|
QsNet II
Quadrics was a supercomputer company formed in 1996 as a joint venture between Alenia Spazio and the technical team from Meiko Scientific. They produced hardware and software for clustering commodity computer systems into massively parallel systems. Their highpoint was in June 2003 when six out of the ten fastest supercomputers in the world were based on Quadrics' interconnect. They officially closed on June 29, 2009. Company history The Quadrics name was first used in 1993 for a commercialized version of the APE100 SIMD parallel computer produced by Alenia Spazio and originally developed by INFN, the Italian National Institute of Nuclear Physics. In 1996, a new Alenia subsidiary, Quadrics Supercomputers World (QSW) was formed, based in Bristol, UK and Rome, Italy, inheriting the Quadrics SIMD product line and the Meiko CS-2 massively parallel supercomputer architecture. In 2002 the company name was shortened to be simply Quadrics. Initially, the new company focussed on the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrics Logo
In mathematics, a quadric or quadric surface (quadric hypersurface in higher dimensions), is a generalization of conic sections (ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas). It is a hypersurface (of dimension ''D'') in a -dimensional space, and it is defined as the zero set of an irreducible polynomial of degree of a polynomial, degree two in ''D'' + 1 variables; for example, in the case of conic sections. When the defining polynomial is not absolutely irreducible, the zero set is generally not considered a quadric, although it is often called a ''degenerate quadric'' or a ''reducible quadric''. In coordinates , the general quadric is thus defined by the algebraic equationSilvio LevQuadricsin "Geometry Formulas and Facts", excerpted from 30th Edition of ''CRC Standard Mathematical Tables and Formulas'', CRC Press, from The Geometry Center at University of Minnesota : \sum_^ x_i Q_ x_j + \sum_^ P_i x_i + R = 0 which may be compactly written in vector and matrix notation as: : x Q x^ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UltraSPARC
The UltraSPARC is a microprocessor developed by Sun Microsystems and fabricated by Texas Instruments, introduced in mid-1995. It is the first microprocessor from Sun to implement the 64-bit SPARC V9 instruction set architecture (ISA). Marc Tremblay was a co-microarchitect. Microarchitecture The UltraSPARC is a four-issue superscalar microprocessor that executes instructions in in-order. It has a nine-stage integer pipeline. Functional units The execution units were simplified relative to the SuperSPARC to achieve higher clock frequencies - an example of a simplification is that the ALUs were not cascaded, unlike the SuperSPARC, to avoid restricting clock frequency. The integer register file has 32 64-bit entries. As the SPARC ISA uses register windows, of which the UltraSPARC has eight, the actual number of registers is 144. The register file has seven read and three write ports. The integer register file provides registers to two arithmetic logic units and the load/store ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flops
In computing, floating point operations per second (FLOPS, flops or flop/s) is a measure of computer performance, useful in fields of scientific computations that require floating-point calculations. For such cases, it is a more accurate measure than measuring instructions per second. Floating-point arithmetic Floating-point arithmetic is needed for very large or very small real numbers, or computations that require a large dynamic range. Floating-point representation is similar to scientific notation, except everything is carried out in base two, rather than base ten. The encoding scheme stores the sign, the exponent (in base two for Cray and VAX, base two or ten for IEEE floating point formats, and base 16 for IBM Floating Point Architecture) and the significand (number after the radix point). While several similar formats are in use, the most common is ANSI/IEEE Std. 754-1985. This standard defines the format for 32-bit numbers called ''single precision'', as well as 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is a federal research facility in Livermore, California, United States. The lab was originally established as the University of California Radiation Laboratory, Livermore Branch in 1952 in response to the detonation of the first atomic bomb by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. It later became autonomous in 1971 and was designated a national laboratory in 1981. A federally funded research and development center, Lawrence Livermore Lab is primarily funded by the U.S. Department of Energy and it is managed privately and operated by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC (a partnership of the University of California), Bechtel, BWX Technologies, AECOM, and Battelle Memorial Institute in affiliation with the Texas A&M University System. In 2012, the laboratory had the synthetic chemical element livermorium (element 116) named after it. Overview LLNL is self-described as a "premier research and development institution for sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SHARCNET
SHARCNET is a consortium of universities in Ontario, Canada, that aggregate funding to purchase supercomputer systems, which are shared among the members to perform research, rather than individually purchasing smaller systems at each university. It was formed to allow members access to larger, faster, and more modern computer resources than they would otherwise be able to afford, and to retain researchers at their organizations. SHARCNET is part of the larger Compute Canada umbrella. , the fastest computer at SHARCNET according to the Top 500 list iGraham which entered the list as the 95th fastest computer in the world with a High Performance Linpack result of 1,228 TeraFLOPS. History SHARCNET was originally founded in June, 2001 with seven institutions: McMaster University, the University of Western Ontario, University of Guelph, University of Windsor, Wilfrid Laurier University, Fanshawe College, and Sheridan College. Initial seed funding of C$42.1 million came from govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, and Ubuntu, the latter of which itself consists of many different distributions and modifications, including Lubuntu and Xubuntu. Commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland, and a desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE Plasma. Distributions intended for ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AlphaServer
AlphaServer is a series of server computers, produced from 1994 onwards by Digital Equipment Corporation, and later by Compaq and HP. AlphaServers were based on the DEC Alpha 64-bit microprocessor. Supported operating systems for AlphaServers are Tru64 UNIX (formerly Digital UNIX), OpenVMS, MEDITECH MAGIC and Windows NT (on earlier systems, with AlphaBIOS ARC firmware), while enthusiasts have provided alternative operating systems such as Linux, NetBSD, OpenBSD and FreeBSD. The Alpha processor was also used in a line of workstations, AlphaStation. Some AlphaServer models were rebadged in white enclosures as Digital Servers for the Windows NT server market. These so-called "white box" models comprised the following: * Digital Server 3300/3305: rebadged AlphaServer 800 * Digital Server 5300/5305: rebadged AlphaServer 1200 * Digital Server 7300/7305/7310: rebadged AlphaServer 4100 As part of the roadmap to phase out Alpha-, MIPS- and PA-RISC-based systems in favor of Itan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LANL) is one of the sixteen research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy (DOE), located a short distance northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, in the American southwest. Best known for its central role in helping develop the first atomic bomb, LANL is one of the world's largest and most advanced scientific institutions. Los Alamos was established in 1943 as Project Y, a top-secret site for designing nuclear weapons under the Manhattan Project during World War II.The site was variously called Los Alamos Laboratory and Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory. Chosen for its remote yet relatively accessible location, it served as the main hub for conducting and coordinating nuclear research, bringing together some of the world's most famous scientists, among them numerous Nobel Prize winners. The town of Los Alamos, directly north of the lab, grew extensively through this period. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASCI Q
The Advanced Simulation and Computing Program (or ASC) is a super-computing program run by the National Nuclear Security Administration, in order to simulate, test, and maintain the United States nuclear stockpile. The program was created in 1995 in order to support the Stockpile Stewardship Program (or SSP). The goal of the initiative is to extend the lifetime of the current aging stockpile. History After the United States' 1992 moratorium on live nuclear testing, the Stockpile Stewardship Program was created in order to find a way to test, and maintain the nuclear stockpile. In response, the National Nuclear Security Administration began to simulate the nuclear warheads using supercomputers. As the stockpile ages, the simulations have become more complex, and the maintenance of the stockpile requires more computing power. Over the years, due to Moore's Law, the ASC program has created several different supercomputers with increasing power, in order to compute the simulation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
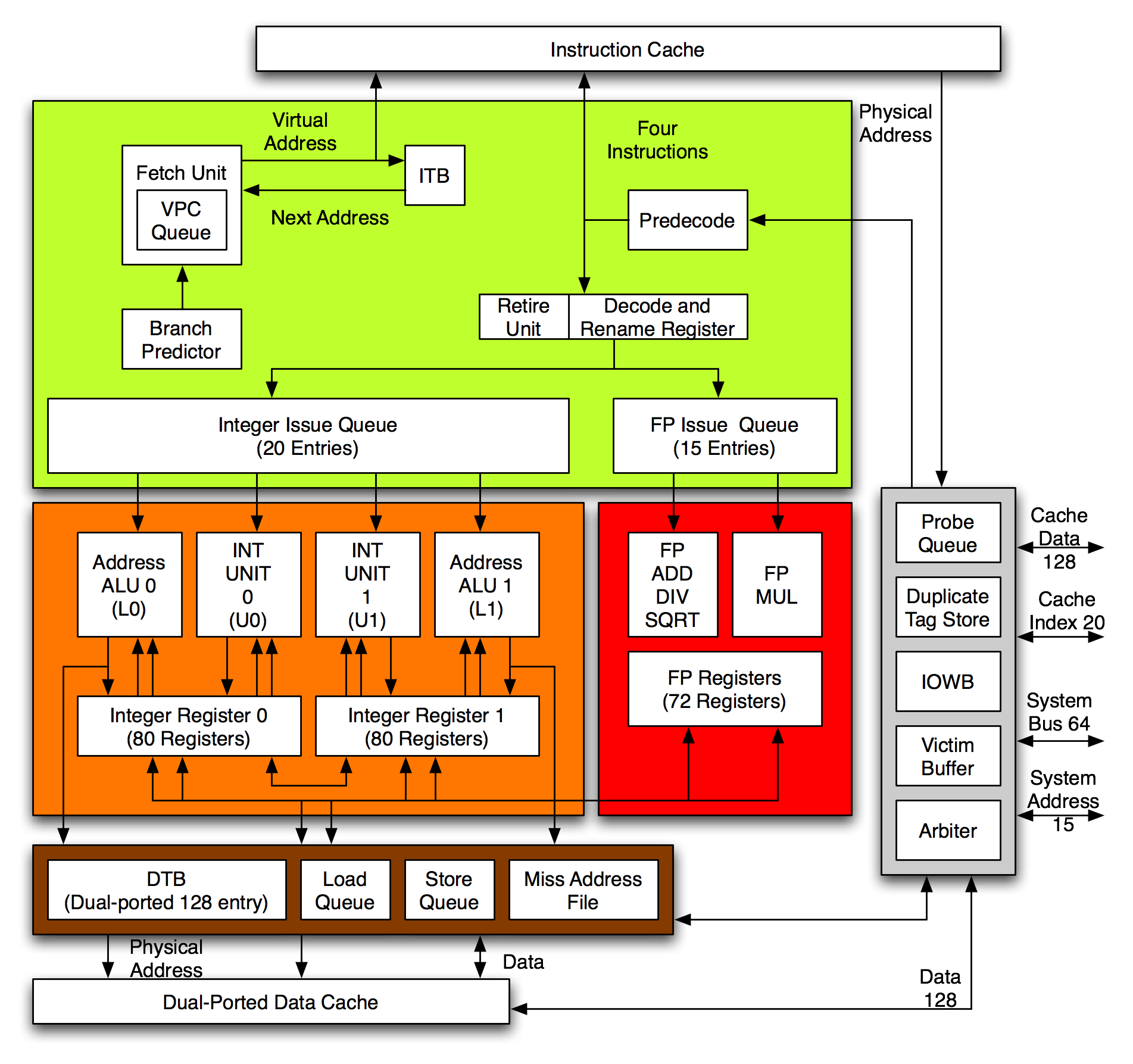
Alpha 21264
The Alpha 21264 is a Digital Equipment Corporation RISC microprocessor launched on 19 October 1998. The 21264 implemented the Alpha instruction set architecture (ISA). Description The Alpha 21264 is a four-issue superscalar microprocessor with out-of-order execution and speculative execution. It has a peak execution rate of six instructions per cycle and could sustain four instructions per cycle. It has a seven-stage instruction pipeline. Out of order execution At any given stage, the microprocessor could have up to 80 instructions in various stages of execution, surpassing any other contemporary microprocessor. Decoded instructions are held in instruction queues and are issued when their operands are available. The integer queue contained 20 entries and the floating-point queue 15. Each queue could issue as many instructions as there were pipelines. Ebox The Ebox executes integer, load and store instructions. It has two integer units, two load store units and two integer r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until forced to resign in 1992, after the company had gone into precipitous decline. The company produced many different product lines over its history. It is best known for the work in the minicomputer market starting in the mid-1960s. The company produced a series of machines known as the PDP line, with the PDP-8 and PDP-11 being among the most successful minis in history. Their success was only surpassed by another DEC product, the late-1970s VAX "supermini" systems that were designed to replace the PDP-11. Although a number of competitors had successfully competed with Digital through the 1970s, the VAX cemented the company's place as a leading vendor in the computer space. As microcomputers improved in the late 1980s, especially wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)