|
Queen Munjeong
Queen Munjeong (Hangul: 문정왕후, Hanja: 文定王后; 2 December 1501 – 5 May 1565), of the Papyeong Yun clan, was a posthumous name bestowed to the wife and third queen consort of Yi Yeok, King Jungjong. She was queen consort of Joseon from 1517 until her husband's death in 1544, after which she was honoured as Queen Dowager Seongryeol (성렬왕대비) during the reign of her step-son, Yi Ho, King Injong. She was honored as Grand Queen Dowager Seongryeol (성렬대왕대비) during the reign of her son, Yi Hwan, King Myeongjong. Queen Munjeong acted as regent during the minority of her son between 1545 and 1553. She was an effective administrator and the most influential supporter of Buddhism during the early Joseon dynasty. She gave out the land to the common people that had been formerly owned by the nobility. During her regency, her brother, Yun Won-hyeong, wielded enormous power to wipe out their opposition and led the Fourth Literati Purge of 1545. Life Early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goryeo
Goryeo (; ) was a Korean kingdom founded in 918, during a time of national division called the Later Three Kingdoms period, that unified and ruled the Korean Peninsula until 1392. Goryeo achieved what has been called a "true national unification" by Korean historians as it not only unified the Later Three Kingdoms but also incorporated much of the ruling class of the northern kingdom of Balhae, who had origins in Goguryeo of the earlier Three Kingdoms of Korea. The name "Korea" is derived from the name of Goryeo, also spelled Koryŏ, which was first used in the early 5th century by Goguryeo. According to Korean historians, it was during the Goryeo period that the individual identities of Goguryeo, Baekje, and Silla were successfully merged into a single entity that became the basis of modern-day 'Korean' identity. Throughout its existence, Goryeo, alongside Unified Silla, was known to be the "Golden Age of Buddhism" in Korea. As the state religion, Buddhism achieved its highes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
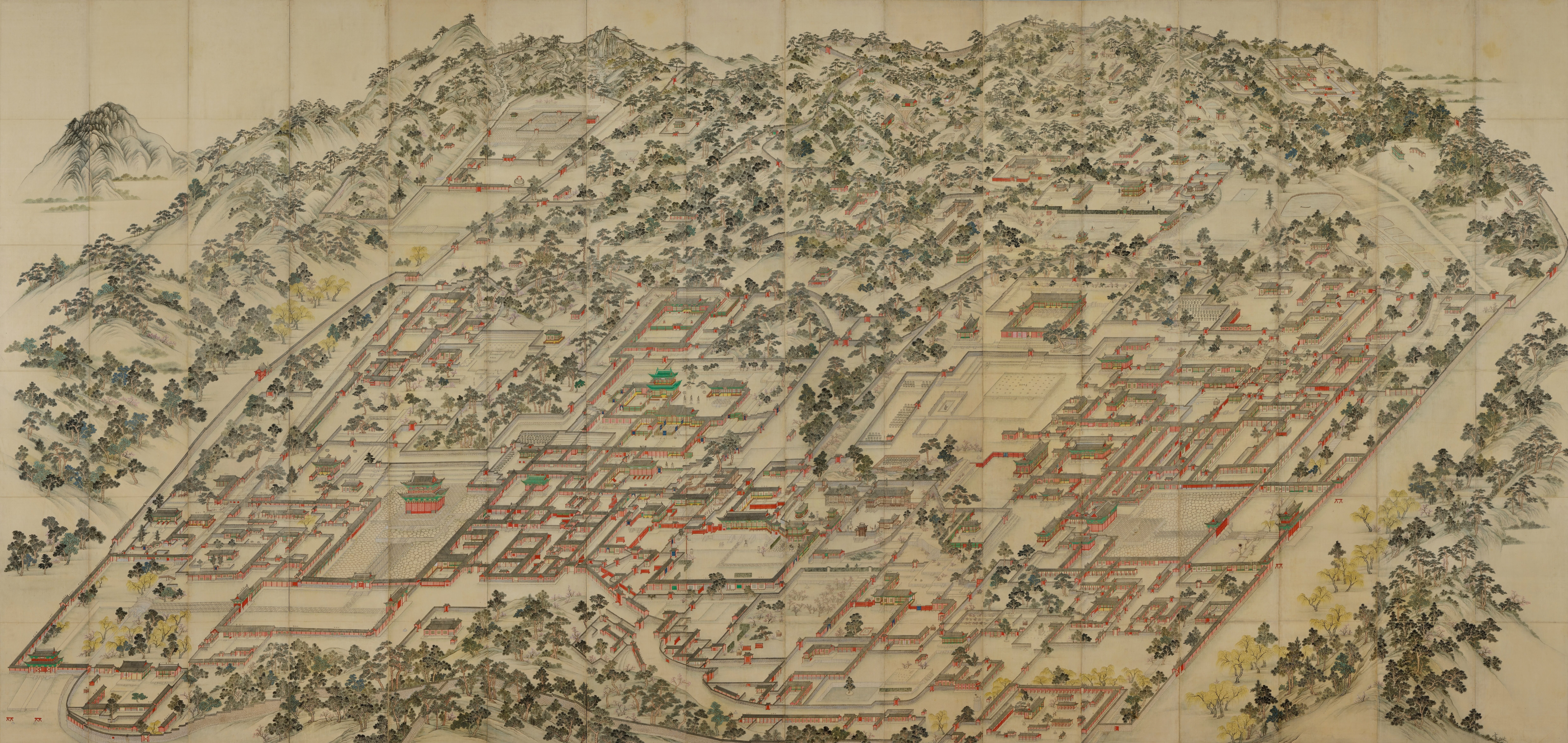
Changdeokgung
Changdeokgung (Hangul: 창덕궁, Hanja: 昌德宮; literally, "The Palace of Prospering Virtue"), also known as Changdeokgung Palace or Changdeok Palace, is set within a large park in Jongno District, Seoul, South Korea. It is one of the "Five Grand Palaces" built by the kings of the Joseon dynasty (1392–1897). As it is located east of Gyeongbok Palace, Changdeokgung—along with Changgyeonggung—is also referred to as the "East Palace" (동궐, 東闕, ''Donggwol''). Changdeokgung was the most favored palace of many Joseon kings and retained many elements dating from the Three Kingdoms of Korea period that were not incorporated in the more contemporary Gyeongbokgung. One such element is the fact that the buildings of Changdeokgung blend with the natural topography of the site instead of imposing themselves upon it. Like the other Five Grand Palaces in Seoul, it was heavily damaged during the Japanese occupation of Korea (1910–1945). Currently, only about 30% of the pre-Japa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yun Im
Yun Im (윤임, 尹任; 26 July 1487 - 30 August 1545) was a politician, general, and soldier of the Korean Joseon Dynasty. He was from the aristocratic family of the Papyeong Yun clan (파평 윤씨, 波平 尹氏), and related to the Royal Jeonju Yi clan through his mother. He was the older brother of Queen Janggyeong (Joseon), Queen Janggyeong, the second wife of King Jungjong of Joseon, and the uncle of King Injong of Joseon. He was also the nephew of Bak Wonjong, Park Won-jong, and was titled as Prince Paeun.(파은군, 波恩君) Family * Father − Yun Yeo-Pil (1466 – 1555) (윤여필, 尹汝弼) * Uncle - Yun Yeo-hae (윤여해, 尹汝諧) ** 1) Grandfather − Yun Bo (? – 1494) (윤보, 尹甫) *** 2) Great-Grandfather − Yun Sa-yoon (윤사윤, 尹士昀) (1409 - 7 December 1461); Queen Jeonghui’s second older brother **** 3) Great-Great-Grandfather − Yun Byeon (윤번, 尹璠) (1384 - 1448); Queen Jeonghui’s father ***** 4) Great-Great-Great-Grandfather � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Dangyeong
Queen Dangyeong (7 February 1487 – 27 December 1557), of the Geochang Shin clan, was a posthumous name bestowed to the wife and first queen consort of Yi Yeok, King Jungjong, the 11th Joseon monarch. She was queen consort of Joseon for seven days in September 1506, after which she was known as Deposed Queen Shin (폐비 신씨). Life The future Queen was born on 7 February 1487 during the reign of King Seongjong. Her father, Shin Soo-geun was member of the Geochang Shin clan. Her paternal aunt, Queen Jeinwondeok, was King Yeonsangun's primary consort. Her mother, Shin Soo-geun's second wife, was member of the Cheongju Han clan. In 1499 at the age of 13, she married the 12-year-old Grand Prince Jinseong, Seongjong's only son. Through her mother, Lady Shin is a first cousin thrice removed of her husband. As grand prince's wife, she received title the ''Bubuin'' (Hangul: 부부인, Hanja: 府夫人). Her mother was given the royal title of “Internal Princess Consort Cheongwon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarim
The Sarim (sometimes Saarim), or "forest of scholars", was a powerful faction of literati that dominated Middle and Late Joseon politics in Korea. History of Sarim faction Early beginning The philosophical lineage of the Sarim scholars originated from the neo-Confucian school of Gil Jae (1353–1419), a Goryeo scholar who studied under Yi Saek and Jeong Mong-ju. After the fall of the Goryeo dynasty, he retreated to his home village refusing to serve the new Joseon dynasty despite King Taejong's request. Gil Jae concentrated on cultivating a new generation of neo-Confucian scholars including Kim Suk-ja and his son Kim Jong-jik. When King Seongjong became the ninth king of Joseon, he invited Kim Jong-jik and his disciples, who came to be called Sarim scholars, to his court and supported their political growth. They primarily served in so-called Three Offices, from which challenged the entrenched "Hungu" officials, who accumulated great power and wealth by supporting King Sejo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kim Ahn-ro
Kim Ahn-ro ( ko, 김안로, 金安老; 1481 – 27 October 1537) was a Korean Joseon Dynasty politician and scholar. His pen name was Huirakdang, Yongcheon, Toejae, and his customary name was Yisuk. He was from the Yeonan Kim clan. Family * Great-Grandfather ** Kim Hae (김해, 金侅) * Grandfather ** Kim Woo-shin (김우신, 金友臣) * Grandmother ** Lady Lee of the Incheon Lee clan The Incheon Yi clan (Hangul: 인천 이씨, Hanja: 仁川 李氏) is a Korean clan. Historically known as the Gyeongwon Lee clan or Inju Lee clan, it was one of the most powerful clans in the early Goryeo period due their status as in-laws of th ... (이천 이씨) * Father ** Kim Heun (김흔, 金訢) (1448 - 1492) ** Uncle - Kim Sim (김심, 金諶) ** Uncle - Kim Jeon (김전, 金詮) (1458 - 1523) ** Aunt - Lady No of the Pungcheon No clan (풍천 노씨) ** Aunt - Lady Song of the Jincheon Song clan (진천 송씨) *** Cousin - Kim Ahn-do (김안도, 金安道) *** Cousin - Kim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeonsangun Of Joseon
Yeonsangun of Joseon or Prince Yeonsan of Joseon (23 November 1476 – 20 November 1506), personal name Yi Yung (Korean: 이융; Hanja: 李㦕), was the tenth ruler of the Joseon dynasty of Korea. Often considered the worst tyrant in Joseon's history and perhaps all Korean history, he is notorious for launching two bloody purges, seizing hundreds of women from all over the peninsula to serve as palace entertainers, and appropriating Sungkyunkwan as a personal pleasure ground. Yeonsangun's despotic rule provided a stark contrast to the liberal era of his father, and as a much-despised overthrown monarch, he did not receive a temple name. Biography Execution of his mother Lady Yun, later known as the Deposed Queen Yun, served Yeonsangun's father, King Seongjong, as a concubine until the death of Queen Gonghye, Seongjong's first wife. With no heir, the king was urged by counselors to take a second wife to secure the royal succession. Lady Yun was chosen for her beauty and was f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Literati Purges
The term "Literati purges" is a translation of the Korean term 'sahwa' ( ko, 사화 士禍), whose literal meaning is "scholars' calamity". It refers to a series of political purges in the late 15th and 16th centuries, in which Sarim scholars suffered persecution at the hands of their political rivals. The politics of the Middle Joseon Dynasty were primarily marked by a power struggle between two social groups among the yangban aristocracy. People in place were the 'Meritorious Subjects', rewarded for helping the establishment of Joseon against the former Goryeo, and subsequent accomplishments. Referred as the Hungu faction (Hungupa, 훈구파, 勳舊派), they held the key positions in the State Council and the Six Ministries that carried out state affairs. The newcomers were the so-called Sarim (Sarimpa, 사림파, 士林派), who belonged to the neo-Confucian school of Kim Jong-jik and other thinkers. The Sarim scholars generally shunned the royal court and studied neo-Confu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yun Won-hyeong
Yun Won-hyeong ( ko, 윤원형, 尹元衡; 1503 – 18 November 1565) was a Korean political figure of the Joseon period. He was the younger brother of Queen Munjeong, the 3rd wife of 11th King Jungjong and was the maternal uncle of the 13th King Myeongjong. He was Chief State Councillor from 1563 to 1565. His courtesy name was ''Eonpyung'' (언평; 彦平). In 1565, after the death of Queen Munjeong, both Yun Won-hyeong and his wife Jeong Nan-jeong were exiled from the capital. Unable to make a political comeback, both committed suicide by poison. Life In 1503, Yun Won-hyeong was born as the fifth son of Yun Ji-im, father of Queen Munjung and third cousin of Queen Janggyeong and Yun Im. He was also the great-great-grandnephew of Queen Jeonghui, who was the wife of Joseon Dynasty's 7th King Sejo of Joseon. Yun Won-hyeong was a political figure from an aristocratic family and a maternal relation of the royal family of the Joseon Dynasty. His family was of the Papyeong Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Injong Of Joseon
Injong of Joseon (10 March 1515 – 8 August 1545, r. 1544–1545), personal name Yi Ho (Hangul: 이호, Hanja: 李峼), was the 12th ruler of the Joseon Dynasty of Korea. His father was King Jungjong, and his mother was Queen Janggyeong, whose brother was Yun Im. As the firstborn, he became Crown Prince in 1520 and succeeded his father to the throne following Jungjong's death in 1544. Biography Reign The young king was very ambitious, and tried to reform the government of the time that was rife with corruption, a legacy of the failed reforms during his father's reign. He rehabilitated Jo Gwang-jo and recruited Sarim scholars who turned away from politics after Third Literati Purge of 1519. His maternal uncle Yun Im exercised great power during this period. However, Injong was too often ill and died in 1545, just one year after coming to the throne. Following his death, Yun Im was executed by Yun Won-Hyung in the Fourth Purge of 1545 when King Myeongjong (son of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanja
Hanja (Hangul: ; Hanja: , ), alternatively known as Hancha, are Chinese characters () used in the writing of Korean. Hanja was used as early as the Gojoseon period, the first ever Korean kingdom. (, ) refers to Sino-Korean vocabulary, which can be written with Hanja, and (, ) refers to Classical Chinese writing, although "Hanja" is also sometimes used to encompass both concepts. Because Hanja never underwent any major reforms, they are mostly resemble to ''kyūjitai'' and traditional Chinese characters, although the stroke orders for some characters are slightly different. For example, the characters and as well as and . Only a small number of Hanja characters were modified or are unique to Korean, with the rest being identical to the traditional Chinese characters. By contrast, many of the Chinese characters currently in use in mainland China, Malaysia and Singapore have been simplified, and contain fewer strokes than the corresponding Hanja characters. In Japan, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hangul
The Korean alphabet, known as Hangul, . Hangul may also be written as following South Korea's standard Romanization. ( ) in South Korea and Chosŏn'gŭl in North Korea, is the modern official writing system for the Korean language. The letters for the five basic consonants reflect the shape of the speech organs used to pronounce them, and they are systematically modified to indicate phonetic features; similarly, the vowel letters are systematically modified for related sounds, making Hangul a featural writing system. It has been described as a syllabic alphabet as it combines the features of alphabetic and syllabic writing systems, although it is not necessarily an abugida. Hangul was created in 1443 CE by King Sejong the Great in an attempt to increase literacy by serving as a complement (or alternative) to the logographic Sino-Korean ''Hanja'', which had been used by Koreans as its primary script to write the Korean language since as early as the Gojoseon period (spanni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |