|
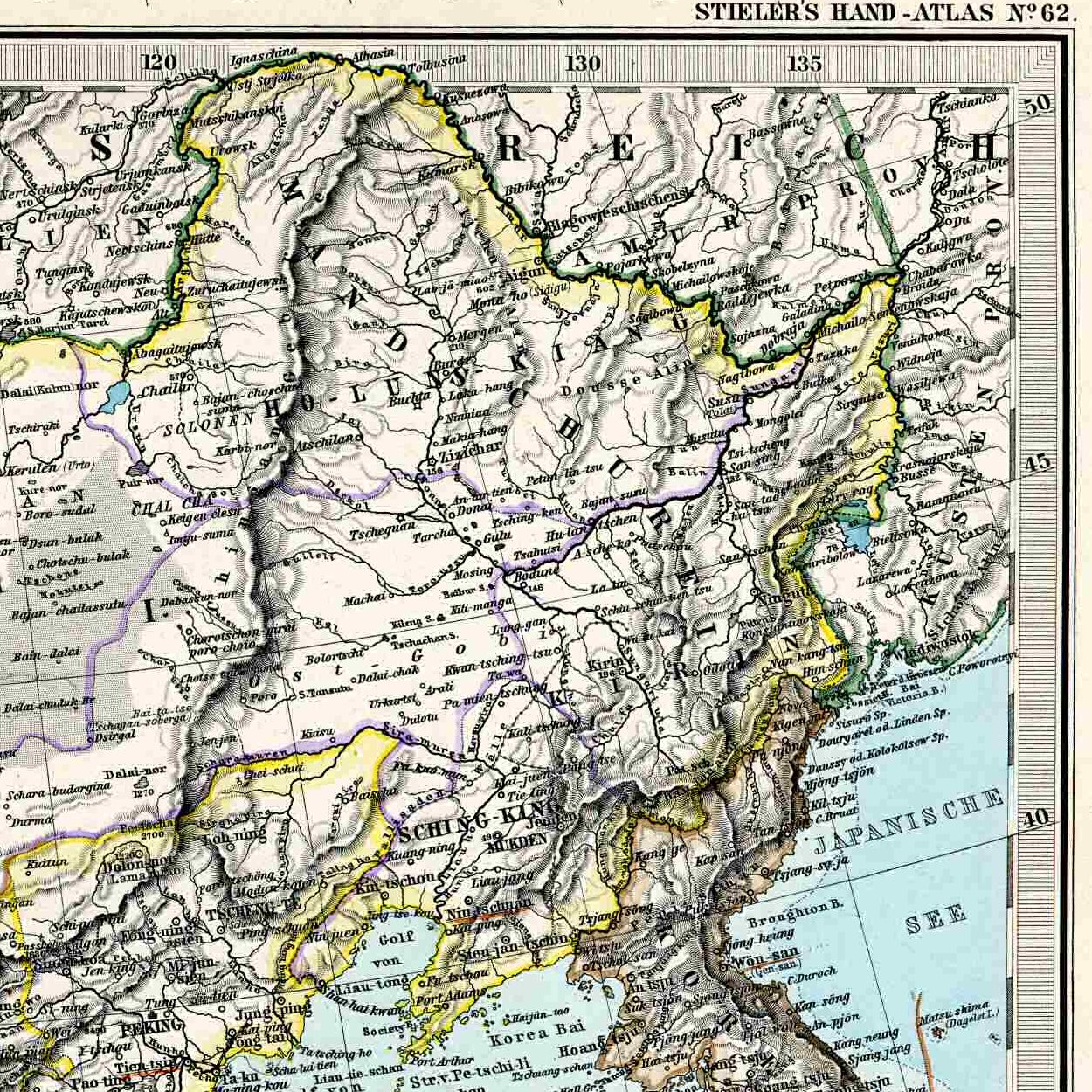
Posyet
Posyet (russian: Посье́т) is an urban locality (an urban-type settlement) in Khasansky District of Primorsky Krai, Russia, and an ice-free port on the Possiet Bay. Population: Etymology It is named after the Russian navigator Konstantin Posyet (1819—1899). History It is the oldest settlement in Primorsky Krai. It was established on April 11, 1860 as Novgorodsky-Posyet.Хасанский районИстория посёлка Посьет/ref> The name Novgorodsky was given after the bay named by Nikolay Muravyov-Amursky's expedition. Economy Largest enterprise JSC ''Commercial port of Posyet'' is owned by Mechel. It is in possession of three mooring lines of gravitational type. Climate Posyet has a monsoonal humid continental climate (Köppen ''Dwb'') with warm, humid and stormy summers and cold, dry winters with little snowfall. References External linksUnofficial website of Posyet *Great Soviet Encyclopedia The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstantin Posyet
Konstantin Nikolayevich Posyet (russian: Константин Николаевич Посьет, french: Constantin Possiet, – ) was a Russian Empire statesman and admiral of French origin, who served as Minister of Transport Communications between 1874 and 1888. Biography Posyet was a descendant of one Possiet de Rossier, a French noble who was commissioned by Peter the Great to lay out vineyards near Astrakhan and Anna Chappuzeau, a descendant of playwright Samuel Chappuzeau, who was also the widow of famous botanist Samuel Gmelin. Konstantin was born in Pärnu, Estonia, a town of which he later became an honorary freeman. After attending the Naval Cadet Corps in St. Petersburg, he pursued the career of a military author. ''Artillerie-Exercitium'' (1847), a comprehensive treatise about modern artillery, won him a Demidov Prize from the Russian Academy of Sciences. In 1852-54, Posyet followed Admiral Yevfimy Putyatin on the frigate ''Pallas'' to Japan. Accompanied by nov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Possiet Bay
The Possiet Gulf or Posyet Bay (Russian: Залив Посьета) is a bay in the south-western part of the Peter the Great Gulf, between the promontories of Suslov and Gamov. It stretches for 31 kilometres from northeast to southwest and for 33 kilometers from northwest to southeast. The coastline, which forms part of the Khasansky District, is irregular and indented. Several townlets are situated on the bay, including Possiet, Zarubino, and Kraskino. The crew of the French corvette ''Caprice'' visited the bay in 1852, giving it the name of d'Anville. Two years later, the coastline was mapped by the expedition of Yevfimy Putyatin, including the schooner ''Vostok'' and the frigate ''Pallas''. Putyatin had the bay renamed after Constantine Possiet, one of his associates. In 1855, at the height of the Crimean War, the bay was visited by an Anglo-French squadron whose leaders called it "The Raid of Napoleon", after the first French battleship, '' Le Napoléon''. In July 1938, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechel
Mechel (russian: ПАО «Мечел») is one of Russia's mining and metals companies, comprising producers of coal, iron ore in concentrate, steel, rolled steel products. Headquartered in Moscow, it sells its products in Russia and overseas, and is formally known as ''Public Joint Stock Company Mechel''. History Southern Kuzbass Coal Company acquired control over Chelyabinsk Steel Plant in the summer of 2002 and subsequently announced a merger of Southern Kuzbass and Mechel into Mechel Steel Group. Igor Zyuzin was elected as Chairman of the Board of Mechel Steel Group OAO in January 2004. Mergers and acquisitions Mechel acquired Posyet Sea Commercial Port on the Russian coast of the Sea of Japan in 2004. Mechel submitted a winning bid for a 26.9% stake in Izhstal in May 2004, subsequently increasing its stake to control. Mechel won an auction in January 2005 to buy a blocking stake (25% plus one share of stock) in Yakutugol. Also in 2005, Mechel acquired a controlling stak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khasansky District
Khasansky District (russian: Хаса́нский райо́н) is an administrativeLaw #161-KZ and municipalLaw #187-KZ district (raion), one of the twenty-two in Primorsky Krai, Russia. It is located in the southwest of the krai, wedged between the Tumen River and the Peter the Great Gulf, and shares a border with both China and North Korea. The area of the district is . (Official website of the Legislative Assembly of Primorsky Krai. ''Municipal Formations of Primorsky Krai'') Its administrative center is the urban locality (an ) of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primorsky Krai
Primorsky Krai (russian: Приморский край, r=Primorsky kray, p=prʲɪˈmorskʲɪj kraj), informally known as Primorye (, ), is a federal subject (a krai) of Russia, located in the Far East region of the country and is a part of the Far Eastern Federal District. The city of Vladivostok is the administrative center of the krai, and the second largest city in the Russian Far East, after Khabarovsk. The krai has the largest economy among the federal subjects in the Russian Far East, and a population of 1,956,497 as of the 2010 Census. The krai shares Russia's only border with North Korea, along the Tumen River in Khasansky District in the southwestern corner of the krai. Peter the Great Gulf, the largest gulf in the Sea of Japan, is located along the south coast. Historically part of Manchuria, Primorsky Krai was ceded to the Russian Empire by Qing China in 1860 as part of a region known as Outer Manchuria, forming most of the territory of Primorskaya Oblast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (GSE; ) is one of the largest Russian-language encyclopedias, published in the Soviet Union from 1926 to 1990. After 2002, the encyclopedia's data was partially included into the later ''Bolshaya rossiyskaya entsiklopediya'' (or '' Great Russian Encyclopedia'') in an updated and revised form. The GSE claimed to be "the first Marxist–Leninist general-purpose encyclopedia". Origins The idea of the ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' emerged in 1923 on the initiative of Otto Schmidt, a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences. In early 1924 Schmidt worked with a group which included Mikhail Pokrovsky, (rector of the Institute of Red Professors), Nikolai Meshcheryakov (Former head of the Glavit, the State Administration of Publishing Affairs), Valery Bryusov (poet), Veniamin Kagan (mathematician) and Konstantin Kuzminsky to draw up a proposal which was agreed to in April 1924. Also involved was Anatoly Lunacharsky, People's Commissar of Education ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humid Continental Climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing cold (sometimes severely cold in the northern areas) winters. Precipitation is usually distributed throughout the year but often do have dry seasons. The definition of this climate regarding temperature is as follows: the mean temperature of the coldest month must be below or depending on the isotherm, and there must be at least four months whose mean temperatures are at or above . In addition, the location in question must not be semi-arid or arid. The cooler ''Dfb'', ''Dwb'', and ''Dsb'' subtypes are also known as hemiboreal climates. Humid continental climates are generally found between latitudes 30° N and 60° N, within the central and northeastern portions of North America, Europe, and Asia. They are rare and isolat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mooring Line
A mooring is any permanent structure to which a vessel may be secured. Examples include quays, wharfs, jetties, piers, anchor buoys, and mooring buoys. A ship is secured to a mooring to forestall free movement of the ship on the water. An ''anchor mooring'' fixes a vessel's position relative to a point on the bottom of a waterway without connecting the vessel to shore. As a verb, ''mooring'' refers to the act of attaching a vessel to a mooring. The term likely stems from the Dutch verb ''meren'' (to ''moor''), used in English since the end of the 15th century. Permanent anchor mooring These moorings are used instead of temporary anchors because they have considerably more holding power, for example because of lesser damage to the marine environment, and are convenient. Where there is a row of moorings they are termed a tier. They are also occasionally used to hold floating docks in place. There are several kinds of moorings: Swing moorings Swing moorings also known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint-stock Company
A joint-stock company is a business entity in which shares of the company's capital stock, stock can be bought and sold by shareholders. Each shareholder owns company stock in proportion, evidenced by their share (finance), shares (certificates of ownership). Shareholders are able to transfer their shares to others without any effects to the continued existence of the company. In modern-day corporate law, the existence of a joint-stock company is often synonymous with incorporation (business), incorporation (possession of legal personality separate from shareholders) and limited liability (shareholders are liable for the company's debts only to the value of the money they have invested in the company). Therefore, joint-stock companies are commonly known as corporations or limited company, limited companies. Some jurisdiction (area), jurisdictions still provide the possibility of registering joint-stock companies without limited liability. In the United Kingdom and in other count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolay Muravyov-Amursky
Count Nikolay Nikolayevich Muravyov-Amursky (also spelled as Nikolai Nikolaevich Muraviev-Amurskiy; russian: link=no, Никола́й Никола́евич Муравьёв-Аму́рский; – ) was a Russian general, statesman and diplomat, who played a major role in the expansion of the Russian Empire into the Amur River basin and to the shores of the Sea of Japan. The surname Muravyov has also been transcribed as Muravyev or Murav'ev. Early life and career Nikolay Muravyov was born in Saint Petersburg and graduated from the Page Corps in 1827. He participated in the Siege of Varna in the Russo-Turkish War in 1828–1829, and later in suppression of the November Uprising in Poland in 1831. Due to health reasons, he retired from the military in 1833 and returned home to manage his father's estate. However, he returned to active duty in 1838, as General Golovin's aide-de-camp, to serve in the Caucasus region. During one of the campaigns against the mountain people Muravyo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |