|
Presbylarynx
The presbylarynx is a condition in which age-related atrophy of the soft tissues of the larynx results in weak voice and restricted vocal range and stamina. In other words, it is the loss of vocal fold tone and elasticity due to aging which affects voice quality. Symptoms The list of signs and symptoms mentioned in various sources for presbylarynx includes the 4 symptoms listed below: # Hoarseness # Breathy voice # Reduced voice volume # Unstable voice pitch Note that presbylarynx symptoms usually refers to various symptoms known to a patient, but the phrase "presbylarynx signs" may refer to those signs only noticeable by a doctor. Treatment The list of treatments mentioned in various sources for presbylarynx includes the following list. Always seek professional medical advice about any treatment or change in treatment plans. * Voice therapy See also * Acoustic phonetics * Epiglottitis * Intubation * Laryngitis * Mechanical larynx * Phonation * Phonetics * Vocology * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
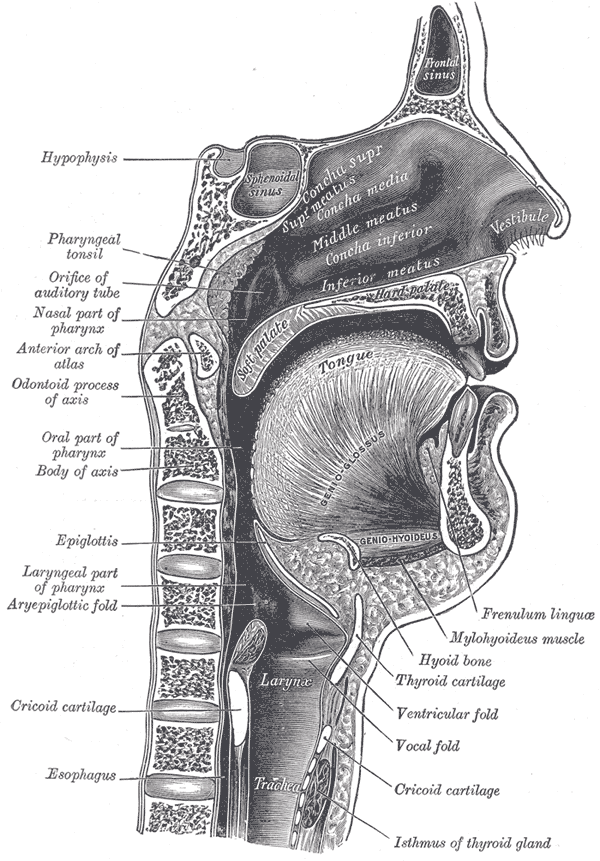
Larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word ʻlarynxʼ (plural ʻlaryngesʼ) comes from the Ancient Greek word ''lárunx'' ʻlarynx, gullet, throat.ʼ Structure The triangle-shaped larynx consists largely of cartilages that are attached to one another, and to surrounding structures, by muscles or by fibrous and elastic tissue components. The larynx is lined by a ciliated columnar epithelium except for the vocal folds. The cavity of the larynx extends from its triangle-shaped inlet, to the epiglottis, and to the circular outlet at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocal Fold
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedality, bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex Human brain, brain. This has enabled the development of ad ... using the vocal tract, including Speech, talking, singing, Laughter, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production in which the vocal folds (vocal cords) are the primary sound source. (Other sound production mechanisms produced from the same general area of the body involve the production of Voicelessness, unvoiced consonants, Click consonant, clicks, whistling and whispering.) Generally speaking, the mechanism for generating the human voice can be subdivided into three parts; the lungs, the vocal folds within the larynx (voice box), and the articulators. The lungs, the "pump" must produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voice Therapy
Voice therapy consists of techniques and procedures that target vocal parameters, such as vocal fold closure, pitch, volume, and quality. This therapy is provided by speech-language pathologists and is primarily used to aid in the management of voice disorders, or for altering the overall quality of voice, as in the case of transgender voice therapy. Vocal pedagogy is a related field to alter voice for the purpose of singing. Voice therapy may also serve to teach preventive measures such as vocal hygiene and other safe speaking or singing practices. Orientations There are several orientations towards management in voice therapy. The approach taken to voice therapy varies between individuals, as no set treatment method applies for all individuals. The specific method of treatment should consider the type and severity of the disorder, as well as individual qualities such as personal and cultural characteristics. Some common orientations are described below. Symptomatic Symptomat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustic Phonetics
Acoustic phonetics is a subfield of phonetics, which deals with acoustic aspects of speech sounds. Acoustic phonetics investigates time domain features such as the mean squared amplitude of a waveform, its duration, its fundamental frequency, or frequency domain features such as the frequency spectrum, or even combined spectrotemporal features and the relationship of these properties to other branches of phonetics (e.g. articulatory or auditory phonetics), and to abstract linguistic concepts such as phonemes, phrases, or utterances. The study of acoustic phonetics was greatly enhanced in the late 19th century by the invention of the Edison phonograph. The phonograph allowed the speech signal to be recorded and then later processed and analyzed. By replaying the same speech signal from the phonograph several times, filtering it each time with a different band-pass filter, a spectrogram of the speech utterance could be built up. A series of papers by Ludimar Hermann published i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epiglottitis
Epiglottitis is the inflammation of the epiglottis—the flap at the base of the tongue that prevents food entering the trachea (windpipe). Symptoms are usually rapid in onset and include trouble swallowing which can result in drooling, changes to the voice, fever, and an increased breathing rate. As the epiglottis is in the upper airway, swelling can interfere with breathing. People may lean forward in an effort to open the airway. As the condition worsens, stridor and bluish skin may occur. Epiglottitis was historically mostly caused by infection by '' H. influenzae type b'' (commonly referred to as "Hib"). With vaccination, it is now more often caused by other bacteria, most commonly ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', ''Streptococcus pyogenes'', or ''Staphylococcus aureus''. Predisposing factors include burns and trauma to the area. The most accurate way to make the diagnosis is to look directly at the epiglottis. X-rays of the neck from the side may show a "thumbprint sign" bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intubation
Intubation (sometimes entubation) is a medical procedure involving the insertion of a tube into the body. Patients are generally anesthetized beforehand. Examples include tracheal intubation, and the balloon tamponade with a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube (a tube into the gastrointestinal tract). Examples * Catheterization * Nasogastric intubation * Tracheal intubation Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic catheter, tube into the vertebrate trachea, trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer ce ... References Airway management Emergency medical procedures Medical equipment Routes of administration {{surgery-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laryngitis
Laryngitis is inflammation of the larynx (voice box). Symptoms often include a hoarse voice and may include fever, cough, pain in the front of the neck, and trouble swallowing. Typically, these last under two weeks. Laryngitis is categorised as acute if it lasts less than three weeks and chronic if symptoms last more than three weeks. Acute cases usually occur as part of a viral upper respiratory tract infection, other infections and trauma such as from coughing are other causes. Chronic cases may occur due to smoking, tuberculosis, allergies, acid reflux, rheumatoid arthritis, or sarcoidosis. The underlying mechanism involves irritation of the vocal cords. Concerning signs that may require further investigation include stridor, history of radiation therapy to the neck, trouble swallowing, duration of more than three weeks, and a history of smoking. If concerning signs are present the vocal cords should be examined via laryngoscopy. Other conditions that can produce simil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Larynx
An electrolarynx, sometimes referred to as a "throat back", is a medical device about the size of a small electric razor used to produce clearer speech by those people who have lost their voice box, usually due to cancer of the larynx. The most common device is a handheld, battery-operated device pressed against the skin under the mandible which produces vibrations to allow speech; other variations include a device similar to the " talk box" electronic music device, which delivers the basis of the speech sound via a tube placed in the mouth. Earlier non-electric devices were called mechanical larynxes. Along with developing esophageal voice, using a speech synthesizer, or undergoing a surgical procedure, the electrolarynx serves as a mode of speech recovery for laryngectomy patients. The Voice Quality Symbol for electrolaryngeal phonation in speech is И, approximating the symbol for electricity. Overview Initially, the pneumatic mechanical larynx was developed in the 192 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the definition used among those who study laryngeal anatomy and physiology and speech production in general. Phoneticians in other subfields, such as linguistic phonetics, call this process '' voicing'', and use the term ''phonation'' to refer to any oscillatory state of any part of the larynx that modifies the airstream, of which voicing is just one example. Voiceless and supra-glottal phonations are included under this definition. Voicing The phonatory process, or voicing, occurs when air is expelled from the lungs through the glottis, creating a pressure drop across the larynx. When this drop becomes sufficiently large, the vocal folds start to oscillate. The minimum pressure drop required to achieve phonation is called the phonation threshold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonetics
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that studies how humans produce and perceive sounds, or in the case of sign languages, the equivalent aspects of sign. Linguists who specialize in studying the physical properties of speech are phoneticians. The field of phonetics is traditionally divided into three sub-disciplines based on the research questions involved such as how humans plan and execute movements to produce speech (articulatory phonetics), how various movements affect the properties of the resulting sound (acoustic phonetics), or how humans convert sound waves to linguistic information (auditory phonetics). Traditionally, the minimal linguistic unit of phonetics is the phone—a speech sound in a language which differs from the phonological unit of phoneme; the phoneme is an abstract categorization of phones. Phonetics deals with two aspects of human speech: production—the ways humans make sounds—and perception—the way speech is understood. The communicative modali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocology
Vocology is the science and practice of vocal habilitation, or vocal training and therapy.Titze IR. (1996). What is vocology? Logopedics Phoniatrics Vocology, 21:5-6. Its concerns include the nature of speech and language pathology, the defects of the vocal tract (laryngology), the remediation of speech therapy, and the voice training (voice therapy) and voice pedagogy of song and speech for actors and public speakers. In its broadest sense, vocology is the study of voice, but as a professional discipline it has a narrower focus: the science and practice of voice habilitation, which includes evaluation, diagnosis, and intervention. History Vocology was invented (simultaneously, but independently) by Ingo Titze, and an otolaryngologist at Washington University, Prof. George Gates. Titze defines vocology as "the science and practice of voice habilitation, with a strong emphasis on habilitation". To habilitate means to “enable”, to “equip for”, to “capacitate”; in other w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voice Organ
In articulatory phonetics, the place of articulation (also point of articulation) of a consonant is a location along the vocal tract where its production occurs. It is a point where a constriction is made between an active and a passive articulator. Active articulators are organs capable of voluntary movement which create the constriction, while passive articulators are so called because they are normally fixed and are the parts with which an active articulator makes contact. Along with the manner of articulation and phonation, the place of articulation gives the consonant its distinctive sound. Since vowels are produced with an open vocal tract, the point where their production occurs cannot be easily determined. Therefore, they are not described in terms of a place of articulation but by the relative positions in vowel space. This is mostly dependent on their formant frequencies and less on the specific tongue position and lip rounding. The terminology used in describing place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |