|
ProbCons
In bioinformatics and proteomics, ProbCons is an open source software for probabilistic consistency-based multiple alignment of amino acid sequences. It is one of the most efficient protein multiple sequence alignment programs, since it has repeatedly demonstrated a statistically significant advantage in accuracy over similar tools, including Clustal and MAFFT. Algorithm The following describes the basic outline of the ProbCons algorithm. Step 1: Reliability of an alignment edge For every pair of sequences compute the probability that letters x_i and y_i are paired in a^* an alignment that is generated by the model. \begin P(x_i \sim y_i, x,y) \ \overset& \ \Pr x,y\\ pt =& \ \sum_ \Pr x,y\\ pt =& \ \sum_ \mathbf\ \Pr x,y\end (Where \mathbf\ is equal to 1 if x_i and y_i are in the alignment and 0 otherwise.) Step 2: Maximum expected accuracy The accuracy of an alignment a^* with respect to another alignment a is defined as the number of common aligned pairs divided by the le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
MUSCLE (alignment Software)
MUltiple Sequence Comparison by Log-Expectation (MUSCLE) is a computer software for multiple sequence alignment of protein and nucleotide sequences. It is Software license, licensed as public domain. The method was published by Robert C. Edgar in two papers in 2004. The first paper, published in ''Nucleic Acids Research'', introduced the sequence alignment algorithm. The second paper, published in ''BMC Bioinformatics'', presented more technical details. MUSCLE up to version 3 uses a progressive-refinement method. Since version 5 it uses a hidden Markov model similar to ProbCons. History Robert C. Edgar Edgar graduated in 1982 from University College London, BSc in Physics, PhD in Particle physics. He pursued software development post-graduation and founded his own company, Parity Software, in 1988. In 2001, he began working with coding algorithms after attending a seminar at the University of California Berkley. From 2001-present day Edgar has contributed to or been the sole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Clustal
Clustal is a computer program used for multiple sequence alignment in bioinformatics. The software and its algorithms have gone through several iterations, with ClustalΩ (Omega) being the latest version . It is available as standalone software, via a Clustal#External links, web interface, and through a server hosted by the European Bioinformatics Institute. Clustal has been an important bioinformatic software, with two of its academic publications amongst the top 100 papers cited of all time, according to Nature (journal), Nature in 2014. History Version history * Clustal: The original software for multiple sequence alignments, created by Desmond G. Higgins, Des Higgins in 1988, was based on deriving a guide tree from pairwise sequences of Amino acid, amino acids or Nucleotide, nucleotides. * ClustalV: The second generation of Clustal, released in 1992. It introduced the ability to create new alignments from existing alignments in a process known as phylogenetic tree re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
T-Coffee
T-Coffee (Tree-based Consistency Objective Function for Alignment Evaluation) is a multiple sequence alignment software using a progressive approach. It generates a library of pairwise alignments to guide the multiple sequence alignment. It can also combine multiple sequences alignments obtained previously and in the latest versions can use structural information from Protein Data Bank (PDB) files (3D-Coffee). It has advanced features to evaluate the quality of the alignments and some capacity for identifying occurrence of motifs (Mocca). It produces alignment in the aln format (Clustal) by default, but can also produce PIR, MSF, and FASTA format. The most common input formats are supported (FASTA, Protein Information Resource (PIR)). Algorithm T-Coffee algorithm consist of two main features, the first by, using heterogeneous data sources, can provide simple and flexible means to generate multiple alignments. T-coffee can compute multiple alignments using a library that was generat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sequence Alignment Software
This list of sequence alignment software is a compilation of software tools and web portals used in pairwise sequence alignment and multiple sequence alignment. See structural alignment software for structural alignment of proteins. Database search only *Sequence type: protein or nucleotide Pairwise alignment *Sequence type: protein or nucleotide **Alignment type: local or global Multiple sequence alignment *Sequence type: protein or nucleotide. **Alignment type: local or global Genomics analysis *Sequence type: protein or nucleotide Motif finding *Sequence type: protein or nucleotide Benchmarking Alignment viewers, editors Please see List of alignment visualization software. Short-read sequence alignment See also * List of open source bioinformatics software References {{Reflist Seq Sequence In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Probalign
Probalign is a sequence alignment tool that calculates a maximum expected accuracy alignment using partition function posterior probabilities. Base pair probabilities are estimated using an estimate similar to Boltzmann distribution. The partition function is calculated using a dynamic programming approach. Algorithm The following describes the algorithm used by probalign to determine the base pair probabilities. Alignment score To score an alignment of two sequences two things are needed: * a similarity function \sigma(x,y) (e.g. PAM, BLOSUM,...) * affine gap penalty: g(k) = \alpha + \beta k The score S(a) of an alignment a is defined as: S(a) = \sum_ \sigma(x_i,y_j) + \text Now the boltzmann weighted score of an alignment a is: e^ = e^ = \left( \prod_ e^ \right) \cdot e^ Where T is a scaling factor. The probability of an alignment assuming boltzmann distribution is given by Pr x,y= \frac Where Z is the partition function, i.e. the sum of the boltzmann weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field of science that develops methods and Bioinformatics software, software tools for understanding biological data, especially when the data sets are large and complex. Bioinformatics uses biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, data science, computer programming, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret biological data. The process of analyzing and interpreting data can sometimes be referred to as computational biology, however this distinction between the two terms is often disputed. To some, the term ''computational biology'' refers to building and using models of biological systems. Computational, statistical, and computer programming techniques have been used for In silico, computer simulation analyses of biological queries. They include reused specific analysis "pipelines", particularly in the field of genomics, such as by the identification of genes and single nucleotide polymorphis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins. Proteins are vital macromolecules of all living organisms, with many functions such as the formation of structural fibers of muscle tissue, enzymatic digestion of food, or synthesis and replication of DNA. In addition, other kinds of proteins include antibodies that protect an organism from infection, and hormones that send important signals throughout the body. The proteome is the entire set of proteins produced or modified by an organism or system. Proteomics enables the identification of ever-increasing numbers of proteins. This varies with time and distinct requirements, or stresses, that a cell or organism undergoes. Proteomics is an interdisciplinary domain that has benefited greatly from the genetic information of various genome projects, including the Human Genome Project. It covers the exploration of proteomes from the overall level of protein composition, structure, and activity, and is an important component of function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Open Source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use and view the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open source model is a decentralized software development model that encourages open collaboration. A main principle of Open-source software, open source software development is peer production, with products such as source code, blueprints, and documentation freely available to the public. The open source movement in software began as a response to the limitations of proprietary code. The model is used for projects such as in open source appropriate technology, and open source drug discovery. Open source promotes universal access via an open-source or free license to a product's design or blueprint, and universal redistribution of that design or blueprint. Before the phrase ''open source'' became widely adopted, developers and producers used a variety of other terms, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups ( alpha- , beta- , gamma- amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence. Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC- IUBMB Joint Commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
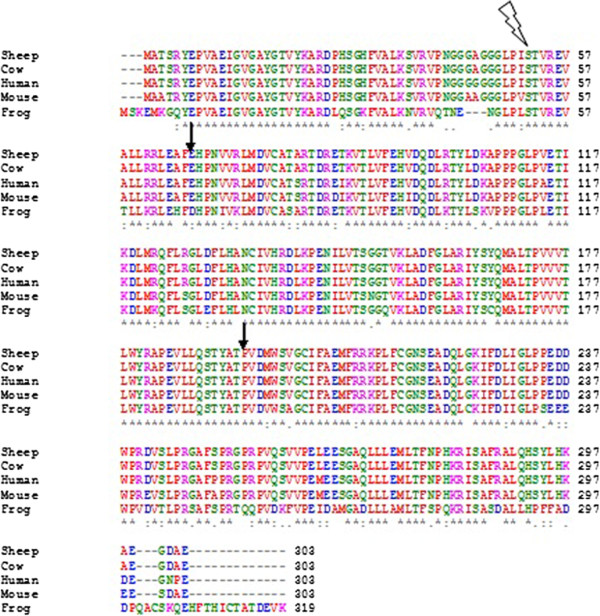
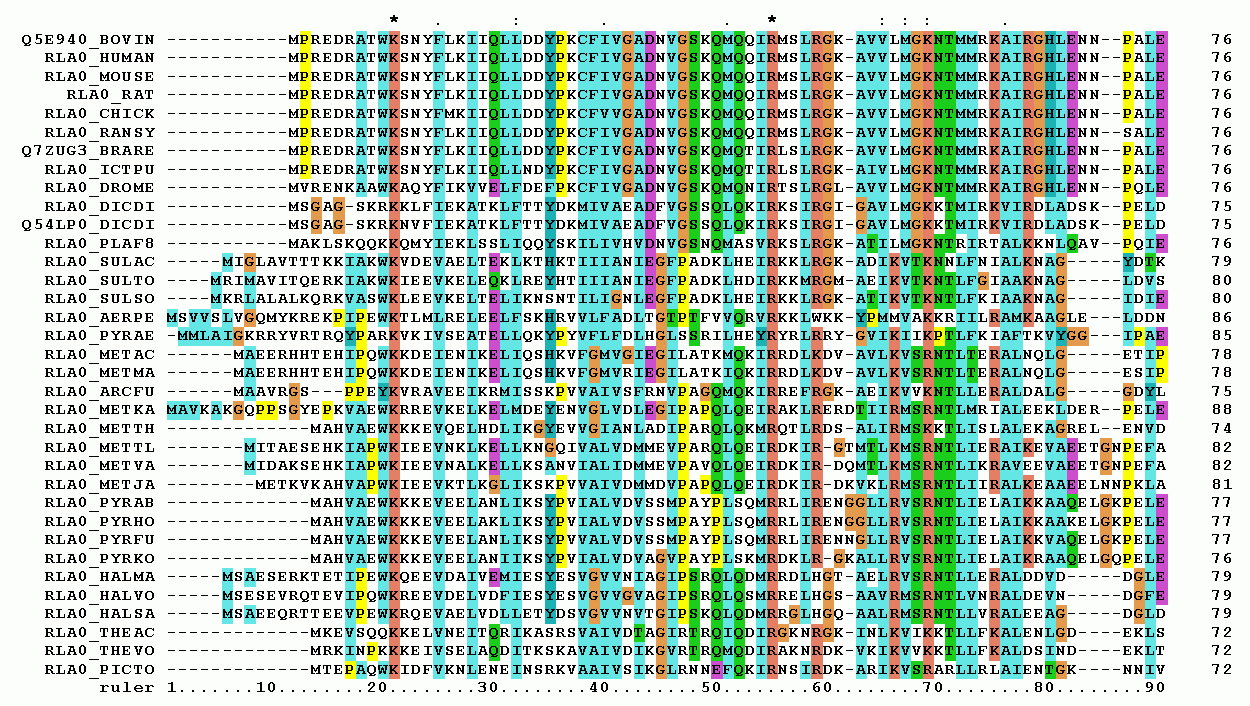
Multiple Sequence Alignment
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) is the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. These alignments are used to infer evolutionary relationships via phylogenetic analysis and can highlight homologous features between sequences. Alignments highlight mutation events such as point mutations (single amino acid or nucleotide changes), insertion mutations and deletion mutations, and alignments are used to assess sequence conservation and infer the presence and activity of protein domains, tertiary structures, secondary structures, and individual amino acids or nucleotides. Multiple sequence alignments require more sophisticated methodologies than pairwise alignments, as they are more computationally complex. Most multiple sequence alignment programs use heuristic methods rather than global optimization because identifying the optimal alignment between more than a few sequences of moderate length is prohibiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
MAFFT
In bioinformatics, MAFFT (multiple alignment using fast Fourier transform) is a program used to create multiple sequence alignments of amino acid or nucleotide sequences. Published in 2002, the first version used an algorithm based on multiple sequence alignment#Progressive alignment construction, progressive alignment, in which the sequences were clustered with the help of the fast Fourier transform. Subsequent versions of MAFFT have added other algorithms and modes of operation, including options for faster alignment of large numbers of sequences, higher accuracy alignments, alignment of non-coding RNA sequences, and the addition of new sequences to existing alignments. History There have been many variations of the MAFFT software, some of which are listed below: * ''MAFFT'' – The first version, created by Kazutaka Katoh in 2002, used an algorithm based on multiple sequence alignment#Progressive alignment construction, progressive alignment, in which the sequences were cluste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
AMAP
AutoNavi Software Co., Ltd. () is a Chinese web mapping, navigation and location-based services provider, founded in 2001. One of its subsidiary companies, Beijing Mapabc Co. Ltd. (www.mapabc.com), is a map website in China. AutoNavi was acquired by Alibaba Group in 2014. It offers its map services at Amap.com and as the Amap mobile app. It is known as Gaode in Chinese. AutoNavi provides mapping data of China and Taiwan for Apple Maps, which was introduced with iOS 6. Previously this was the only method of viewing their map in English, and was only available when the Apple device was located within China. As of 2025 however, there is a standalone app called Amap available for Android, iOS and HarmonyOS. The app is available in English, traditional Chinese and simplified Chinese. AutoNavi previously provided mapping data to Google from 2006, although this has not been updated for some years. AutoNavi's own map application was the top mobile map app in China in 2012, with over 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |