|
Quantile
In statistics and probability, quantiles are cut points dividing the range of a probability distribution into continuous intervals with equal probabilities or dividing the observations in a sample in the same way. There is one fewer quantile than the number of groups created. Common quantiles have special names, such as '' quartiles'' (four groups), '' deciles'' (ten groups), and '' percentiles'' (100 groups). The groups created are termed halves, thirds, quarters, etc., though sometimes the terms for the quantile are used for the groups created, rather than for the cut points. -quantiles are values that partition a finite set of values into subsets of (nearly) equal sizes. There are partitions of the -quantiles, one for each integer satisfying . In some cases the value of a quantile may not be uniquely determined, as can be the case for the median (2-quantile) of a uniform probability distribution on a set of even size. Quantiles can also be applied to continuous di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quantile Function
In probability and statistics, the quantile function is a function Q: ,1\mapsto \mathbb which maps some probability x \in ,1/math> of a random variable v to the value of the variable y such that P(v\leq y) = x according to its probability distribution. In other words, the function returns the value of the variable below which the specified cumulative probability is contained. For example, if the distribution is a standard normal distribution then Q(0.5) will return 0 as 0.5 of the probability mass is contained below 0. The quantile function is also called the percentile function (after the percentile), percent-point function, inverse cumulative distribution function (after the cumulative distribution function or c.d.f.) or inverse distribution function. Definition Strictly increasing distribution function With reference to a continuous and strictly increasing cumulative distribution function (c.d.f.) F_X\colon \mathbb \to ,1/math> of a random variable , the quantile function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
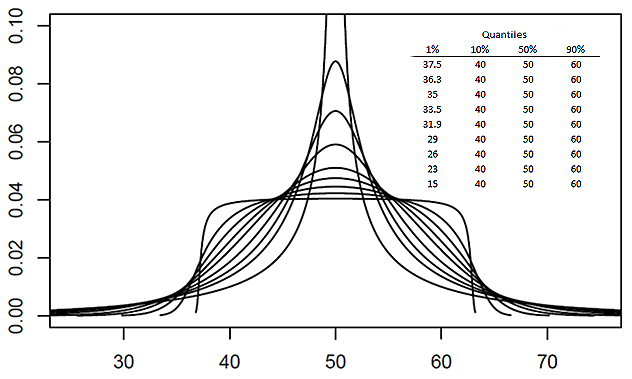
Quantile-parameterized Distribution
A quantile-parameterized distribution (QPD) is a probability distributions that is directly parameterized by data. They were created to meet the need for easy-to-use continuous probability distributions flexible enough to represent a wide range of uncertainties, such as those commonly encountered in business, economics, engineering, and science. Because QPDs are directly parameterized by data, they have the practical advantage of avoiding the intermediate step of Estimation theory, parameter estimation, a time-consuming process that typically requires non-linear iterative methods to estimate probability-distribution parameters from data. Some QPDs have virtually unlimited shape flexibility and closed-form moments as well. History The development of quantile-parameterized distributions was inspired by the practical need for flexible continuous probability distributions that are easy to fit to data. Historically, the Pearson distribution, Pearson and Norman Lloyd Johnson, Johnson fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Percentile
In statistics, a ''k''-th percentile, also known as percentile score or centile, is a score (e.g., a data point) a given percentage ''k'' of all scores in its frequency distribution exists ("exclusive" definition) or a score a given percentage of the all scores exists ("inclusive" definition); i.e. a score in the ''k''-th percentile would be above approximately ''k''% of all scores in its set. For example, the 97th percentile of data is a data point below which 97% of all data points exist (by the exclusive definition). Percentiles depends on how scores are arranged. Percentiles are a type of quantiles, obtained adopting a subdivision into 100 groups. The 25th percentile is also known as the first '' quartile'' (''Q''1), the 50th percentile as the ''median'' or second quartile (''Q''2), and the 75th percentile as the third quartile (''Q''3). For example, the 50th percentile (median) is the score (or , depending on the definition) which 50% of the scores in the distribution are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quartile
In statistics, quartiles are a type of quantiles which divide the number of data points into four parts, or ''quarters'', of more-or-less equal size. The data must be ordered from smallest to largest to compute quartiles; as such, quartiles are a form of order statistic. The three quartiles, resulting in four data divisions, are as follows: * The first quartile (''Q''1) is defined as the 25th percentile where lowest 25% data is below this point. It is also known as the ''lower'' quartile. * The second quartile (''Q''2) is the median of a data set; thus 50% of the data lies below this point. * The third quartile (''Q''3) is the 75th percentile where lowest 75% data is below this point. It is known as the ''upper'' quartile, as 75% of the data lies below this point. Along with the minimum and maximum of the data (which are also quartiles), the three quartiles described above provide a five-number summary of the data. This summary is important in statistics because it provides infor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Median
The median of a set of numbers is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a Sample (statistics), data sample, a statistical population, population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as the “middle" value. The basic feature of the median in describing data compared to the Arithmetic mean, mean (often simply described as the "average") is that it is not Skewness, skewed by a small proportion of extremely large or small values, and therefore provides a better representation of the center. Median income, for example, may be a better way to describe the center of the income distribution because increases in the largest incomes alone have no effect on the median. For this reason, the median is of central importance in robust statistics. Median is a 2-quantile; it is the value that partitions a set into two equal parts. Finite set of numbers The median of a finite list of numbers is the "middle" number, when those numbers are liste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Probability Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is a Function (mathematics), function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of possible events for an Experiment (probability theory), experiment. It is a mathematical description of a Randomness, random phenomenon in terms of its sample space and the Probability, probabilities of Event (probability theory), events (subsets of the sample space). For instance, if is used to denote the outcome of a coin toss ("the experiment"), then the probability distribution of would take the value 0.5 (1 in 2 or 1/2) for , and 0.5 for (assuming that fair coin, the coin is fair). More commonly, probability distributions are used to compare the relative occurrence of many different random values. Probability distributions can be defined in different ways and for discrete or for continuous variables. Distributions with special properties or for especially important applications are given specific names. Introduction A prob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Percentile Rank
In statistics, the percentile rank (PR) of a given score is the percentage of scores in its frequency distribution that are less than that score. Formulation Its mathematical formula is : PR = \frac \times 100, where ''CF''—the cumulative frequency—is the count of all scores less than or equal to the score of interest, ''F'' is the frequency for the score of interest, and ''N'' is the number of scores in the distribution. Alternatively, if ''CF'' is the count of all scores less than the score of interest, then : PR = \frac \times 100. Example The figure illustrates the percentile rank computation and shows how the 0.5 × ''F'' term in the formula ensures that the percentile rank reflects a percentage of scores less than the specified score. For example, for the 10 scores shown in the figure, 60% of them are below a score of 4 (five less than 4 and half of the two equal to 4) and 95% are below 7 (nine less than 7 and half of the one equal to 7). Occasionally the percentile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cumulative Distribution Function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution function of X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x. Every probability distribution Support (measure theory), supported on the real numbers, discrete or "mixed" as well as Continuous variable, continuous, is uniquely identified by a right-continuous Monotonic function, monotone increasing function (a càdlàg function) F \colon \mathbb R \rightarrow [0,1] satisfying \lim_F(x)=0 and \lim_F(x)=1. In the case of a scalar continuous distribution, it gives the area under the probability density function from negative infinity to x. Cumulative distribution functions are also used to specify the distribution of multivariate random variables. Definition The cumulative distribution function of a real-valued random variable X is the function given by where the right-hand side represents the probability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Decile
In descriptive statistics, a decile is any of the nine values that divide the sorted data into ten equal parts, so that each part represents 1/10 of the sample or population. A decile is one possible form of a quantile; others include the quartile and percentile.. A decile rank arranges the data in order from lowest to highest and is done on a scale of one to ten where each successive number corresponds to an increase of 10 percentage points. Special usage: The decile mean A moderately robust measure of central tendency - known as the decile mean - can be computed by making use of a sample's deciles D_ to D_ (D_ = 10th percentile, D_ = 20th percentile and so on). It is calculated as follows: : DM = \frac Apart from serving as an alternative for the mean and the truncated mean, it also forms the basis for robust measures of skewness and kurtosis In probability theory and statistics, kurtosis (from , ''kyrtos'' or ''kurtos'', meaning "curved, arching") refers to the degree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Real Number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a continuous one- dimensional quantity such as a duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that pairs of values can have arbitrarily small differences. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion. The real numbers are fundamental in calculus (and in many other branches of mathematics), in particular by their role in the classical definitions of limits, continuity and derivatives. The set of real numbers, sometimes called "the reals", is traditionally denoted by a bold , often using blackboard bold, . The adjective ''real'', used in the 17th century by René Descartes, distinguishes real numbers from imaginary numbers such as the square roots of . The real numbers include the rational numbers, such as the integer and the fraction . The rest of the real numbers are called irrational numbers. Some irrational numbers (as well as all the rationals) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Estimating Quantiles From A Sample
Estimation (or estimating) is the process of finding an estimate or approximation, which is a value that is usable for some purpose even if input data may be incomplete, uncertain, or unstable. The value is nonetheless usable because it is derived from the best information available.C. Lon Enloe, Elizabeth Garnett, Jonathan Miles, ''Physical Science: What the Technology Professional Needs to Know'' (2000), p. 47. Typically, estimation involves "using the value of a statistic derived from a sample to estimate the value of a corresponding population parameter".Raymond A. Kent, "Estimation", ''Data Construction and Data Analysis for Survey Research'' (2001), p. 157. The sample provides information that can be projected, through various formal or informal processes, to determine a range most likely to describe the missing information. An estimate that turns out to be incorrect will be an overestimate if the estimate exceeds the actual result and an underestimate if the estimate fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |