|
Potassium Cobaltinitrite
Potassium hexanitritocobaltate(III) is a salt with the formula K3 o(NO2)6 It is a yellow solid that is poorly soluble in water. The compound finds some use as a yellow pigment under the name Indian Yellow. The salt features potassium cations and an trianionic coordination complex. In the anion, cobalt is bound by six nitrito ligands, the overall complex having octahedral molecular geometry. The oxidation state of cobalt is 3+. Its low-spin d6 configuration confers kinetic stability and diamagnetism. The compound is prepared by combining cobalt(II) and nitrite salts in the presence of oxygen. The corresponding sodium cobaltinitrite is significantly more soluble in water. The compound was first described in 1848 by Nikolaus Wolfgang Fischer in Breslau, and it is used as a yellow pigment called Aureolin. See also *Sodium hexanitritocobaltate(III) Sodium hexanitritocobaltate(III) is inorganic compound with the formula . The anion of this yellow-coloured salt consists of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Crystal System
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the Crystal_structure#Unit_cell, unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals. There are three main varieties of these crystals: *Primitive cubic (abbreviated ''cP'' and alternatively called simple cubic) *Body-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cI'' or bcc) *Face-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cF'' or fcc, and alternatively called Close-packing_of_equal_spheres, ''cubic close-packed'' or ccp) Each is subdivided into other variants listed below. Although the ''unit cells'' in these crystals are conventionally taken to be cubes, the primitive_cell, primitive unit cells often are not. Bravais lattices The three Bravais lattices in the cubic crystal system are: The primitive cubic lattice (cP) consists of one Lattice_(group), lattice point on each corner of the cube; this means each simple cubic unit cell has in total one latt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a ''transaction''. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction. In 1983, Andreas Reuter and Theo Härder coined the acronym ''ACID'', building on earlier work by Jim Gray who named atomicity, consistency, and durability, but not isolation, when characterizing the transaction concept. These four properties are the major guarantees of the transaction paradigm, which has influenced many aspects of development in database systems. According to Gray and Reuter, the IBM Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, Combustibility and flammability, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of Carbohydrate, sugars by yeasts or via Petrochemistry, petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of organic compounds, and as a Alcohol fuel, fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Complex
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedral Molecular Geometry
In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry, also called square bipyramidal, describes the shape of compounds with six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron. The octahedron has eight faces, hence the prefix ''octa''. The octahedron is one of the Platonic solids, although octahedral molecules typically have an atom in their centre and no bonds between the ligand atoms. A perfect octahedron belongs to the point group Oh. Examples of octahedral compounds are sulfur hexafluoride SF6 and molybdenum hexacarbonyl Mo(CO)6. The term "octahedral" is used somewhat loosely by chemists, focusing on the geometry of the bonds to the central atom and not considering differences among the ligands themselves. For example, , which is not octahedral in the mathematical sense due to the orientation of the bonds, is referred to as octahedral. The concept of octahedral coordination geometry was developed by Alfred Wern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolaus Wolfgang Fischer
Nikolaus Wolfgang Fischer (15 January 1782 – 19 August 1850) was a German chemist. He first synthesized the Potassium cobaltinitritelater used as Aureolin Aureolin (sometimes called cobalt yellow) is a pigment sparingly used in oil and watercolor painting. Its color index name is PY40 (40th entry on list of yellow pigments). It was first made in 1831 by Nikolaus Wolfgang Fischer in Breslau character ... pigment. References * 1782 births 1850 deaths 19th-century German chemists {{Germany-chemist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aureolin
Aureolin (sometimes called cobalt yellow) is a pigment sparingly used in oil and watercolor painting. Its color index name is PY40 (40th entry on list of yellow pigments). It was first made in 1831 by Nikolaus Wolfgang Fischer in Breslau characterizing it as "Doppelsalze" or double-salts and its chemical composition is potassium cobaltinitrite. He characterized it again and wrote more extensively about it in 1842, naming it "Salpetrichtsaures Kobaltoxydkali". In 1851-1852, Edouard Saint-Evre synthesized cobalt yellow independently. He is credited with the introduction of cobalt yellow as an artists pigment. The investigation by Gates gives the exact modern procedures for the preparation of aureolin and also the methods for its identification in paintings.- Aureolin is rated as permanent in some reports but there are other sources which rate it as unstable in oils but pronounce it stable in watercolors. Others find it unstable in watercolors, fading to greyish or brownish hues. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Hexanitritocobaltate(III)
Sodium hexanitritocobaltate(III) is inorganic compound with the formula . The anion of this yellow-coloured salt consists of the transition metal nitrite complex . It was a reagent for the qualitative test for potassium and ammonium ions. Synthesis and reactions The compound is prepared by oxidation of cobalt(II) salts in the presence of sodium nitrite Sodium nitrite is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaNO2. It is a white to slightly yellowish crystalline powder that is very soluble in water and is hygroscopic. From an industrial perspective, it is the most important nitrite ...: : Application for analysis of potassium Although the sodium cobaltinitrite is soluble in water, it forms the basis of a quantitative determination of potassium, thallium, and ammonium ions. Under the recommended reaction conditions the insoluble double salt, is precipitated and weighed. In geochemical analysis, sodium cobaltinitrite is used to distinguish alkali feldspars from pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Compounds
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash, the ashes of plants, from which its name derives. In the periodic table, potassium is one of the alkali metals, all of which have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell, that is easily removed to create an ion with a positive charge – a cation, that combines with anions to form salts. Potassium in nature occurs only in ionic salts. Elemental potassium reacts vigorously with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite hydrogen emitted in the reaction, and burning with a lilac- colored flame. It is found dissolved in sea water (which is 0.04% potassium by weight), and occurs in many minerals such as orthoclase, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalt Compounds
Cobalt compounds are chemical compounds formed by cobalt with other elements. In the compound, the most stable oxidation state of cobalt is the +2 oxidation state, and in the presence of specific ligands, there are also stable compounds with +3 valence. In addition, there are cobalt compounds in high oxidation states +4, +5 and low oxidation states -1, 0, +1. Inorganic compounds Halides Four halides of cobalt(II) are known, which are cobalt(II) fluoride (CoF2) which is a pink solid, cobalt(II) chloride (CoCl2) which is a blue solid, cobalt(II) bromide (CoBr2) which is a green solid, and cobalt(II) iodide (CoI2) which is a blue-black solid. In addition to the anhydrous forms, these cobalt halides also have hydrates. Anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride is blue, while the hexahydrate is red-purple. Because the color change of cobalt(II) chloride in different hydrates, it can be used to manufacture color-changing silica gel. Anhydrous cobalt halides react with nitric oxide at 70~120 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
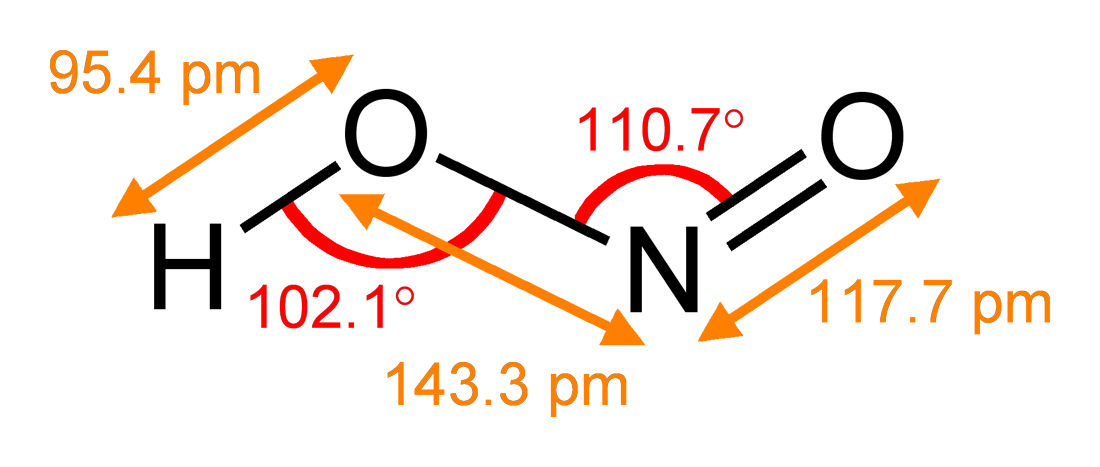
Nitrites
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid. Production Sodium nitrite is made industrially by passing a mixture of nitrogen oxides into aqueous sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate solution: : The product is purified by recrystallization. Alkali metal nitrites are thermally stable up to and beyond their melting point (441 °C for KNO2). Ammonium nitrite can be made from dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3, which is formally the anhydride of nitrous acid: :2 NH3 + H2O + N2O3 → 2 NH4NO2 Structure The nitrite ion has a symmetrical structure (C2v symmetry), with both N–O bonds having equal length and a bond angle of about 115°. In valence bond theory, it is described as a resonance hybrid with equal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




-chloride-hexahydrate-sample.jpg)