Oily Fish on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
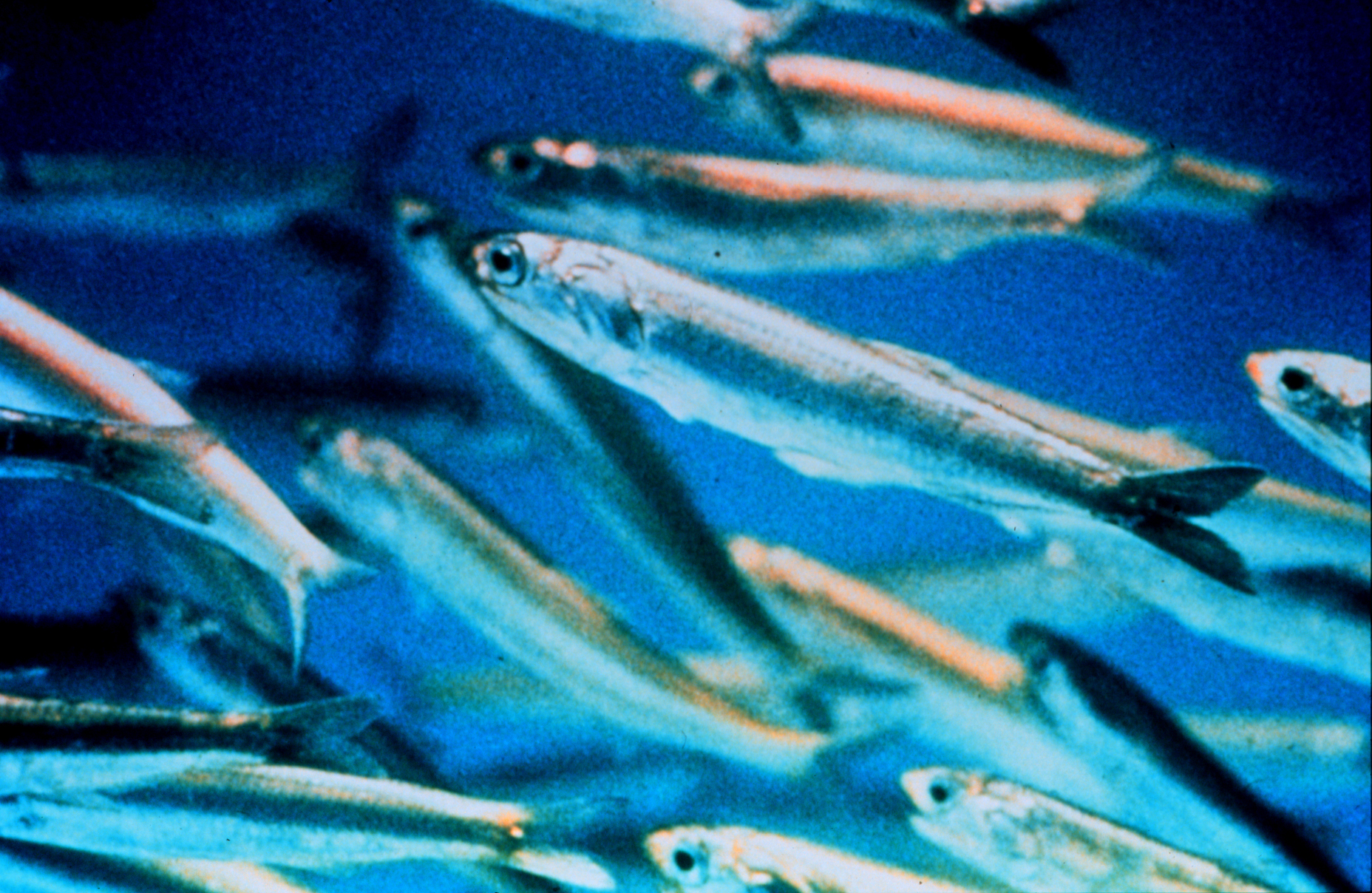
 Oily fish are
Oily fish are

 In 1994, the UK Committee on Medical Aspects of Food and Nutrition Policy recommended that people eat at least two portions of fish per week, one of which should be oily fish.
In 2004 the UK
In 1994, the UK Committee on Medical Aspects of Food and Nutrition Policy recommended that people eat at least two portions of fish per week, one of which should be oily fish.
In 2004 the UK
Achieving optimal essential fatty acid status in vegetarians: current knowledge and practical implications
(American Journal of Clinical Nutrition)
George Monbiot on the environmental problems of sourcing omega-3 from fish
{{DEFAULTSORT:Oily Fish Biologically-based therapies Fishing industry

 Oily fish are
Oily fish are fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
species with oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
(fats) in soft tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligam ...
s and in the coelomic cavity
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in most animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, it r ...
around the gut. Their fillet
Fillet may refer to:
*Annulet (architecture), part of a column capital, also called a fillet
*Fillet (aircraft), a fairing smoothing the airflow at a joint between two components
*Fillet (clothing), a headband
*Fillet (cut), a piece of meat
*Fille ...
s may contain up to 30% oil, although this figure varies both within and between species. Examples of oily fish include small forage fish
Forage fish, also called prey fish or bait fish, are small pelagic fish which are preyed on by larger predators for food. Predators include other larger fish, seabirds and marine mammals. Typical ocean forage fish feed near the base of the food ...
such as sardine
"Sardine" and "pilchard" are common names for various species of small, oily forage fish in the herring family Clupeidae. The term "sardine" was first used in English during the early 15th century, a folk etymology says it comes from the Ital ...
s, herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans, i ...
and anchovies
An anchovy is a small, common forage fish of the family Engraulidae. Most species are found in marine waters, but several will enter brackish water, and some in South America are restricted to fresh water.
More than 140 species are placed in 1 ...
, and other larger pelagic fish
Pelagic fish live in the pelagic zone of ocean or lake waters—being neither close to the bottom nor near the shore—in contrast with demersal fish that do live on or near the bottom, and reef fish that are associated with coral reef ...
such as salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the ...
, trout
Trout are species of freshwater fish belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', ''Salmo'' and ''Salvelinus'', all of the subfamily Salmoninae of the family Salmonidae. The word ''trout'' is also used as part of the name of some non-salmoni ...
, tuna
A tuna is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae (mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bullet tuna (max length: ...
, swordfish
Swordfish (''Xiphias gladius''), also known as broadbills in some countries, are large, highly migratory predatory fish characterized by a long, flat, pointed bill. They are a popular sport fish of the billfish category, though elusive. Swordfis ...
and mackerel
Mackerel is a common name applied to a number of different species of pelagic fish, mostly from the family Scombridae. They are found in both temperate and tropical seas, mostly living along the coast or offshore in the oceanic environment.
...
.
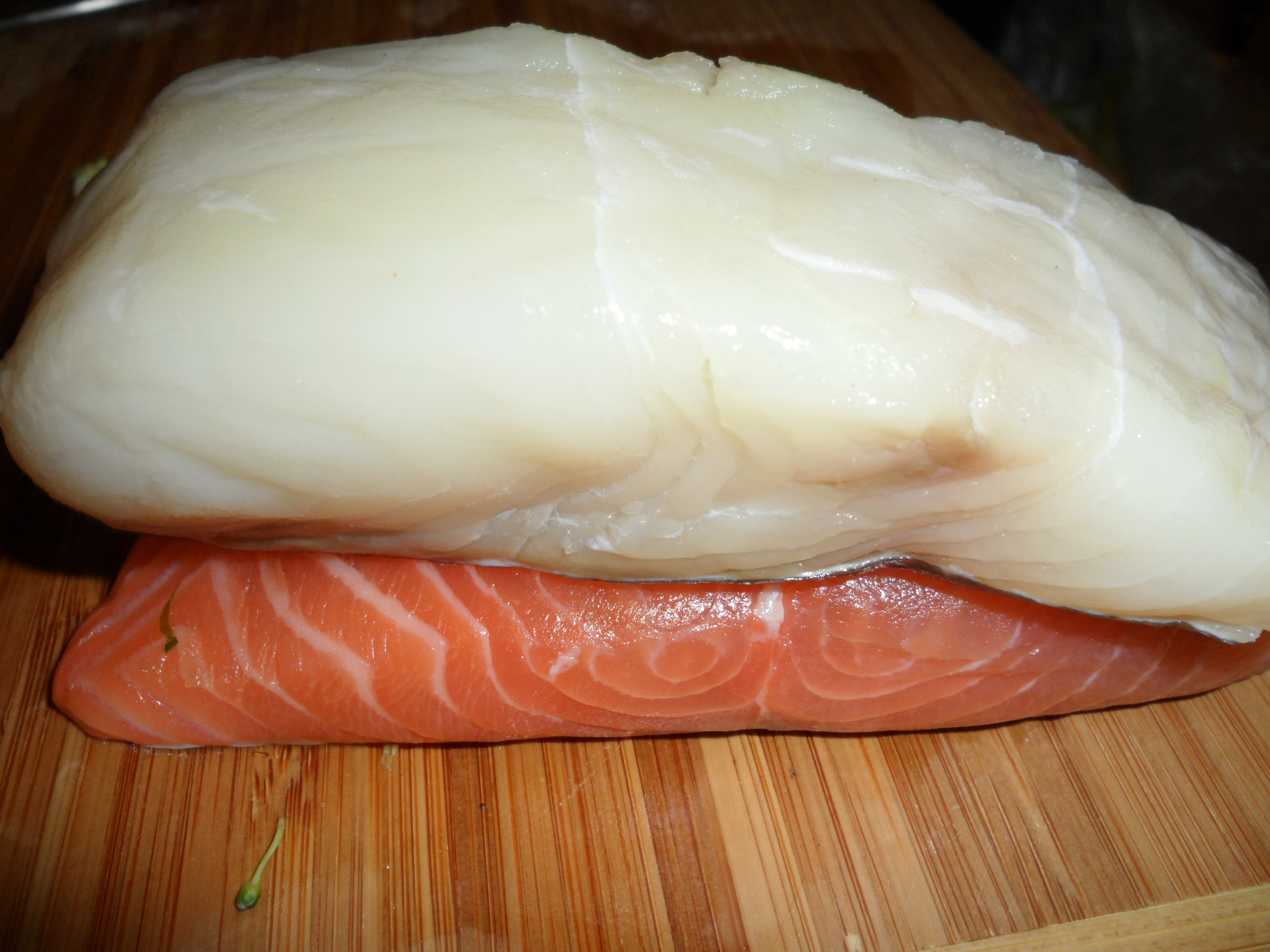
Oily fish can be contrasted with whitefish, which contain oil only in the liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for ...
