|
Postpartum Physiological Changes
The postpartum physiological changes are those expected changes that occur in the woman's body after childbirth, in the postpartum period. These changes mark the beginning of the return of pre-pregnancy physiology and of breastfeeding. Most of the time these postnatal changes are normal and can be managed with medication and comfort measures, but in a few situations complications may develop. Postpartum physiological changes may be different for women delivering by cesarean section. Other postpartum changes, may indicate developing complications such as, postpartum bleeding, engorged breasts, postpartum infections. Breasts and lactation The breasts change during pregnancy to prepare for lactation, and more changes occur immediately after the birth. Progesterone is the hormone that influences the growth of breast tissue before the birth. Afterwards, the endocrine system shifts from producing hormones that prevent lactation to ones that trigger milk production. The first secretions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births globally. In the developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in the developing countries most are home births. The most common childbirth method worldwide is vaginal delivery. It involves four stages of labour: the shortening and opening of the cervix during the first stage, descent and birth of the baby during the second, the delivery of the placenta during the third, and the recovery of the mother and infant during the fourth stage, which is referred to as the postpartum. The first stage is characterized by abdominal cramping or back pain that typically lasts half a minute and occurs every 10 to 30 minutes. Contractions gradually becomes stronger and closer together. Since the pain of childbirth correlates with contractions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
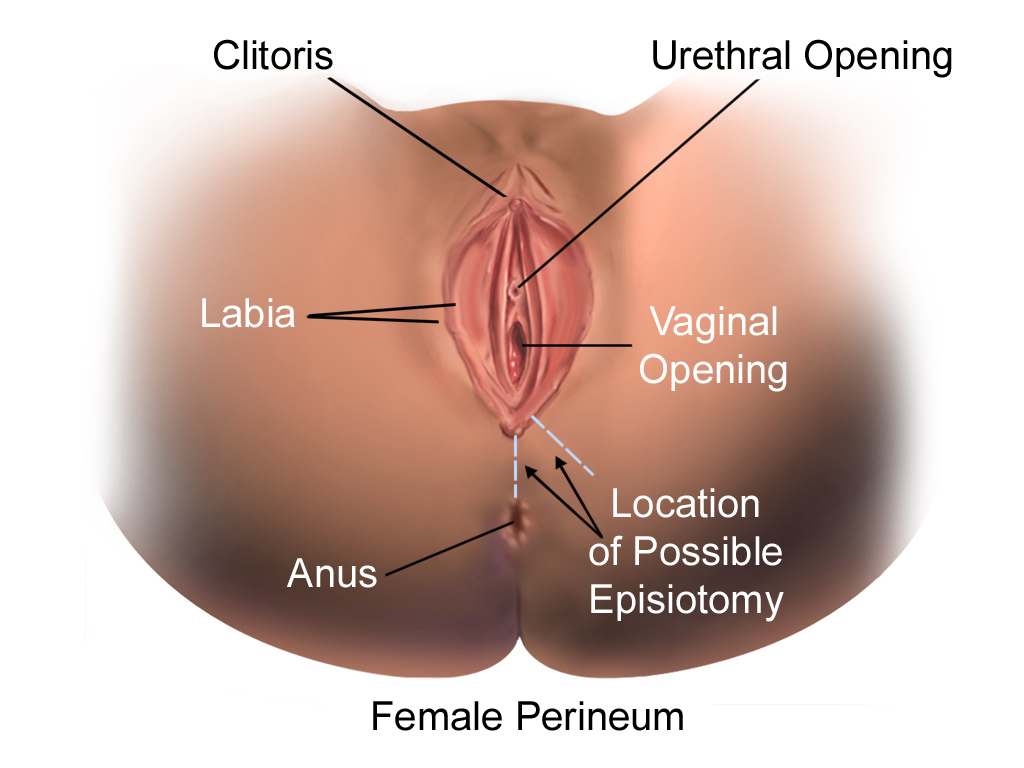
Episiotomy
Episiotomy, also known as perineotomy, is a surgical incision of the perineum and the posterior vaginal wall generally done by a midwife or obstetrician. Episiotomy is usually performed during second stage of labor to quickly enlarge the opening for the baby to pass through. The incision, which can be done from the posterior midline of the vulva straight toward the anus or at an angle to the right or left (medio-lateral episiotomy), is performed under local anesthetic (pudendal anesthesia), and is sutured after delivery. Its routine use is no longer recommended, as perineal massage is an alternative painless method of enlarging the opening for baby. Despite this, it is one of the most common surgical procedures specific to women. In the United States, as of 2012, it was performed in 12% of vaginal births. It is still widely practiced in many parts of the world, including Korea, Japan, Taiwan, China, and Spain. Uses Vaginal tears can occur during childbirth, most often at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births globally. In the developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in the developing countries most are home births. The most common childbirth method worldwide is vaginal delivery. It involves four stages of labour: the shortening and opening of the cervix during the first stage, descent and birth of the baby during the second, the delivery of the placenta during the third, and the recovery of the mother and infant during the fourth stage, which is referred to as the postpartum. The first stage is characterized by abdominal cramping or back pain that typically lasts half a minute and occurs every 10 to 30 minutes. Contractions gradually becomes stronger and closer together. Since the pain of childbirth correlates with contractions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postpartum Care
Postpartum care or postnatal care is a service provided to individuals in the postpartum period, to help with postpartum recuperation and restoration. Traditional postpartum care Many traditional forms of postpartum confinement exist throughout the world. Chinese '' Zuo Yuezi'' (sitting the month) and European Lying-in are examples. Korea ''Sanhujori'' is Korea's version of postpartum care. It draws on principles that emphasize activities and foods that keep the body warm, rest and relaxation to maximize the body's return to its normal state, maintaining cleanliness, eating nutritious foods, and peace of mind and heart. The confinement period is known as ''samchil-il'' (three seven days). Modern commercial versions Traditionally, women were taken care of by their elders: their mother, mother-in-law, sister, or aunt. The lying-in hospitals provided an institutional variation which gave women weeks of bedrest and a respite from household chores. Increasingly, these older wome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compression Stockings
Compression stockings (Flight Socks, Support Bandage) are a specialized hosiery designed to help prevent the occurrence of, and guard against further progression of, venous disorders such as edema, phlebitis and thrombosis. Compression stockings are elastic compression garments worn around the leg, compressing the limb. This reduces the diameter of distended veins and increases venous blood flow velocity and valve effectiveness. Compression therapy helps decrease venous pressure, prevents venous stasis and impairments of venous walls, and relieves heavy and aching legs. Knee-high compression stockings are used not only to help increase circulation, but also to help prevent the formation of blood clots in the lower legs. They also aid in the treatment of ulcers of the lower legs. Unlike traditional dress or athletic stockings and socks, compression stockings use stronger elastics to create significant pressure on the legs, ankles and feet. Compression stockings are tightest at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumatic Pressure Device
Pneumatics (from Greek ‘wind, breath’) is a branch of engineering that makes use of gas or pressurized air. Pneumatic systems used in industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A centrally located and electrically-powered compressor powers cylinders, air motors, pneumatic actuators, and other pneumatic devices. A pneumatic system controlled through manual or automatic solenoid valves is selected when it provides a lower cost, more flexible, or safer alternative to electric motors, and hydraulic actuators. Pneumatics also has applications in dentistry, construction, mining, and other areas. Gases used in pneumatic systems Pneumatic systems in fixed installations, such as factories, use compressed air because a sustainable supply can be made by compressing atmospheric air. The air usually has moisture removed, and a small quantity of oil is added at the compressor to prevent corrosion and lubricate mechanical components. Factory-pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Clot
A thrombus (plural thrombi), colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cross-linked fibrin protein. The substance making up a thrombus is sometimes called cruor. A thrombus is a healthy response to injury intended to stop and prevent further bleeding, but can be harmful in thrombosis, when a clot obstructs blood flow through healthy blood vessels in the circulatory system. In the microcirculation consisting of the very small and smallest blood vessels the capillaries, tiny thrombi known as microclots can obstruct the flow of blood in the capillaries. This can cause a number of problems particularly affecting the alveoli in the lungs of the respiratory system resulting from reduced oxygen supply. Microclots have been found to be a characteristic feature in severe cases of COVID-19, and in long COVID. Mural thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bedrest
Bed rest, also referred to as the rest-cure, is a medical treatment in which a person lies in bed for most of the time to try to cure an illness. Bed rest refers to voluntarily lying in bed as a treatment and not being confined to bed because of a health impairment which physically prevents leaving bed. The practice is still used although a 1999 systematic review found no benefits for any of the 17 conditions studied and no proven benefit for any conditions at all, beyond that imposed by symptoms. In the United States, nearly 20% of pregnant women have some degree of restricted activity prescribed despite the growing data showing it to be dangerous, causing some experts to call its use "unethical". Medical uses Extended bed rest has been proven to be a potentially harmful treatment needing more careful evaluation. Pregnancy Women who are pregnant and are experiencing early labor, vaginal bleeding, and cervix complications have been prescribed bed rest. This practice in 2013 wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Retention
Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include loss of bladder control, mild lower abdominal pain, and a weak urine stream. Those with long-term problems are at risk of urinary tract infections. Causes include blockage of the urethra, nerve problems, certain medications, and weak bladder muscles. Blockage can be caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), urethral strictures, bladder stones, a cystocele, constipation, or tumors. Nerve problems can occur from diabetes, trauma, spinal cord problems, stroke, or heavy metal poisoning. Medications that can cause problems include anticholinergics, antihistamines, tricyclic antidepressants, cyclobenzaprine, diazepam, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID), amphetamines, and opioids. Diagnosis is typically based on measuring the amount of urine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Catheter
In urinary catheterization a latex, polyurethane, or silicone tube known as a urinary catheter is inserted into the bladder through the urethra to allow urine to drain from the bladder for collection. It may also be used to inject liquids used for treatment or diagnosis of bladder conditions. A clinician, often a nurse, usually performs the procedure, but self-catheterization is also possible. A catheter may be in place for long periods of time (indwelling catheter) or removed after each use (intermittent catheterization). Catheter types Catheters come in several basic designs: *A Foley catheter ( indwelling urinary catheter) is retained by means of a balloon at the tip that is inflated with sterile water. The balloons typically come in two different sizes: 5 cm3 and 30 cm3. They are commonly made in silicone rubber or natural rubber. *An intermittent catheter/Robinson catheter is a flexible catheter that is removed after each use. Unlike the Foley catheter, it has no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oily Fish
Oily fish are fish species with oil (fats) in soft tissues and in the coelomic cavity around the gut. Their fillets may contain up to 30% oil, although this figure varies both within and between species. Examples of oily fish include small forage fish such as sardines, herring and anchovies, and other larger pelagic fish such as salmon, trout, tuna, swordfish and mackerel. Oily fish can be contrasted with whitefish, which contain oil only in the liver and in much less overall quantity than oily fish. Examples of whitefish are cod, haddock and flatfish. White fish are usually demersal fish which live on or near the seafloor, whereas oily fish are pelagic, living in the water column away from the bottom. Oily fish meat is a good source of important fat-soluble vitamins such as Vitamin A and D, and is rich in omega-3 fatty acids (white fish also contain these nutrients but at a much lower concentration). For this reason the consumption of oily fish rather than white fish c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maternal Mortality
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to pregnancy, underlying conditions worsened by the pregnancy or management of these conditions. This can occur either while they are pregnant or within six weeks of resolution of the pregnancy. The CDC definition of pregnancy-related deaths extends the period of consideration to include one year from the resolution of the pregnancy. Pregnancy associated death, as defined by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), are all deaths occurring within one year of a pregnancy resolution. Identification of pregnancy associated deaths is important for deciding whether or not the pregnancy was a direct or indirect contributing cause of the death. There are two main measures used when talking about the rates of maternal mortality in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |