|
Awan Dynasty
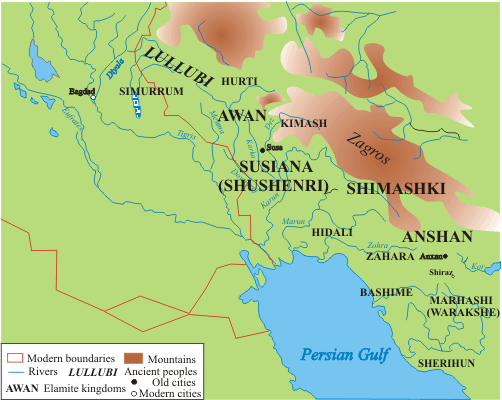
The Awan Dynasty ( Sumerian: ''lugal-e-ne a-wa-anki'', "Kings of Awan") was the first dynasty of Elam of which very little of anything is known today, appearing at the dawn of historical record. The Dynasty corresponds to the early part of the Old Elamite period (dated c. 2700 – c. 1600 BC), it was succeeded by the Shimashki Dynasty (2200-1900 BC) and later the Sukkalmah Dynasty. The Elamites were likely major rivals of neighboring Sumer from remotest antiquity; they were said to have been defeated by Enmebaragesi of Kish (c. 25th century BC), who is the earliest archaeologically attested Sumerian king, as well as by a later monarch, Eannatum I of Lagash. Awan was a city-state or possibly a region of Elam whose precise location is not certain, but it has been variously conjectured to be north of Susa, in south Luristan, close to Dezful, or Godin Tepe. Elam and Sumer According to the '' Sumerian King List'', a dynasty from Awan exerted hegemony in Sumer after defeating the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shimashki Dynasty
The Shimashki or Simashki dynasty (, ''lugal-ene si-mash-giki'' "Kings of the country of Simashgi"), was an early dynasty of the ancient region of Elam, to the southeast of Babylonia, in approximately 2100-1900 BCE. A list of twelve kings of Shimashki is found in the Elamite king-list of Susa, which also contains a list of kings of Awan dynasty. It is uncertain how historically accurate the list is (and whether it reflects a chronological order), although some of its kings can be corroborated by their appearance in the records of neighboring peoples. The Dynasty corresponds to the middle part of the Old Elamite period (dated c.2700 – c. 1600 BC). It was followed by the Sukkalmah Dynasty. Shimashki was likely near today's Masjed Soleyman. Nature of the "Dynasty" Daryaee suggests that, despite the impression from the king-list that the rulers of Shimashki was a dynasty of sequential rulers, it is perhaps better to think of Shimashki as an alliance of various peoples "rather than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumerian King List
The ''Sumerian King List'' (abbreviated ''SKL'') or ''Chronicle of the One Monarchy'' is an ancient literary composition written in Sumerian that was likely created and redacted to legitimize the claims to power of various city-states and kingdoms in southern Mesopotamia during the late third and early second millennium BC. It does so by repetitively listing Sumerian cities, the kings that ruled there, and the lengths of their reigns. Especially in the early part of the list, these reigns often span thousands of years. In the oldest known version, dated to the Ur III period (c. 2112–2004 BC) but probably based on Akkadian source material, the ''SKL'' reflected a more linear transition of power from Kish, the first city to receive kingship, to Akkad. In later versions from the Old Babylonian period, the list consisted of a large number of cities between which kingship was transferred, reflecting a more cyclical view of how kingship came to a city, only to be inevitably replace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naram-Sin Of Akkad
Naram-Sin, also transcribed Narām-Sîn or Naram-Suen ( akk, : '' DNa-ra-am D Sîn'', meaning "Beloved of the Moon God Sîn", the "𒀭" being a silent honorific for "Divine"), was a ruler of the Akkadian Empire, who reigned c. 2254–2218 BC (middle chronology), and was the third successor and grandson of King Sargon of Akkad. Under Naram-Sin the empire reached its maximum strength. He was the first Mesopotamian king known to have claimed divinity for himself, taking the title "God of Akkad", and the first to claim the title "King of the Four Quarters, King of the Universe". As part of that he became city god of Akkade in the same way Enlil was city god of Nippur. Biography Naram-Sin was born as a son of Manishtushu. He was thus a nephew of King Rimush and grandson of Sargon and Tashlultum. Naram-Sin's aunt was the High Priestess En-hedu-ana. To be fully correct, rather than Naram-Sin or Naram-Suen "in Old Akkadian, the name in question should rather be reconstructed as Nar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marhashi
Marhaši ( Sumerian: ''Mar-ḫa-šiKI'' , ''Marhashi'', ''Marhasi'', ''Parhasi'', ''Barhasi''; in earlier sources Waraḫše. Akkadian: "Parahshum" ''pa2-ra-ah-shum2-ki'') was a 3rd millennium BC polity situated east of Elam, on the Iranian plateau, in Makran. It is known from Mesopotamian sources, but its precise location has not been identified, though some scholars link it with the Jiroft culture. Henri-Paul Francfort and Xavier Tremblay proposed identifying the kingdom of Marhashi with Ancient Margiana on the basis of the Akkadian textual and archaeological evidence. History The main inscription describing the rule of Lugal-Anne-Mundu of Adab in the 24th century BC mentions Marhasi among the seven provinces of his empire, between the names of Elam and Gutium: "the Cedar Mountains, Elam, Marḫaši, Gutium, Subartu, Amurru, Sutium, or the Eanna Mountain". The same inscription also recorded that he confronted Migir-Enlil, the governor ( ensi) of Marhashi, who had led a coal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rimush
Rimush (or Rimuš, ''Ri-mu-uš'') was the second king of the Akkadian Empire. He was the son of Sargon of Akkad and Queen Tashlultum. He was succeeded by his brother Manishtushu, and was an uncle of Naram-Sin of Akkad. Rimush reported having a statue of himself made out of tin, then a recent introduction to the region. Background According to the ''Sumerian King List'', his reign lasted 9 years (though variant copies read 7 or 15 years.) There is one surviving year-name for an unknown year in his reign: "mu ud-nun / adab hul-a = Year in which Adab was destroyed". Tradition gives that he was assassinated, as the Bārûtu, “art of the diviner”, a first millennium compendium of extispicy, records “Omen of king Rimuš, whom his courtiers killed with their seals”. He was succeeded by his brother Manishtushu. The Ur III version of the Sumerian King List inverts the order of Rimush and Manishtushu. A number of his votive offerings have been found in excavated temples in several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sargon Of Akkad
Sargon of Akkad (; akk, ''Šarrugi''), also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC.The date of the reign of Sargon is highly uncertain, depending entirely on the (conflicting) regnal years given in the various copies of the Sumerian King List, specifically the uncertain duration of the Gutian dynasty. The added regnal years of the Sargonic and the Gutian dynasties have to be subtracted from the accession of Ur-Nammu of the Third Dynasty of Ur, which is variously dated to either 2047 BC (Short Chronology) or 2112 BC (Middle Chronology). An accession date of Sargon of 2334 BC assumes: (1) a Sargonic dynasty of 180 years (fall of Akkad 2154 BC), (2) a Gutian interregnum of 42 years and (3) the Middle Chronology accession year of Ur-Nammu (2112 BC). He is sometimes identified as the first person in recorded history to rule over an empire. He was the founder of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Plateau
The Iranian plateau or Persian plateau is a geological feature in Western Asia, Central Asia, and South Asia. It comprises part of the Eurasian Plate and is wedged between the Arabian Plate and the Indian Plate; situated between the Zagros Mountains to the west, the Caspian Sea and the Köpet Dag to the north, the Armenian Highlands and the Caucasus Mountains to the northwest, the Strait of Hormuz and the Persian Gulf to the south, and the Indian subcontinent to the east. As a historical region, it includes Parthia, Media, Persis, and some of the previous territories of Greater Iran."Old Iranian Online" University of Texas College of Liberal Arts (retrieved 10 February 2007) The Zagros form the plateau's western boundary, and its eastern slopes may also be included in the term. The '' |
Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire () was the first ancient empire of Mesopotamia after the long-lived civilization of Sumer. It was centered in the city of Akkad (city), Akkad () and its surrounding region. The empire united Akkadian language, Akkadian and Sumerian language, Sumerian speakers under one rule. The Akkadian Empire exercised influence across Mesopotamia, the Levant, and Anatolia, sending military expeditions as far south as Dilmun and Magan (civilization), Magan (modern Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, and Oman) in the Arabian Peninsula.Mish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. "Akkad" ''Webster’s Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary''. ninth ed. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster 1985. ). The Akkadian Empire reached its political peak between the 24th and 22nd centuries BC, following the conquests by its founder Sargon of Akkad. Under Sargon and his successors, the Akkadian language was briefly imposed on neighboring conquered states such as Elam and Gutian people, Gutium. Akkad is sometimes regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Noah Kramer
Samuel Noah Kramer (September 28, 1897 – November 26, 1990) was one of the world's leading Assyriologists, an expert in Sumerian history and Sumerian language. After high school, he attended Temple University, before Dropsie and Penn, both in Philadelphia. Among scholars, his work is considered transformative for the field of Sumerian history. His popular book ''History Begins at Sumer'' made Sumerian literature accessible to the general public. Biography Kramer was born on September 28, 1897, in Zhashkiv near Uman in the Kiev Governorate, Russian Empire (modern day Ukraine), the son of Benjamin and Yetta Kramer. His family was Jewish. In 1905, as a result of the anti-Semitic pogroms under Czar Nicholas II of Russia, his family emigrated to Philadelphia, where his father established a Hebrew school. After graduating from South Philadelphia High School, obtaining an Academic Diploma, Kramer tried a variety of occupations, including teaching in his father's school, becoming a wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History History 4Y1A6592 Louvre (24420942315)
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kindattu
Kindattu (, ''ki-in-da-tu'', also Kindadu, reigned ca. 2000 BC, middle Chronology) was the 6th king of the Shimashki Dynasty,D. T. Potts (2016). ''The Archaeology of Elam.'' Cambridge University Press. p. 135. in Elam (in present-day southwest Iran), at the time of the third dynasty of Ur in ancient Lower Mesopotamia. He is mentioned in the Shilhak-Inshushinak list of kings who did work on the Inshushinak temple in Susa. Apparently, Kindattu invaded and conquered Ur (2004 BC), and captured Ibbi-Sin, the last of the third dynasty of Ur, and made him a prisoner. The Elamites sacked Ur and settled there, but then were defeated by Ishbi-Erra, the first king of the Isin dynasty in his year 16, and later expelled from Mesopotamia. The destructions are related in the Lament for Ur: The Lament for Sumer and Ur then describes the fate of Ibbi-Sin: An Hymn to Ishbi-Erra, although quite fragmentary, mentions the role played by Kindattu in the destruction of Ur. See also * City Lament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puzur-Inšušinak
Puzur-Inshushinak (Linear Elamite: ''Puzur Šušinak'', Akkadian: , ''puzur3- dinšušinak'', also , ''puzur4- dinšušinak'' "Calling Inshushinak"), also sometimes thought to read Kutik-Inshushinak in Elamite, was king of Elam, around 2100 BC, and the last from the Awan dynasty according to the Susa kinglist. He mentions his father's name as Šimpi-išhuk, which, being an Elamite name, suggests that Puzur-Inshuhinak himself was Elamite. In the inscription of the "Table au Lion", he appears as "Puzur-Inshushin(ak) Ensi (Governor) of Susa, Shakkanakku (Military Governor) of the country of Elam" ( , a title used by his predecessors Eshpum, Epirmupi and Ili-ishmani as governors of the Akkadian Empire for the territory of Elam.Translation into French in In another inscription, he calls himself the "Mighty King of Elam", suggesting an accession to independence from the weakening Akkadian Empire. Rule His father was Shinpi-khish-khuk, the crown prince, and most likely a brother of k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

_on_his_victory_stele.jpg)


.jpg)
