|
Ptolemais In Phoenicia
Ptolemais was an ancient port city on the Canaanite coast in the region of Palestine, in the location of the present-day city of Acre, Israel. It was also called Ptolemais in Canaan (or ''Akko'', ''Ake'', or ''Akre'' in Canaanite Language). It was an Ancient bishopric, which became a double Catholic titular see. In the Middle Ages, it was known as ''Acre'' amongst some Western European crusaders, who started a new, militantly Latin chapter there. History Greek historians refer to the city as ''Ake'' ( grc, Ἄκη), meaning "cure." According to the Greek myth, Heracles found curative herbs here to heal his wounds. Josephus calls it ''Akre''. The name was changed to ''Antiochia Ptolemais'' ( grc, Ἀντιόχεια Πτολεμαΐς) shortly after Alexander the Great's conquest, and then to Ptolemais, probably by Ptolemy I Soter, after the Wars of the Diadochi lead to the partition of the kingdom of Alexander the Great and its inclusion first into the Egypt-based Lagid empire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old City Of Acre
Acre ( ), known locally as Akko ( he, עַכּוֹ, ''ʻAkō'') or Akka ( ar, عكّا, ''ʻAkkā''), is a city in the coastal plain region of the Northern District of Israel. The city occupies an important location, sitting in a natural harbour at the extremity of Haifa Bay on the coast of the Mediterranean's Levantine Sea."Old City of Acre." , World Heritage Center. World Heritage Convention. Web. 15 Apr 2013 Aside from coastal trading, it was also an important waypoint on the region's coastal road and the road cutting inland along the Jezre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenicia Under Roman Rule
Phoenicia under Roman rule describes the Phoenician city states (in the area of modern Lebanon and northern part of northern Galilee and Acre and the Northern Coastal Plain) ruled by Rome from 64 BCE to the Muslim conquests of the 7th century. The area around Berytus (and to a lesser degree around Heliopolis) was the only Latin speaking and Romanized part of Aramaic-speaking Phoenicia. This was one of the most prosperous periods in the history of the area that is now Lebanon. Phoenicia became one of the intellectual and economic hubs of the eastern half of the empire and a destination for merchants and intellectuals. The Romans built the temples of Baalbek, the temples at Mount Hermon, the temples of Niha and various other structures now in ruins that include smaller temples, hippodromes, baths and the Law school of Berytus. History The last century of Seleucid rule in Lebanon was marked by disorder and dynastic struggles. These ended in 64 BC, when the Roman general Pompey a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titus
Titus Caesar Vespasianus ( ; 30 December 39 – 13 September 81 AD) was Roman emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death. Before becoming emperor, Titus gained renown as a military commander, serving under his father in Judea during the First Jewish–Roman War. The campaign came to a brief halt with the death of emperor Nero in 68, launching Vespasian's bid for the imperial power during the Year of the Four Emperors. When Vespasian was declared Emperor on 1 July 69, Titus was left in charge of ending the Jewish rebellion. In 70, he besieged and captured Jerusalem, and destroyed the city and the Second Temple. For this achievement Titus was awarded a triumph; the Arch of Titus commemorates his victory to this day. During his father's rule, Titus gained notoriety in Rome serving as prefect of the Praetorian Guard, and for carrying on a controversial relationship with the Jewish queen Berenice. Despite concer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empire for 27 years. His fiscal reforms and consolidation of the empire generated political stability and a vast Roman building program. Vespasian was the first emperor from an equestrian family and only rose later in his lifetime into the senatorial rank as the first member of his family to do so. Vespasian's renown came from his military success; he was legate of Legio II Augusta during the Roman invasion of Britain in 43 and subjugated Judaea during the Jewish rebellion of 66. While Vespasian besieged Jerusalem during the Jewish rebellion, emperor Nero committed suicide and plunged Rome into a year of civil war known as the Year of the Four Emperors. After Galba and Otho perished in quick succession, Vitellius became emperor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Language
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman '' municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania Baetica and he came from a branch of the gens Aelia that originated in the Picenean town of Hadria, the ''Aeli Hadriani''. His father was of senatorial rank and was a first cousin of Emperor Trajan. Hadrian married Trajan's grand-niece Vibia Sabina early in his career before Trajan became emperor and possibly at the behest of Trajan's wife Pompeia Plotina. Plotina and Trajan's close friend and adviser Lucius Licinius Sura were well disposed towards Hadrian. When Trajan died, his widow claimed that he had nominated Hadrian as emperor immediately before his death. Rome's military and Senate approved Hadrian's succession, but four leading senators were unlawfully put to death soon after. They had opposed Hadrian or seemed to threat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanization (cultural)
Romanization or Latinization (Romanisation or Latinisation), in the historical and cultural meanings of both terms, indicate different historical processes, such as acculturation, integration and assimilation of newly incorporated and peripheral populations by the Roman Republic and the later Roman Empire. The term was used in Ancient Roman historiography and Italian historiography until the fascist period, when the various processes were called the " civilizing of barbarians". Characteristics Acculturation proceeded from the top down, with the upper classes adopting Roman culture first and the old ways lingering for the longest among peasants in outlying countryside and rural areas. Hostages played an important part in this process, as elite children, from Mauretania to Gaul, were taken to be raised and educated in Rome. Ancient Roman historiography and traditional Italian historiography confidently identified the different processes involved with a "civilization of barbarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesarea Maritima
Caesarea Maritima (; Greek: ''Parálios Kaisáreia''), formerly Strato's Tower, also known as Caesarea Palestinae, was an ancient city in the Sharon plain on the coast of the Mediterranean, now in ruins and included in an Israeli national park. For centuries it was a major intellectual hub of the Mediterranean and cultural capital of Palestine. The city and harbour were built under Herod the Great during c. 22–10 or 9 BCE near the site of a former Phoenician naval station known as ''Stratonos pyrgos'' (Στράτωνος πύργος, "Straton's Tower"), probably named after the 4th century BCE king of Sidon, Strato I. It later became the provincial capital of Roman Judea, Roman Syria Palaestina and Byzantine Palaestina Prima provinces. The city was populated throughout the 1st to 6th centuries AD and became an important early centre of Christianity during the Byzantine period. Its importance may have waned starting during the Muslim conquest of 640 in the early Middle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
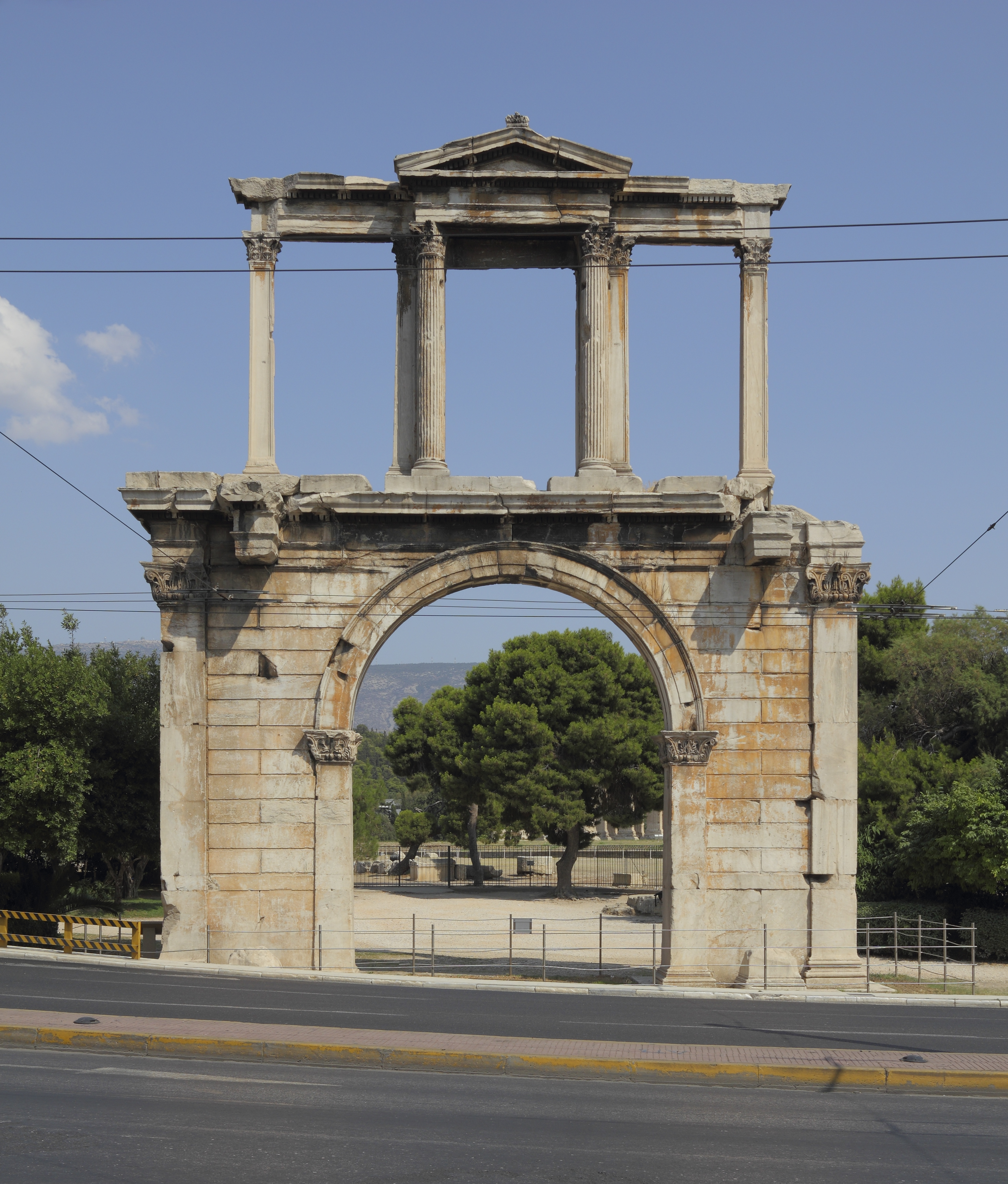
Aelia Capitolina
Aelia Capitolina (Traditional English Pronunciation: ; Latin in full: ) was a Roman colony founded during Emperor Hadrian's trip to Judah in 129/130, centered around Jerusalem, which had been almost totally razed after the siege of 70 CE. The foundation of Aelia Capitolina and the construction of a temple to Jupiter at the site of the former temple may have been one of the causes for the outbreak of the Bar Kokhba revolt in 132. Aelia Capitolina remained as the official name until Late Antiquity and the Aelia part of the name transliterated to ''Īlyāʾ'' was also used by the Umayyad Caliphate. Name ''Aelia'' came from Hadrian's ''nomen gentile'', ''Aelius'', while ''Capitolina'' meant that the new city was dedicated to ''Jupiter Capitolinus'', to whom a temple was built. The Latin name ''Aelia'' is the source of the much later Arabic term ''Īlyāʾ'' (إيلياء), a 7th-century Islamic name for Jerusalem. History Jerusalem, once heavily rebuilt by Herod, was still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
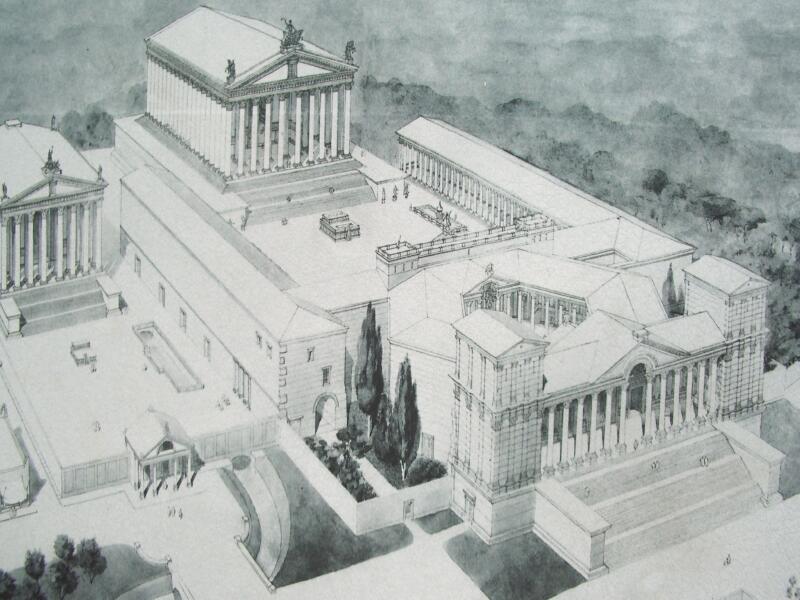
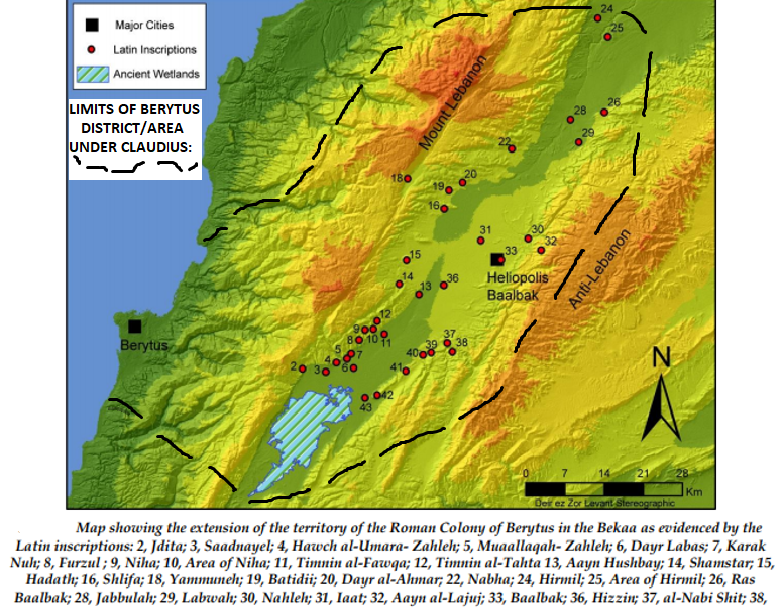
Berytus
) or Laodicea in Canaan (2nd century to 64 BCE) , image = St. George's Cathedral, Beirut.jpg , image_size = , alt = , caption = Roman ruins of Berytus, in front of Saint George Greek Orthodox Cathedral in modern-day Beirut , map = , map_type = Lebanon , map_alt = , map_size = 270 , coordinates = , altitude_m = , altitude_ref = , relief = , gbgridref = , map_dot_label = , location = Beirut, Lebanon , region = , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , volume = , diameter = , circumference = , height = , builder = , material = , built = Roman republic (merchants from early Laodicea/Berytus recorded by 110–109 BCE) , abandoned = , epochs = Roman and Early Byzantine/late antiquity; previous port dating back to Ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Drusus and Antonia Minor at Lugdunum in Roman Gaul, where his father was stationed as a military legate. He was the first Roman emperor to be born outside Italy. Nonetheless, Claudius was an Italian of Sabine origins. As he had a limp and slight deafness due to sickness at a young age, he was ostracized by his family and was excluded from public office until his consulship (which was shared with his nephew, Caligula, in 37). Claudius's infirmity probably saved him from the fate of many other nobles during the purges throughout the reigns of Tiberius and Caligula, as potential enemies did not see him as a serious threat. His survival led to him being declared emperor by the Praetorian Guard after Caligula's assassination, at which point he was the last adult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herod The Great
Herod I (; ; grc-gre, ; c. 72 – 4 or 1 BCE), also known as Herod the Great, was a History of the Jews in the Roman Empire, Roman Jewish client state, client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian Kingdom of Judea, Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renovation of the Second Temple#Herod's Temple, Second Temple in Jerusalem and the expansion of the Temple Mount towards its north, the enclosure around the Cave of the Patriarchs in Hebron, the construction of the port at Caesarea Maritima, the fortress at Masada, and Herodium. Vital details of his life are recorded in the works of the 1st century CE Roman–Jewish historian Josephus. Herod also appears in the Christian Gospel of Matthew as the ruler of Judea who orders the Massacre of the Innocents at the time of the Nativity of Jesus, birth of Jesus, although most Herod biographers do not believe that this event occurred. Despite his successes, including singleh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |