Parkinson's can also have problems with their sleep and sensory systems. The motor symptoms of the disease result from the death of cells in the substantia nigra, a region of the midbrain, leading to a dopamine deficit. The cause of this cell death is poorly understood, but involves the build-up of misfolded proteins into Lewy bodies in the neurons. Collectively, the main motor symptoms are also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroprotective
Neuroprotection refers to the relative preservation of neuronal structure and/or function. In the case of an ongoing insult (a neurodegenerative insult) the relative preservation of neuronal integrity implies a reduction in the rate of neuronal loss over time, which can be expressed as a differential equation. It is a widely explored treatment option for many central nervous system (CNS) disorders including neurodegenerative diseases, stroke, traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury, and acute management of neurotoxin consumption (i.e. methamphetamine overdoses). Neuroprotection aims to prevent or slow disease progression and secondary injuries by halting or at least slowing the loss of neurons. Despite differences in symptoms or injuries associated with CNS disorders, many of the mechanisms behind neurodegeneration are the same. Common mechanisms of neuronal injury include decreased delivery of oxygen and glucose to the brain, energy failure, increased levels in oxidative stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
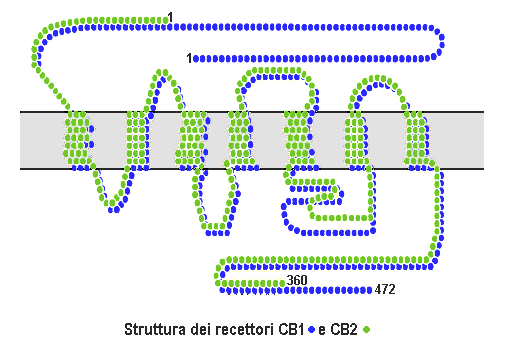
Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1
Cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1), also known as cannabinoid receptor 1, is a G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''CNR1'' gene. The human CB1 receptor is expressed in the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system. It is activated by: endocannabinoids, a group of retrograde neurotransmitters that include anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG); plant phytocannabinoids, such as the compound THC which is an active ingredient of the psychoactive drug cannabis; and, synthetic analogs of THC. CB1 is antagonized by the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV). The primary endogenous agonist of the human CB1 receptor is anandamide. Structure The CB1 receptor shares the structure characteristic of all G-protein-coupled receptors, possessing seven transmembrane domains connected by three extracellular and three intracellular loops, an extracellular N-terminal tail, and an intracellular C-terminal tail. The receptor may exist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinoid Receptor
Cannabinoid receptors, located throughout the body, are part of the endocannabinoid system a class of cell membrane receptors in the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. As is typical of G protein-coupled receptors, the cannabinoid receptors contain seven transmembrane spanning domains. Cannabinoid receptors are activated by three major groups of ligands: endocannabinoids; plant cannabinoids (such as Tetrahydrocannabinol, produced by the cannabis plant); and synthetic cannabinoids (such as HU-210). All of the endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids (plant based cannabinoids) are lipophilic. There are two known subtypes of cannabinoid receptors, termed CB1 and CB2. The CB1 receptor is expressed mainly in the brain (central nervous system or "CNS"), but also in the lungs, liver and kidneys. The CB2 receptor is expressed mainly in the immune system, in hematopoietic cells, and in parts of the brain. The protein sequences of CB1 and CB2 receptors are about 44% similar. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Obsession may refer to: Psychology * Celebrity worship syndrome, obsessive addictive disorder to a celebrity's personal and professional life * Fixation (psychology), a persistent attachment to an object or idea * Idée fixe (psychology), a preoccupation of mind believed to be firmly resistant to any attempt to modify it * Obsessive love, an overwhelming, obsessive desire to possess another person * Obsessive–compulsive disorder, an anxiety disorder characterized by obsessive thoughts Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Ossessione'' (1943), an Italian crime drama * ''Obsession'' (1949 film), a British thriller also released as ''The Hidden Room'' * ''Obsession'' (1954 film), a French-language crime drama * ''Obsession'' (1976 film), a psychological thriller/mystery directed by Brian De Palma * ''Obsession'' (1997 film), a Franco-German drama starring Daniel Craig * ''Obsession'' (2022 film), a Nigerian drama * '' Circle of Two'', 1981 Canadian drama also distributed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term ''THC'' usually refers to the Delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-''trans''-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. THC is a lipid found in cannabis and, like most pharmacologically active secondary metabolites of plants, it is assumed to be involved in the plant's evolutionary adaptation, putatively against insect predation, ultraviolet light, and environmental stress. THC was first discovered and isolated by Israeli chemist Raphael Mechoulam in Israel in 1964. It was found that, when smoked, THC is absorbed into the bloodstream and travels to the brain, attaching itself to endocannabinoid receptors located in the cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and basal ganglia. These are the parts of the brain responsible for thinking, memory, pleasure, coordination a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Chemical
Research chemicals are chemical substances used by scientists for medical and scientific research purposes. One characteristic of a research chemical is that it is for laboratory research use only; a research chemical is not intended for human or veterinary use. This distinction is required on the labels of research chemicals, and is what exempts them from regulation under parts 100-740 in Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations ( 21CFR). Background Pharmacological research chemicals Research chemicals are fundamental in the development of novel pharmacotherapies. Common medical laboratory uses include ''in vivo'' and animal testing to determine therapeutic value, toxicology testing by contract research organizations to determine drug safety, and analysis by drug test and forensic toxicology labs for the purposes of evaluating human exposure. Many pharmacologically active chemicals are sold online under the guise of "research chemicals," when in reality they are untested d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |