|
Probainognathidae
Probainognathidae is an extinct family of insectivorous cynodonts which lived in what is now South America during the Middle to Late Triassic. The family was established by Alfred Romer in 1973 and includes two genera, ''Probainognathus'' from the Chañares Formation of Argentina and ''Bonacynodon'' from the ''Dinodontosaurus'' Assemblage Zone of Brazil. Probainognathids were closely related to the clade Prozostrodontia, which includes mammals and their close relatives. Description Members of Probainognathidae were relatively small-bodied animals, with skull lengths of around . The temporal region (area behind the eye sockets) was rather wide, and longer than the snout. The secondary palate was well-developed compared to earlier cynodonts, and the portion made up by the maxilla was larger than the part made from the palatine bone. The dentary, the tooth-bearing bone of the lower jaw, was quite tall when seen from the side. The mandibular symphysis (the joint between the two h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probainognathus
''Probainognathus'' meaning “progressive jaw” is an extinct genus of cynodonts that lived around 235 to 221.5 million years ago, during the Late Triassic in what is now South America. ''Probainognathus'' is a member of the family Probainognathidae, and is a close relative of the family Chiniquodontidae.Fossilworks: Gateway to the Paleobiology Database. Probainognathus Romer 1970 (therapsid). PaleoDB taxon number: 39225 , http://www.fossilworks.org/cgi-bin/bridge.pl?a=taxonInfo&taxon_no=80895 The various similarities to Chiniquodontidae led Alfred Romer to initially suggest ''Probainognathus'' be placed within that family, but it was subsequently decided that the differences were enough to warrant its placement within Probainognathidae.Romer, A.S. 1973. The Chanares (Argentina) Triassic reptile fauna. XVIII. Probelesodon minor, a new species of carnivorous cynodont; family Probainognathidae nov. Breviora, 401:1-4 ''Probainognathus jenseni'' was a species of small, carnivorous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
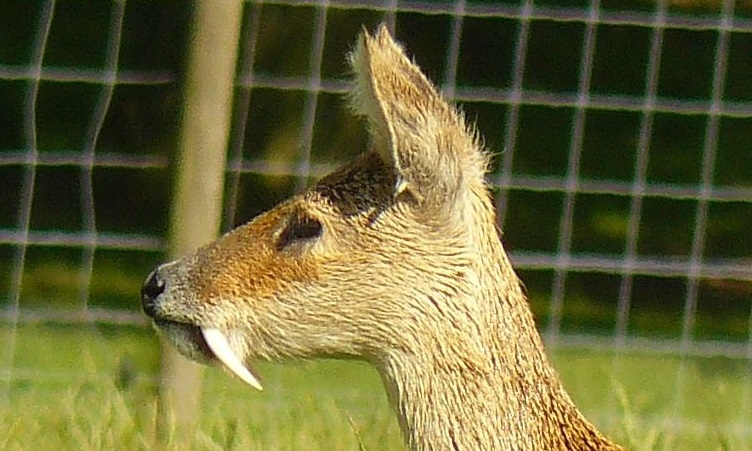
Bonacynodon
''Bonacynodon'' is an extinct genus of cynodonts that lived in what is now southern Brazil during the Triassic period (Ladinian–Carnian ages). The genus is monotypic, containing only the type species ''Bonacynodon schultzi''. ''B. schultzi'' is known from two specimens, consisting of two partial skulls and some badly preserved parts of the postcranium. Both specimens were recovered from the Pinheiros-Chiniquá Sequence, part of the Santa Maria Supersequence of the Paraná Basin. This sequence preserves a faunal association known as the ''Dinodontosaurus'' Assemblage Zone, which contains numerous other species of cynodonts, dicynodonts and reptiles. ''Bonacynodon'' was a small, likely insectivorous cynodont, whose length has been estimated at around . It can be distinguished from other cynodonts by its large, serrated (saw-like) canine teeth. Together with the genus ''Probainognathus'' of Argentina, it made up the family Probainognathidae, one of the earliest-diverging line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonacynodon Witout Visible Ears
''Bonacynodon'' is an extinct genus of cynodonts that lived in what is now southern Brazil during the Triassic period (Ladinian–Carnian ages). The genus is monotypic, containing only the type species ''Bonacynodon schultzi''. ''B. schultzi'' is known from two specimens, consisting of two partial skulls and some badly preserved parts of the postcranium. Both specimens were recovered from the Pinheiros-Chiniquá Sequence, part of the Santa Maria Supersequence of the Paraná Basin. This sequence preserves a faunal association known as the ''Dinodontosaurus'' Assemblage Zone, which contains numerous other species of cynodonts, dicynodonts and reptiles. ''Bonacynodon'' was a small, likely insectivorous cynodont, whose length has been estimated at around . It can be distinguished from other cynodonts by its large, serrated (saw-like) canine teeth. Together with the genus ''Probainognathus'' of Argentina, it made up the family Probainognathidae, one of the earliest-diverging line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chañares Formation
The Chañares Formation is a Carnian-age geologic formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin, located in La Rioja Province, Argentina. It is characterized by drab-colored fine-grained volcaniclastic claystones, siltstones, and sandstones which were deposited in a fluvial to lacustrine environment. The formation is most prominently exposed within Talampaya National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site within La Rioja Province. The Chañares formation is the lowermost stratigraphic unit of the Agua de la Peña Group, overlying the Tarjados Formation of the Paganzo Group, and underlying the Los Rastros Formation. Though previously considered Ladinian in age, U-Pb dating has determined that most or all of the Chañares Formation dates to the early Carnian stage of the Late Triassic.Kent et al, 2014, p.7959 The Chañares Formation has provided a diverse and well-preserved faunal assemblage which has been studied intensively since the 1960s. The most common reptiles were pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrate Bone
The quadrate bone is a skull bone in most tetrapods, including amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, birds), and early synapsids. In most tetrapods, the quadrate bone connects to the quadratojugal and squamosal bones in the skull, and forms upper part of the jaw joint. The lower jaw articulates at the articular bone, located at the rear end of the lower jaw. The quadrate bone forms the lower jaw articulation in all classes except mammals. Evolutionarily, it is derived from the hindmost part of the primitive cartilaginous upper jaw. Function in reptiles In certain extinct reptiles, the variation and stability of the morphology of the quadrate bone has helped paleontologists in the species-level taxonomy and identification of mosasaur squamates and spinosaurine dinosaurs. In some lizards and dinosaurs, the quadrate is articulated at both ends and movable. In snakes, the quadrate bone has become elongated and very mobile, and contributes greatly to their ability to swallow very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articular Bone
The articular bone is part of the lower jaw of most vertebrates, including most jawed fish, amphibians, birds and various kinds of reptiles, as well as ancestral mammals. Anatomy In most vertebrates, the articular bone is connected to two other lower jaw bones, the suprangular and the angular. Developmentally, it originates from the embryonic mandibular cartilage. The most caudal portion of the mandibular cartilage ossifies to form the articular bone, while the remainder of the mandibular cartilage either remains cartilaginous or disappears. In snakes In snakes, the articular, surangular, and prearticular bones have fused to form the compound bone. The mandible is suspended from the quadrate bone and articulates at this compound bone. Function In amphibians and reptiles In most tetrapods, the articular bone forms the lower portion of the jaw joint. The upper jaw articulates at the quadrate bone. In mammals In mammals, the articular bone evolves to form the malleu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamosal
The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone. In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal The quadratojugal is a skull bone present in many vertebrates, including some living reptiles and amphibians. Anatomy and function In animals with a quadratojugal bone, it is typically found connected to the jugal (cheek) bone from the front and ... bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestral component of the dermal roof and is typically thin compared to other skull bones. The squamosal bone lies Anatomical terms of location, ventral to the temporal series and otic notch, and is bordered anteriorly by the Postorbital bone, postorbital. Posteriorly, the squamosal articulates with the quadrate bone, quadrate and Pterygoid bone, pterygoid bones. The squamosal is bordered anteroventrally by the jugal and ventrally by the quadratojugal. Function in reptiles In reptiles, the Quadrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surangular
The suprangular or surangular is a jaw bone found in most land vertebrates, except mammals. Usually in the back of the jaw, on the upper edge, it is connected to all other jaw bones: dentary, angular, splenial and articular The articular bone is part of the lower jaw of most vertebrates, including most jawed fish, amphibians, birds and various kinds of reptiles, as well as ancestral mammals. Anatomy In most vertebrates, the articular bone is connected to two oth .... It is often a muscle attachment site. References Vertebrate anatomy {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
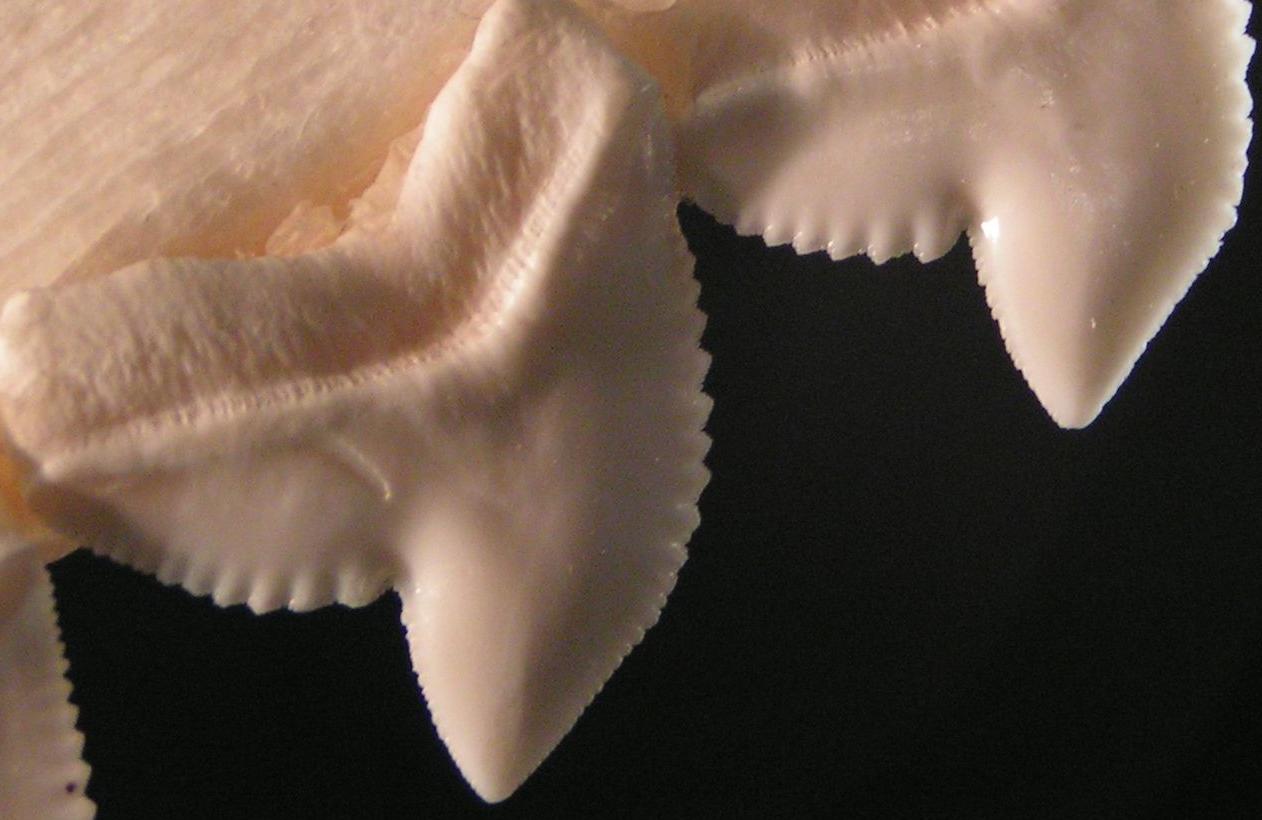
Canine Teeth
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dog teeth, or (in the context of the upper jaw) fangs, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or vampire fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. They can appear more flattened however, causing them to resemble incisors and leading them to be called ''incisiform''. They developed and are used primarily for firmly holding food in order to tear it apart, and occasionally as weapons. They are often the largest teeth in a mammal's mouth. Individuals of most species that develop them normally have four, two in the upper jaw and two in the lower, separated within each jaw by incisors; humans and dogs are examples. In most species, canines are the anterior-most teeth in the maxillary bone. The four canines in humans are the two maxillary canines and the two mandibular canines. Details There are generally four canine teeth: two in the upper (maxillary) and two in the lower (mandibular) arch. A canine is placed laterally t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postcanine
Cheek teeth or post-canines comprise the molar and premolar teeth in mammals. Cheek teeth are multicuspidate (having many folds or tubercles). Mammals have multicuspidate molars (three in placentals, four in marsupials, in each jaw quadrant) and premolars situated between canines and molars whose shape and number varies considerably among particular groups. For example, many modern Carnivora possess carnassials, or secodont teeth. This scissor-like pairing of the last upper premolar and first lower molar is adapted for shearing meat. In contrast, the cheek teeth of deer and cattle are selenodont. Viewed from the side, these teeth have a series of triangular cusps or ridges, enabling the ruminants' sideways jaw motions to break down tough vegetable matter. Cheek teeth are sometimes separated from the incisors by a gap called a diastema. Cheek teeth in reptiles are much simpler as compared to mammals. Roles and significance Apart from helping grind the food to properly reduce the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serrated
Serration is a saw-like appearance or a row of sharp or tooth-like projections. A serrated cutting edge has many small points of contact with the material being cut. By having less contact area than a smooth blade or other edge, the applied pressure at each point of contact is greater and the points of contact are at a sharper angle to the material being cut. This causes a cutting action that involves many small splits in the surface of the material being cut, which cumulatively serve to cut the material along the line of the blade. In nature, serration is commonly seen in the cutting edge on the teeth of some species, usually sharks. However, it also appears on non-cutting surfaces, for example in botany where a toothed leaf margin or other plant part, such as the edge of a carnation petal, is described as being serrated. A serrated leaf edge may reduce the force of wind and other natural elements. Probably the largest serrations on Earth occur on the skylines of mountains (th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentary Bone
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from '' mandere'' "to chew" and ''-bula'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)