|
Pseudo-R-squared
Pseudo-R-squared values are used when the outcome variable is nominal or ordinal such that the coefficient of determination 2 cannot be applied as a measure for goodness of fit and when a likelihood function is used to fit a model. In linear regression, the squared multiple correlation, 2 is used to assess goodness of fit as it represents the proportion of variance in the criterion that is explained by the predictors. In logistic regression analysis, there is no agreed upon analogous measure, but there are several competing measures each with limitations. Four of the most commonly used indices and one less commonly used one are examined in this article: * Likelihood ratio 2 * Cox and Snell 2 * Nagelkerke 2 * McFadden 2 * Tjur 2 2L by Cohen 2L is given by Cohen: ::R^2_\text = \frac . This is the most analogous index to the squared multiple correlations in linear regression. It represents the proportional reduction in the deviance wherein the deviance is treated as a measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logistic Regression
In statistics, the logistic model (or logit model) is a statistical model that models the probability of an event taking place by having the log-odds for the event be a linear function (calculus), linear combination of one or more independent variables. In regression analysis, logistic regression (or logit regression) is estimation theory, estimating the parameters of a logistic model (the coefficients in the linear combination). Formally, in binary logistic regression there is a single binary variable, binary dependent variable, coded by an indicator variable, where the two values are labeled "0" and "1", while the independent variables can each be a binary variable (two classes, coded by an indicator variable) or a continuous variable (any real value). The corresponding probability of the value labeled "1" can vary between 0 (certainly the value "0") and 1 (certainly the value "1"), hence the labeling; the function that converts log-odds to probability is the logistic function, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-R-Squared Outputted Values From R
Pseudo-R-squared values are used when the outcome variable is nominal or ordinal such that the coefficient of determination 2 cannot be applied as a measure for goodness of fit and when a likelihood function is used to fit a model. In linear regression, the squared multiple correlation, 2 is used to assess goodness of fit as it represents the proportion of variance in the criterion that is explained by the predictors. In logistic regression analysis, there is no agreed upon analogous measure, but there are several competing measures each with limitations. Four of the most commonly used indices and one less commonly used one are examined in this article: * Likelihood ratio 2 * Cox and Snell 2 * Nagelkerke 2 * McFadden 2 * Tjur 2 2L by Cohen 2L is given by Cohen: ::R^2_\text = \frac . This is the most analogous index to the squared multiple correlations in linear regression. It represents the proportional reduction in the deviance wherein the deviance is treated as a measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coefficient Of Determination
In statistics, the coefficient of determination, denoted ''R''2 or ''r''2 and pronounced "R squared", is the proportion of the variation in the dependent variable that is predictable from the independent variable(s). It is a statistic used in the context of statistical models whose main purpose is either the prediction of future outcomes or the testing of hypotheses, on the basis of other related information. It provides a measure of how well observed outcomes are replicated by the model, based on the proportion of total variation of outcomes explained by the model. There are several definitions of ''R''2 that are only sometimes equivalent. One class of such cases includes that of simple linear regression where ''r''2 is used instead of ''R''2. When only an intercept is included, then ''r''2 is simply the square of the sample correlation coefficient (i.e., ''r'') between the observed outcomes and the observed predictor values. If additional regressors are included, ''R''2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nico Nagelkerke
Nicolaas Jan Dirk "Nico" Nagelkerke (born 1951) is a Dutch biostatistician and epidemiologist. As of 2012, he was a professor of biostatistics at the United Arab Emirates University. He previously taught at the University of Leiden in the Netherlands. He has now been retired for several years but as of now (January 2023) he is still active in research. He is well known in epidemiology thanks to his invention of what is now known as the "Nagelkerke R2", which is one of a number of generalisations of the coefficient of determination from linear regression to logistic regression, see Pseudo-R-squared, Coefficient of determination, Logistic regression In statistics, the logistic model (or logit model) is a statistical model that models the probability of an event taking place by having the log-odds for the event be a linear function (calculus), linear combination of one or more independent var .... References Living people 1951 births Dutch statisticians Dutch epidemiol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Likelihood Function
The likelihood function (often simply called the likelihood) represents the probability of random variable realizations conditional on particular values of the statistical parameters. Thus, when evaluated on a given sample, the likelihood function indicates which parameter values are more ''likely'' than others, in the sense that they would have made the observed data more probable. Consequently, the likelihood is often written as \mathcal(\theta\mid X) instead of P(X \mid \theta), to emphasize that it is to be understood as a function of the parameters \theta instead of the random variable X. In maximum likelihood estimation, the arg max of the likelihood function serves as a point estimate for \theta, while local curvature (approximated by the likelihood's Hessian matrix) indicates the estimate's precision. Meanwhile in Bayesian statistics, parameter estimates are derived from the converse of the likelihood, the so-called posterior probability, which is calculated via Bayes' r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Regression
In statistics, linear regression is a linear approach for modelling the relationship between a scalar response and one or more explanatory variables (also known as dependent and independent variables). The case of one explanatory variable is called '' simple linear regression''; for more than one, the process is called multiple linear regression. This term is distinct from multivariate linear regression, where multiple correlated dependent variables are predicted, rather than a single scalar variable. In linear regression, the relationships are modeled using linear predictor functions whose unknown model parameters are estimated from the data. Such models are called linear models. Most commonly, the conditional mean of the response given the values of the explanatory variables (or predictors) is assumed to be an affine function of those values; less commonly, the conditional median or some other quantile is used. Like all forms of regression analysis, linear regression focuses on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expectation of the squared deviation of a random variable from its population mean or sample mean. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average value. Variance has a central role in statistics, where some ideas that use it include descriptive statistics, statistical inference, hypothesis testing, goodness of fit, and Monte Carlo sampling. Variance is an important tool in the sciences, where statistical analysis of data is common. The variance is the square of the standard deviation, the second central moment of a distribution, and the covariance of the random variable with itself, and it is often represented by \sigma^2, s^2, \operatorname(X), V(X), or \mathbb(X). An advantage of variance as a measure of dispersion is that it is more amenable to algebraic manipulation than other measures of dispersion such as the expected absolute deviation; for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Likelihood Ratio
The likelihood function (often simply called the likelihood) represents the probability of random variable realizations conditional on particular values of the statistical parameters. Thus, when evaluated on a given sample, the likelihood function indicates which parameter values are more ''likely'' than others, in the sense that they would have made the observed data more probable. Consequently, the likelihood is often written as \mathcal(\theta\mid X) instead of P(X \mid \theta), to emphasize that it is to be understood as a function of the parameters \theta instead of the random variable X. In maximum likelihood estimation, the arg max of the likelihood function serves as a point estimate for \theta, while local curvature (approximated by the likelihood's Hessian matrix) indicates the estimate's precision. Meanwhile in Bayesian statistics, parameter estimates are derived from the converse of the likelihood, the so-called posterior probability, which is calculated via Bayes' ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
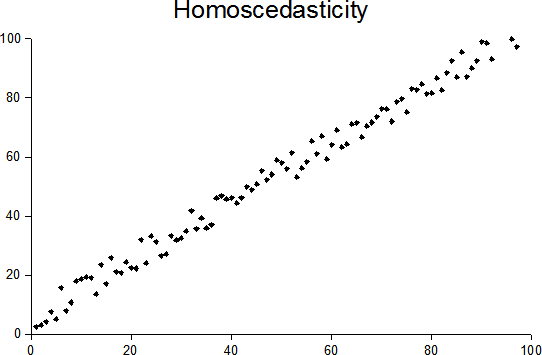
Homoscedasticity
In statistics, a sequence (or a vector) of random variables is homoscedastic () if all its random variables have the same finite variance. This is also known as homogeneity of variance. The complementary notion is called heteroscedasticity. The spellings ''homoskedasticity'' and ''heteroskedasticity'' are also frequently used. Assuming a variable is homoscedastic when in reality it is heteroscedastic () results in unbiased but inefficient point estimates and in biased estimates of standard errors, and may result in overestimating the goodness of fit as measured by the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient, Pearson coefficient. The existence of heteroscedasticity is a major concern in regression analysis and the analysis of variance, as it invalidates statistical hypothesis testing, statistical tests of significance that assume that the errors and residuals in statistics, modelling errors all have the same variance. While the ordinary least squares estimator is stil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heteroscedastic
In statistics, a sequence (or a vector) of random variables is homoscedastic () if all its random variables have the same finite variance. This is also known as homogeneity of variance. The complementary notion is called heteroscedasticity. The spellings ''homoskedasticity'' and ''heteroskedasticity'' are also frequently used. Assuming a variable is homoscedastic when in reality it is heteroscedastic () results in unbiased but inefficient point estimates and in biased estimates of standard errors, and may result in overestimating the goodness of fit as measured by the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient, Pearson coefficient. The existence of heteroscedasticity is a major concern in regression analysis and the analysis of variance, as it invalidates statistical hypothesis testing, statistical tests of significance that assume that the errors and residuals in statistics, modelling errors all have the same variance. While the ordinary least squares estimator is stil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Ratios
Statistics (from German: ''Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample to the population as a whole. An experim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |