|
Premovement Neuronal Activity
Premovement neuronal activity in neurophysiological literature refers to neuronal modulations that alter the rate at which neurons fire before a subject produces movement. Through experimentation with multiple animals, predominantly monkeys, it has been shown that several regions of the brain are particularly active and involved in initiation and preparation of movement. Two specific membrane potentials, the bereitschaftspotential, or the BP, and contingent negative variation, or the CNV, play a pivotal role in premovement neuronal activity. Both have been shown to be directly involved in planning and initiating movement. Multiple factors are involved with premovement neuronal activity including motor preparation, inhibition of motor response, programming of the target of movement, closed-looped and open-looped tasks, instructed delay periods, short-lead and long-lead changes, and mirror motor neurons. Two types of movement Research of pre-movement neuronal activity generally involv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bereitschaftspotential
In neurology, the Bereitschaftspotential or BP (German for "readiness potential"), also called the pre-motor potential or readiness potential (RP), is a measure of activity in the motor cortex and supplementary motor area of the brain leading up to voluntary muscle movement. The BP is a manifestation of cortical contribution to the pre-motor planning of volitional movement. It was first recorded and reported in 1964 by Hans Helmut Kornhuber and Lüder Deecke at the University of Freiburg in Germany. In 1965 the full publication appeared after many control experiments.; Englisch translation: PDF(accessed October 21, 2016). Discovery In the spring of 1964 Hans Helmut Kornhuber (then docent and chief physician at the department of neurology, head Professor Richard Jung, university hospital Freiburg im Breisgau) and Lüder Deecke (his doctoral student) went for lunch to the 'Gasthaus zum Schwanen' at the foot of the Schlossberg hill in Freiburg. Sitting alone in the beautiful garden t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parietal Lobe
The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus. The parietal lobe integrates sensory information among various modalities, including spatial sense and navigation (proprioception), the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch in the somatosensory cortex which is just posterior to the central sulcus in the postcentral gyrus, and the dorsal stream of the visual system. The major sensory inputs from the skin (touch, temperature, and pain receptors), relay through the thalamus to the parietal lobe. Several areas of the parietal lobe are important in language processing. The somatosensory cortex can be illustrated as a distorted figure – the cortical homunculus (Latin: "little man") in which the body parts are rendered according to how much of the somatosensory cortex is devoted to them. The superior parietal lobule and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Neuroscience
Cognitive neuroscience is the scientific field that is concerned with the study of the biological processes and aspects that underlie cognition, with a specific focus on the neural connections in the brain which are involved in mental processes. It addresses the questions of how cognitive activities are affected or controlled by neural circuits in the brain. Cognitive neuroscience is a branch of both neuroscience and psychology, overlapping with disciplines such as behavioral neuroscience, cognitive psychology, physiological psychology and affective neuroscience.Gazzaniga 2002, p. xv Cognitive neuroscience relies upon theories in cognitive science coupled with evidence from neurobiology, and computational modeling. Parts of the brain play an important role in this field. Neurons play the most vital role, since the main point is to establish an understanding of cognition from a neural perspective, along with the different lobes of the cerebral cortex. Methods employed in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentate Nucleus
The dentate nucleus is a cluster of neurons, or nerve cells, in the central nervous system that has a dentate – tooth-like or serrated – edge. It is located within the deep white matter of each cerebellar hemisphere, and it is the largest single structure linking the cerebellum to the rest of the brain.Sultan, F., Hamodeh, S., & Baizer, J. S. (2010). THE HUMAN DENTATE NUCLEUS: A COMPLEX SHAPE UNTANGLED. rticle Neuroscience, 167(4), 965–968. It is the largest and most lateral, or farthest from the midline, of the four pairs of deep cerebellar nuclei, the others being the globose and emboliform nuclei, which together are referred to as the interposed nucleus, and the fastigial nucleus. The dentate nucleus is responsible for the planning, initiation and control of voluntary movements. The dorsal region of the dentate nucleus contains output channels involved in motor function, which is the movement of skeletal muscle, while the ventral region contains output channels involv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms become more common. The most obvious early symptoms are tremor, rigidity, slowness of movement, and difficulty with walking. Cognitive and behavioral problems may also occur with depression, anxiety, and apathy occurring in many people with PD. Parkinson's disease dementia becomes common in the advanced stages of the disease. Those with Parkinson's can also have problems with their sleep and sensory systems. The motor symptoms of the disease result from the death of cells in the substantia nigra, a region of the midbrain, leading to a dopamine deficit. The cause of this cell death is poorly understood, but involves the build-up of misfolded proteins into Lewy bodies in the neurons. Collectively, the main motor symptoms are also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
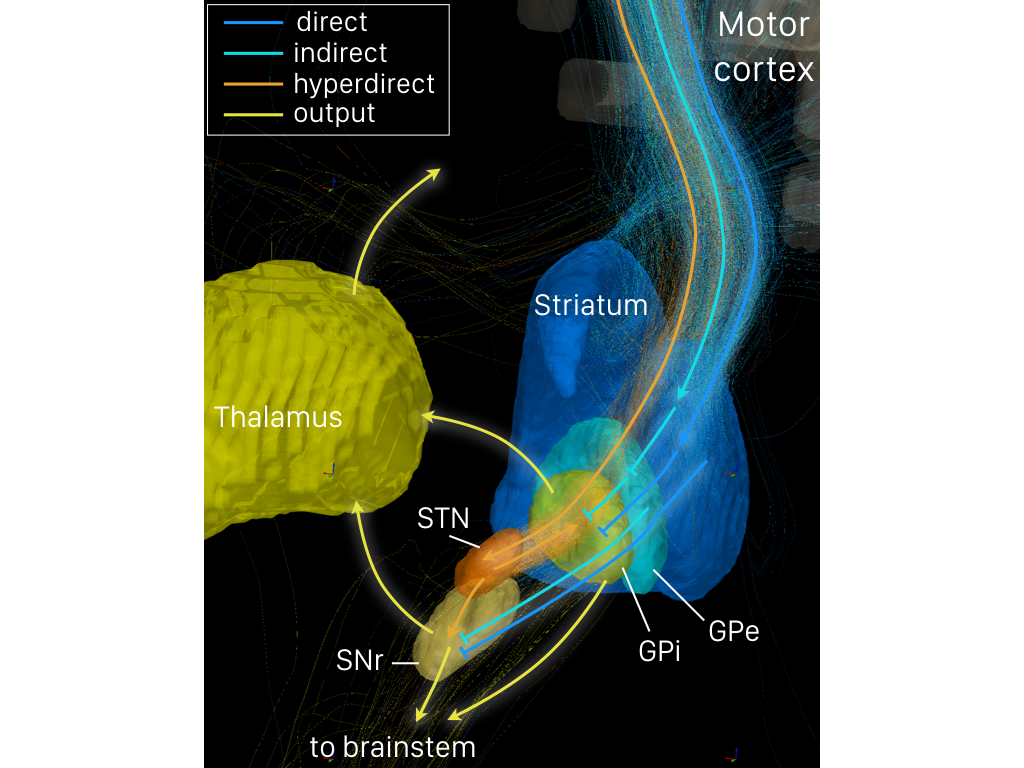
Indirect Pathway Of Movement
The indirect pathway, sometimes known as the indirect pathway of movement, is a neuronal circuit through the basal ganglia and several associated nuclei within the central nervous system (CNS) which helps to prevent unwanted muscle contractions from competing with voluntary movements. It operates in conjunction with the direct pathway of movement, direct pathway. Overview of Neuronal Connections and Normal Function The indirect pathway passes through the caudate nucleus, caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus, which are parts of the basal ganglia. It traverses the subthalamic nucleus, a part of the diencephalon, and enters the substantia nigra, a part of the midbrain. In a resting individual, a specific region of the globus pallidus, known as the internus, and a portion of the substantia nigra, known as the pars reticulata, send spontaneous inhibitory signals to the ventrolateral nucleus (VL) of the thalamus, through the release of GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Inhibition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Pathway Of Movement
The direct pathway, sometimes known as the direct pathway of movement, is a neural pathway within the central nervous system (CNS) through the basal ganglia which facilitates the initiation and execution of voluntary movement. It works in conjunction with the indirect pathway. Both of these pathways are part of the cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. Overview of neuronal connections and normal function The direct pathway passes through the caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus, which are parts of the basal ganglia. It also involves another basal ganglia component the substantia nigra, a part of the midbrain. In a resting individual, a specific region of the globus pallidus, the internal globus pallidus (GPi), and a part of the substantia nigra, the pars reticulata (SNpr), send spontaneous inhibitory signals to the ventral lateral nucleus (VL) of the thalamus, through the release of GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Inhibition of the inhibitory neurons tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GABAergic
In molecular biology and physiology, something is GABAergic or GABAnergic if it pertains to or affects the neurotransmitter GABA. For example, a synapse is GABAergic if it uses GABA as its neurotransmitter, and a GABAergic neuron produces GABA. A substance is GABAergic if it produces its effects via interactions with the GABA system, such as by stimulating or blocking neurotransmission. A GABAergic or GABAnergic agent is any chemical that modifies the effects of GABA in the body or brain. Some different classes of GABAergic drugs include agonists, antagonists, modulators, reuptake inhibitors and enzymes. See also * GABA reuptake inhibitor * Adenosinergic * Adrenergic * Cannabinoidergic * Cholinergic * Dopaminergic * Glycinergic * Histaminergic * Melatonergic * Monoaminergic * Opioidergic * Serotonergic Serotonergic () or serotoninergic () means "pertaining to or affecting serotonin". Serotonin is a neurotransmitter. A synapse is serotonergic if it uses serotonin as its neurotr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substantia Nigra
The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. ''Substantia nigra'' is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra appear darker than neighboring areas due to high levels of neuromelanin in dopaminergic neurons. Parkinson's disease is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. Although the substantia nigra appears as a continuous band in brain sections, anatomical studies have found that it actually consists of two parts with very different connections and functions: the pars compacta (SNpc) and the pars reticulata (SNpr). The pars compacta serves mainly as a projection to the basal ganglia circuit, supplying the striatum with dopamine. The pars reticulata conveys signals from the basal ganglia to numerous other brain structures. Structure The substantia nigra, along with four other nuclei, is part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Pallidus
The globus pallidus (GP), also known as paleostriatum or dorsal pallidum, is a subcortical structure of the brain. It consists of two adjacent segments, one external, known in rodents simply as the globus pallidus, and one internal, known in rodents as the entopeduncular nucleus. It is part of the telencephalon, but retains close functional ties with the subthalamus in the diencephalon – both of which are part of the extrapyramidal motor system. The globus pallidus is a major component of the basal ganglia, with principal inputs from the striatum, and principal direct outputs to the thalamus and the substantia nigra. The latter is made up of similar neuronal elements, has similar afferents from the striatum, similar projections to the thalamus, and has a similar synaptology. Neither receives direct cortical afferents, and both receive substantial additional inputs from the intralaminar thalamus. Globus pallidus is Latin for "pale globe". Structure Pallidal nuclei are m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Goal
A motor goal is a neurally planned motor outcome that is used to organize motor control. Motor goals are experimentally shown to exist since planned movements can when disrupted adjust to achieve their planned outcome. If, for example, a person makes a movement of their hand to touch or grasp something and unexpected their arm is pushedtheir brain automatically reorganizes the movement so it so achieves its intended aim. This also occurs if an arm is perturbed which results in an automatic correction that enables it to fulfill its planned spatial-temporal target. If a lip articulating a consonant is knocked, the vocal apparatus makes a target related correction of movement. Spoken words are sequences of motor movements organized around motor targets. The motor cortex The motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex believed to be involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements. The motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the posteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirror Neuron
A mirror neuron is a neuron that fires both when an animal acts and when the animal observes the same action performed by another. Thus, the neuron "mirrors" the behavior of the other, as though the observer were itself acting. Such neurons have been directly observed in human and primate species, and in birds. In humans, brain activity consistent with that of mirror neurons has been found in the premotor cortex, the supplementary motor area, the primary somatosensory cortex, and the inferior parietal cortex. The function of the mirror system in humans is a subject of much speculation. Birds have been shown to have imitative resonance behaviors and neurological evidence suggests the presence of some form of mirroring system. To date, no widely accepted neural or computational models have been put forward to describe how mirror neuron activity supports cognitive functions. The subject of mirror neurons continues to generate intense debate. In 2014, Philosophical Transactions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |