|
Quadrature Error
Quadrature may refer to: In signal processing: *Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), a modulation method of using both an (in-phase) carrier wave and a 'quadrature' carrier wave that is 90° out of phase with the main, or in-phase, carrier *Quadrature phase, oscillations that are said to be ''in quadrature'' if they are separated in phase by 90° (/2, or /4) * Quadrature filter, the analytic signal of a real-valued filter *Quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK), a phase-shift keying of using four quadrate points on the constellation diagram, equispaced around a circle In mathematics: * Quadrature (mathematics), drawing a square with the same area as a given plane figure (''squaring'') or computing that area ** Quadrature of the circle * Numerical integration is often called 'numerical quadrature' or simply 'quadrature' ** Gaussian quadrature, a special case of numerical integration * Formerly, a synonym for "integral" ** Integral ** Antiderivative * Addition in quadrature, combini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is the name of a family of digital modulation methods and a related family of analog modulation methods widely used in modern telecommunications to transmit information. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing (''modulating'') the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying (ASK) digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation (AM) analog modulation scheme. The two carrier waves are of the same frequency and are out of phase with each other by 90°, a condition known as orthogonality or quadrature. The transmitted signal is created by adding the two carrier waves together. At the receiver, the two waves can be coherently separated (demodulated) because of their orthogonality property. Another key property is that the modulations are low-frequency/low-bandwidth waveforms compared to the carrier frequency, which is known as the narrowband assumption. Phase modulation (analog PM) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addition In Quadrature
In mathematics, Pythagorean addition is a binary operation on the real numbers that computes the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle, given its two sides. According to the Pythagorean theorem, for a triangle with sides a and b, this length can be calculated as a \oplus b = \sqrt, where \oplus denotes the Pythagorean addition operation. This operation can be used in the conversion of Cartesian coordinates to polar coordinates. It also provides a simple notation and terminology for some formulas when its summands are complicated; for example, the energy-momentum relation in physics becomes E = mc^2 \oplus pc. It is implemented in many programming libraries as the hypot function, in a way designed to avoid errors arising due to limited-precision calculations performed on computers. In its applications to signal processing and propagation of measurement uncertainty, the same operation is also called addition in quadrature. Applications Pythagorean addition (and its impleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illusionistic Ceiling Painting
Illusionistic ceiling painting, which includes the techniques of perspective ''di sotto in sù'' and ''quadratura'', is the tradition in Renaissance art, Renaissance, Baroque art, Baroque and Rococo art in which ''trompe-l'œil'', Perspective (graphical), perspective tools such as foreshortening, and other spatial effects are used to create the illusion of three-dimensional space on an otherwise two-dimensional or mostly flat ceiling surface above the viewer. It is frequently used to create the illusion of an open sky, such as with the Oculus (architecture), oculus in Andrea Mantegna's Camera degli Sposi, or the illusion of an architectural space such as the cupola, one of Andrea Pozzo's frescoes in Sant'Ignazio, Rome. Illusionistic ceiling painting belongs to the general class of Illusionism (art), illusionism in art, designed to create accurate representations of reality. Di sotto in sù ''Di sotto in sù'' (or ''sotto in su''), which means "seen from below" or "from below, upw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
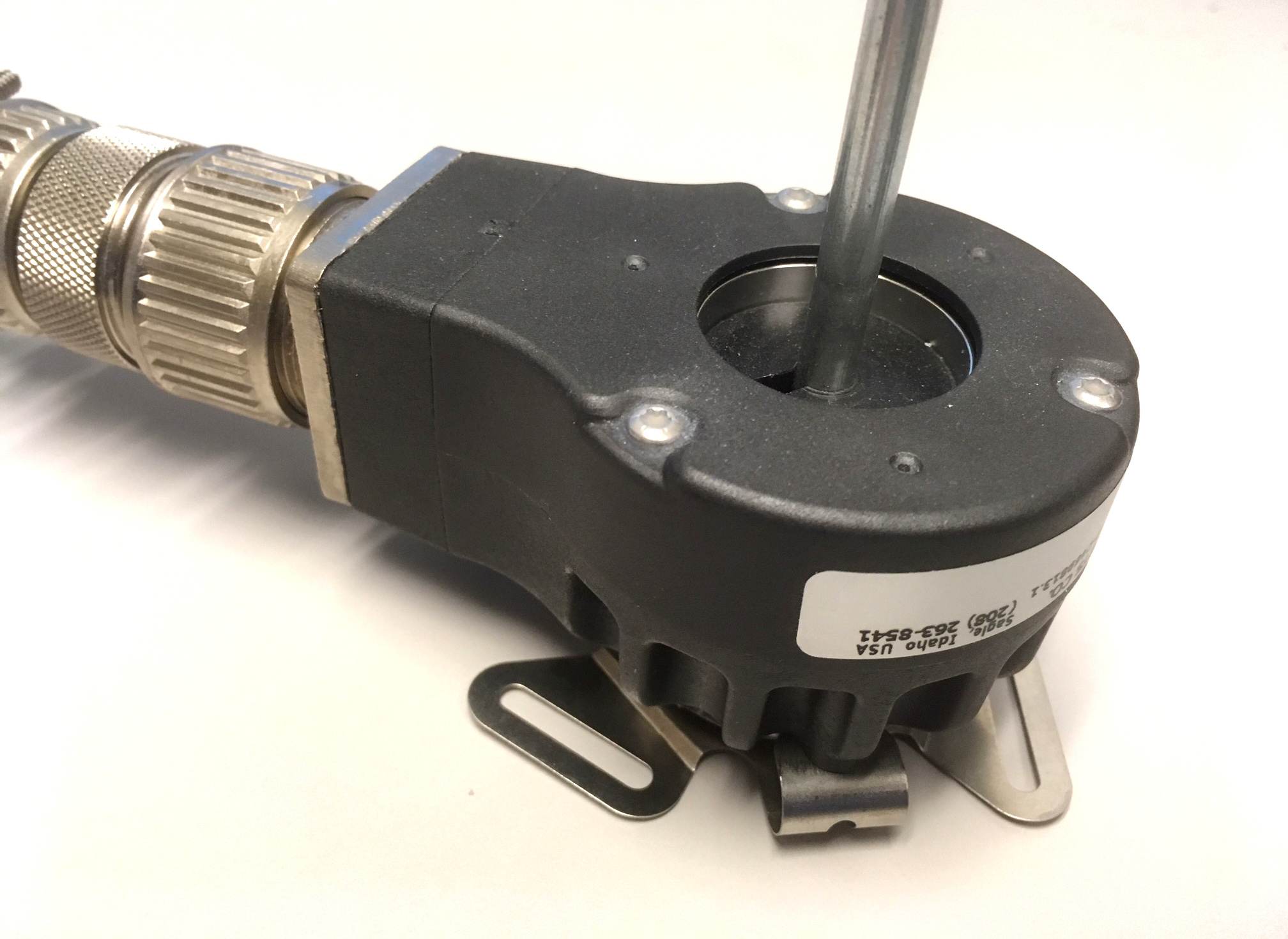
Quadrature Encoder
An incremental encoder is a linear or rotary electromechanical device that has two output signals, ''A'' and ''B'', which issue pulses when the device is moved. Together, the ''A'' and ''B'' signals indicate both the occurrence of and direction of movement. Many incremental encoders have an additional output signal, typically designated ''index'' or ''Z'', which indicates the encoder is located at a particular reference position. Also, some encoders provide a status output (typically designated ''alarm'') that indicates internal fault conditions such as a bearing failure or sensor malfunction. Unlike an absolute encoder, an incremental encoder does not indicate absolute position; it only reports changes in position and, for each reported position change, the direction of movement. Consequently, to determine absolute position at any particular moment, it is necessary to send the encoder signals to an '' incremental encoder interface'', which in turn will "track" and report the enc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrature (hedge-fund)
Quadrature may refer to: In signal processing: *Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), a modulation method of using both an (in-phase) carrier wave and a 'quadrature' carrier wave that is 90° out of phase with the main, or in-phase, carrier *Quadrature phase, oscillations that are said to be ''in quadrature'' if they are separated in phase by 90° (/2, or /4) * Quadrature filter, the analytic signal of a real-valued filter *Quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK), a phase-shift keying of using four quadrate points on the constellation diagram, equispaced around a circle In mathematics: * Quadrature (mathematics), drawing a square with the same area as a given plane figure (''squaring'') or computing that area ** Quadrature of the circle * Numerical integration is often called 'numerical quadrature' or simply 'quadrature' ** Gaussian quadrature, a special case of numerical integration * Formerly, a synonym for "integral" ** Integral ** Antiderivative * Addition in quadrature, combini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrature (astronomy)
In spherical astronomy, quadrature is the configuration of a celestial object in which its elongation is perpendicular to the direction of the Sun. It is applied especially to the position of a superior planet or the Moon at its first and last quarter phases. This is not to be confused with the Moon at dichotomy (exactly half-lit) as viewed from Earth, which occurs at 89.85 degrees and 270.15 degrees. As shown in the diagram, a planet (or other object) can be at the western quadrature (when it is to the west of the Sun when viewed from the Earth) or at the eastern quadrature (when it is to the east of the Sun when viewed from the Earth). Note that an inferior planet can never be at quadrature to the reference planet. At quadrature, the shadow that a planet casts on its planetary rings appears most offset from the planet (e.g., Saturn's rings); the dark side of a planet (e.g., Mars) is maximally visible. See also * Astrological aspect In astrology, an aspect is an angl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In-phase And Quadrature Components
In electrical engineering, a sinusoid with angle modulation can be decomposed into, or synthesized from, two amplitude-modulated sinusoids that are offset in phase by one-quarter cycle (90 degrees or /2 radians). All three functions have the same center frequency. Such amplitude modulated sinusoids are known as the in-phase and quadrature components. In some contexts it is more convenient to refer to only the amplitude modulation (''baseband'') itself by those terms. Concept In vector analysis, a vector with polar coordinates and Cartesian coordinates can be represented as the sum of orthogonal components: Similarly in trigonometry, the angle sum identity expresses: : And in functional analysis, when is a linear function of some variable, such as time, these components are sinusoids, and they are orthogonal functions. A phase-shift of changes the identity to: : , in which case is the in-phase component. In both conventions is the in-phase amplitude modulation, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Amplitude
Complex commonly refers to: * Complexity, the behaviour of a system whose components interact in multiple ways so possible interactions are difficult to describe ** Complex system, a system composed of many components which may interact with each other * Complex (psychology), a core pattern of emotions etc. in the personal unconscious organized around a common theme such as power or status Complex may also refer to: Arts, entertainment and media * Complex (English band), formed in 1968, and their 1971 album ''Complex'' * Complex (band), a Japanese rock band * ''Complex'' (album), by Montaigne, 2019, and its title track * ''Complex'' (EP), by Rifle Sport, 1985 * "Complex" (song), by Gary Numan, 1979 * Complex Networks, publisher of magazine ''Complex'', now online Biology * Protein–ligand complex, a complex of a protein bound with a ligand * Exosome complex, a multi-protein intracellular complex * Protein complex, a group of two or more associated polypeptide chains * Specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Phase Space
In quantum optics, an optical phase space is a phase space in which all quantum states of an optical system are described. Each point in the optical phase space corresponds to a unique state of an ''optical system''. For any such system, a plot of the ''quadratures'' against each other, possibly as functions of time, is called a phase diagram. If the quadratures are functions of time then the optical phase diagram can show the evolution of a quantum optical system with time. An optical phase diagram can give insight into the properties and behaviors of the system that might otherwise not be obvious. This can allude to qualities of the system that can be of interest to an individual studying an optical system that would be very hard to deduce otherwise. Another use for an optical phase diagram is that it shows the evolution of the state of an optical system. This can be used to determine the state of the optical system at any point in time. Background information When discussing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiderivative
In calculus, an antiderivative, inverse derivative, primitive function, primitive integral or indefinite integral of a function is a differentiable function whose derivative is equal to the original function . This can be stated symbolically as . The process of solving for antiderivatives is called antidifferentiation (or indefinite integration), and its opposite operation is called ''differentiation'', which is the process of finding a derivative. Antiderivatives are often denoted by capital Roman letters such as and . Antiderivatives are related to definite integrals through the second fundamental theorem of calculus: the definite integral of a function over a closed interval In mathematics, a (real) interval is a set of real numbers that contains all real numbers lying between any two numbers of the set. For example, the set of numbers satisfying is an interval which contains , , and all numbers in between. Other ... where the function is Riemann integrable is eq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrature Phase
In physics and mathematics, the phase of a periodic function F of some real variable t (such as time) is an angle-like quantity representing the fraction of the cycle covered up to t. It is denoted \phi(t) and expressed in such a scale that it varies by one full turn as the variable t goes through each period (and F(t) goes through each complete cycle). It may be measured in any angular unit such as degrees or radians, thus increasing by 360° or 2\pi as the variable t completes a full period. This convention is especially appropriate for a sinusoidal function, since its value at any argument t then can be expressed as \phi(t), the sine of the phase, multiplied by some factor (the amplitude of the sinusoid). (The cosine may be used instead of sine, depending on where one considers each period to start.) Usually, whole turns are ignored when expressing the phase; so that \phi(t) is also a periodic function, with the same period as F, that repeatedly scans the same range of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral
In mathematics Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ..., an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes Displacement (geometry), displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along with Derivative, differentiation, integration is a fundamental, essential operation of calculus,Integral calculus is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See and , for example. and serves as a tool to solve problems in mathematics and physics involving the area of an arbitrary shape, the length of a curve, and the volume of a solid, among others. The integrals enumerated here are those termed definite integrals, which can be int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)