|
Puzur-Inshushinak
Puzur-Inshushinak (Linear Elamite: ''Puzur Šušinak'', Akkadian: , ''puzur3- dinšušinak'', also , ''puzur4- dinšušinak'' "Calling Inshushinak"), also sometimes thought to read Kutik-Inshushinak in Elamite, was king of Elam, around 2100 BC, and the last from the Awan dynasty according to the Susa kinglist. He mentions his father's name as Šimpi-išhuk, which, being an Elamite name, suggests that Puzur-Inshuhinak himself was Elamite. In the inscription of the "Table au Lion", he appears as "Puzur-Inshushin(ak) Ensi (Governor) of Susa, Shakkanakku (Military Governor) of the country of Elam" ( , a title used by his predecessors Eshpum, Epirmupi and Ili-ishmani as governors of the Akkadian Empire for the territory of Elam.Translation into French in In another inscription, he calls himself the "Mighty King of Elam", suggesting an accession to independence from the weakening Akkadian Empire. Rule His father was Shinpi-khish-khuk, the crown prince, and most likely a brother of k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kutik-Inshushinak (name) In Linear Elamite
Puzur-Inshushinak (Linear Elamite: ''Puzur Šušinak'', Akkadian: , ''puzur3- dinšušinak'', also , ''puzur4- dinšušinak'' "Calling Inshushinak"), also sometimes thought to read Kutik-Inshushinak in Elamite, was king of Elam, around 2100 BC, and the last from the Awan dynasty according to the Susa kinglist. He mentions his father's name as Šimpi-išhuk, which, being an Elamite name, suggests that Puzur-Inshuhinak himself was Elamite. In the inscription of the "Table au Lion", he appears as "Puzur-Inshushin(ak) Ensi (Governor) of Susa, Shakkanakku (Military Governor) of the country of Elam" ( , a title used by his predecessors Eshpum, Epirmupi and Ili-ishmani as governors of the Akkadian Empire for the territory of Elam.Translation into French in In another inscription, he calls himself the "Mighty King of Elam", suggesting an accession to independence from the weakening Akkadian Empire. Rule His father was Shinpi-khish-khuk, the crown prince, and most likely a brother of k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puzur-Inshushinak Name And Titles
Puzur-Inshushinak (Linear Elamite: ''Puzur Šušinak'', Akkadian: , ''puzur3- dinšušinak'', also , ''puzur4- dinšušinak'' "Calling Inshushinak"), also sometimes thought to read Kutik-Inshushinak in Elamite, was king of Elam, around 2100 BC, and the last from the Awan dynasty according to the Susa kinglist. He mentions his father's name as Šimpi-išhuk, which, being an Elamite name, suggests that Puzur-Inshuhinak himself was Elamite. In the inscription of the "Table au Lion", he appears as "Puzur-Inshushin(ak) Ensi (Governor) of Susa, Shakkanakku (Military Governor) of the country of Elam" ( , a title used by his predecessors Eshpum, Epirmupi and Ili-ishmani as governors of the Akkadian Empire for the territory of Elam.Translation into French in In another inscription, he calls himself the "Mighty King of Elam", suggesting an accession to independence from the weakening Akkadian Empire. Rule His father was Shinpi-khish-khuk, the crown prince, and most likely a brother of k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
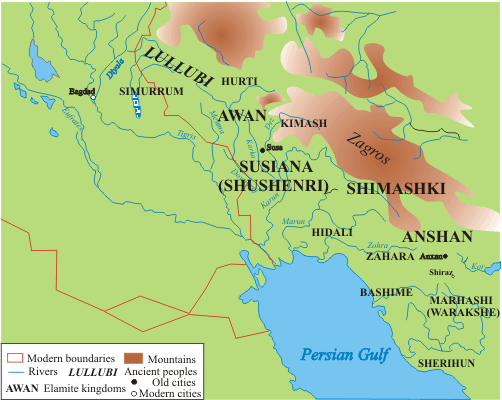
List Of Rulers Of Elam
The kings of Elam were the rulers of Elam, an ancient civilization in modern-day south-western Iran. The earliest known Elamite dynasty was the Awan dynasty, which came to power in the Early Dynastic period. Elam was conquered by the Akkadian Empire in the 24th century BC and was then ruled by a sequence of Akkadian-appointed governors before independence was restored a little over a century later. After the reign of the powerful Elamite king Puzur-Inshushinak, Elam was conquered again around 2100 BC by the Sumerian Third Dynasty of Ur. Native Elamite rule was after a few decades restored under the Shimashki dynasty during the reign of Ur III king Ibbi-Sin. In 2004 BC the Shimashki king Kindattu sacked Ur, whereafter Elam became fully independent. The Sukkulmah dynasty, perhaps a related lineage, was established in another part of Elam shortly thereafter, and after a period of overlap gradually overtook the Shimashki dynasty. The Sukkalmah dynasty was followed by the Kidinuid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Elamite
Linear Elamite was a writing system used in Elam during the Bronze Age between , and known mainly from a few extant monumental inscriptions. It was used contemporaneously with Elamite cuneiform and records the Elamite language. The French archaeologist and his colleagues have argued that it the oldest known purely phonographic writing system, although others, such as the linguist Michael Mäder, have argued that it is partly logographic. There have been multiple attempts to decipher the script, aided by the discovery of a limited number of multilingual and bigraphic inscriptions. Early efforts by (1912) and Ferdinand Bork (1905, 1924) made limited progress. Later work by and furthered the work., , and Starting in 2018, Desset outlined some of his proposed decipherments of the script accomplished with a team of other scholars. Their proposed near-complete decipherment was published in 2022, being received positively by some researchers while others remain sceptical until det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo-Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ; he, שׁוּשָׁן ; grc-gre, Σοῦσα ; syr, ܫܘܫ ; pal, 𐭮𐭥𐭱𐭩 or ; peo, 𐏂𐎢𐏁𐎠 ) was an ancient city in the lower Zagros Mountains about east of the Tigris, between the Karkheh and Dez Rivers in Iran. One of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East, Susa served as the capital of Elam and the Achaemenid Empire, and remained a strategic centre during the Parthian and Sasanian periods. The site currently consists of three archaeological mounds, covering an area of around one square kilometre. The modern Iranian town of Shush is located on the site of ancient Susa. Shush is identified as Shushan, mentioned in the Book of Esther and other Biblical books. Name The English name is derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awan Dynasty
The Awan Dynasty ( Sumerian: ''lugal-e-ne a-wa-anki'', "Kings of Awan") was the first dynasty of Elam of which very little of anything is known today, appearing at the dawn of historical record. The Dynasty corresponds to the early part of the Old Elamite period (dated c. 2700 – c. 1600 BC), it was succeeded by the Shimashki Dynasty (2200-1900 BC) and later the Sukkalmah Dynasty. The Elamites were likely major rivals of neighboring Sumer from remotest antiquity; they were said to have been defeated by Enmebaragesi of Kish (c. 25th century BC), who is the earliest archaeologically attested Sumerian king, as well as by a later monarch, Eannatum I of Lagash. Awan was a city-state or possibly a region of Elam whose precise location is not certain, but it has been variously conjectured to be north of Susa, in south Luristan, close to Dezful, or Godin Tepe. Elam and Sumer According to the '' Sumerian King List'', a dynasty from Awan exerted hegemony in Sumer after defeating the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ur-Nammu
Ur-Nammu (or Ur-Namma, Ur-Engur, Ur-Gur, Sumerian: , ruled c. 2112 BC – 2094 BC middle chronology, or possibly c. 2048–2030 BC short chronology) founded the Sumerian Third Dynasty of Ur, in southern Mesopotamia, following several centuries of Akkadian and Gutian rule. His main achievement was state-building, and Ur-Nammu is chiefly remembered today for his legal code, the Code of Ur-Nammu, the oldest known surviving example in the world. He held the titles of "King of Ur, and King of Sumer and Akkad". Reign According to the ''Sumerian King List'', Ur-Nammu reigned for 18 years.Thorkild Jacobsen, ''The Sumerian King List'' (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1939),pp. 122f Year-names are known for 17 of these years, but their order is uncertain. One year-name of his reign records the devastation of Gutium, while two years seem to commemorate his legal reforms ("Year in which Ur-Nammu the king put in order the ways (of the people in the country) from below to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shakkanakku
Shakkanakku ( Sumerian: , GIR.NITA or ''šagina'', , ''Shakkanakku''), was an Akkadian language title designating a military governor. Mari was ruled by a dynasty of hereditary Shakkanakkus which was originally set by the Akkadian Empire and gained independence following Akkad's collapse. It is considered that the Shakkanakka gained some form of independence and came to be considered as "Kings" from the time of Apil-Kin. A critical analysis of the Shakkanakku List of Mari has been published. The title is also known around the same time in Elam, where several "Shakkanakku (Military Governor) of the country of Elam" with typically Akkadian names ruled for the Akkadian kings.Translation into French in The title also existed in Qatna in the 14th century BC, and Dilmun under the Kassites. Shakkanakkus under the Akkadians Shakkanakkus, or ''Shagina'' military governors are known from the time of the Akkadian Empire. For example, Shar-kali-sharri had a military governor in Nippur t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elamite Language
Elamite, also known as Hatamtite and formerly as Susian, is an extinct language that was spoken by the ancient Elamites. It was used in what is now southwestern Iran from 2600 BC to 330 BC. Elamite works disappear from the archeological record after Alexander the Great entered Iran. Elamite is generally thought to have no demonstrable relatives and is usually considered a language isolate. The lack of established relatives makes its interpretation difficult. A sizeable number of Elamite lexemes are known from the trilingual Behistun inscription and numerous other bilingual or trilingual inscriptions of the Achaemenid Empire, in which Elamite was written using Elamite cuneiform (circa 400 BC), which is fully deciphered. An important dictionary of the Elamite language, the ''Elamisches Wörterbuch'' was published in 1987 by W. Hinz and H. Koch. The Linear Elamite script however, one of the scripts used to write the Elamite language circa 2000 BC, has remained elusive until recen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shimashki
The Shimashki or Simashki dynasty (, ''lugal-ene si-mash-giki'' "Kings of the country of Simashgi"), was an early dynasty of the ancient region of Elam, to the southeast of Babylonia, in approximately 2100-1900 BCE. A list of twelve kings of Shimashki is found in the Elamite king-list of Susa, which also contains a list of kings of Awan dynasty. It is uncertain how historically accurate the list is (and whether it reflects a chronological order), although some of its kings can be corroborated by their appearance in the records of neighboring peoples. The Dynasty corresponds to the middle part of the Old Elamite period (dated c.2700 – c. 1600 BC). It was followed by the Sukkalmah Dynasty. Shimashki was likely near today's Masjed Soleyman. Nature of the "Dynasty" Daryaee suggests that, despite the impression from the king-list that the rulers of Shimashki was a dynasty of sequential rulers, it is perhaps better to think of Shimashki as an alliance of various peoples "rather tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khita
Khita, sometimes Hita in Elamite ( ''hi-ta-a''), was governor of Susa and the 11th king of the Awan Dynasty of Elam, around 2280 BCE. He was most likely the grandfather of the famous Elamite ruler Kutik-Inshushinak, who succeeded him on the throne. Elam had been under the domination of Akkad, at least temporarily, since the time of Sargon. Khita is probably recorded as having signed a peace treaty with Naram-Sin of Akkad, stating: "The enemy of Naram-Sin is my enemy, the friend of Naram-Sin is my friend". The inscription was discovered in Susa. It has been suggested that the formal treaty allowed Naram-Sin to have peace on his eastern borders, so that he could deal more effectively with the threat from Gutium. Further study of the treaty suggests that Khita provided Elamite troops to Naram-Sin, that he married his daughter to the Akkadian king, and that he agreed to set up statues of Naram-Sin in the sanctuaries of Susa. As a matter of fact, it is well known that Naram-Sin ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zagros Mountains
The Zagros Mountains ( ar, جبال زاغروس, translit=Jibal Zaghrus; fa, کوههای زاگرس, Kuh hā-ye Zāgros; ku, چیاکانی زاگرۆس, translit=Çiyakani Zagros; Turkish: ''Zagros Dağları''; Luri: ''Kuh hā-ye Zāgros'' ''کویا زاگرس'') are a long mountain range in Iran, northern Iraq, and southeastern Turkey. This mountain range has a total length of . The Zagros mountain range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border while covering much of southeastern Turkey and northeastern Iraq. From this border region, the range continues to the southeast under also the waters of the Persian Gulf. It spans the southern parts of the Armenian highland, the whole length of the western and southwestern Iranian plateau, ending at the Strait of Hormuz. The highest point is Mount Dena, at . Geology The Zagros fold and thrust belt was mainly formed by the collision of two tectonic plates, the Eurasian Plate and the Arabian Plat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_in_Linear_Elamite.jpg)


.jpg)


.jpg)