and in much less overall quantity than oily fish. Examples of whitefish are cod
Cod is the common name for the demersal fish genus '' Gadus'', belonging to the family Gadidae. Cod is also used as part of the common name for a number of other fish species, and one species that belongs to genus ''Gadus'' is commonly not call ...
, haddock
The haddock (''Melanogrammus aeglefinus'') is a saltwater ray-finned fish from the family Gadidae, the true cods. It is the only species in the monotypic genus ''Melanogrammus''. It is found in the North Atlantic Ocean and associated seas where ...
and flatfish
A flatfish is a member of the Ray-finned fish, ray-finned demersal fish order (biology), order Pleuronectiformes, also called the Heterosomata, sometimes classified as a suborder of Perciformes. In many species, both eyes lie on one side of the ...
. White fish are usually demersal fish
Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes (the demersal zone).Walrond Carl . "Coastal fish - Fish of the open sea floor"Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009 They occ ...
which live on or near the seafloor, whereas oily fish are pelagic, living in the water column
A water column is a conceptual column of water from the surface of a sea, river or lake to the bottom sediment.Munson, B.H., Axler, R., Hagley C., Host G., Merrick G., Richards C. (2004).Glossary. ''Water on the Web''. University of Minnesota-D ...
away from the bottom.
Oily fish meat
Many species of fish are caught by humans and consumed as food in virtually all regions around the world. Fish has been an important dietary source of protein and other nutrients throughout human history.
The English language does not have ...
is a good source of important fat-soluble
Lipophilicity (from Greek λίπος "fat" and φίλος "friendly"), refers to the ability of a chemical compound to dissolve in fats, oils, lipids, and non-polar solvents such as hexane or toluene. Such non-polar solvents are themselves lipop ...
vitamin
A vitamin is an organic molecule (or a set of molecules closely related chemically, i.e. vitamers) that is an Nutrient#Essential nutrients, essential micronutrient that an organism needs in small quantities for the proper functioning of its ...
s such as Vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin and an essential nutrient for humans. It is a group of organic compounds that includes retinol, retinal (also known as retinaldehyde), retinoic acid, and several provitamin A carotenoids (most notably bet ...
and D, and is rich in omega-3 fatty acid
Omega−3 fatty acids, also called Omega-3 oils, ω−3 fatty acids or ''n''−3 fatty acids, are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) characterized by the presence of a double bond, three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their chem ...
s (white fish also contain these nutrients but at a much lower concentration). For this reason the consumption of oily fish rather than white fish can be more beneficial to humans, particularly concerning heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, hea ...
s such as stroke and ischemic heart disease; however, oily fish are known to carry higher levels of contaminant
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that spoils, corrupts, infects, makes unfit, or makes inferior a material, physical body, natural environment, workplace, etc.
Types of contamination
Wi ...
s (such as mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
or dioxin
Dioxin may refer to:
* 1,2-Dioxin or 1,4-Dioxin, two unsaturated heterocyclic 6-membered rings where two carbon atoms have been replaced by oxygen atoms, giving the molecular formula C4H4O2
*Dibenzo-1,4-dioxin, the parent compound also known as ...
or POPs
Pops may refer to:
Name or nickname
* Pops, an informal term of address for a father or elder
* Pops (nickname), a list of people
* Pops (Muppet), a Muppets character
* Pops (Johnny Bravo), a character from the Cartoon Network animated television ...
) than whitefish. Among other benefits, studies suggest that the omega-3 fatty acids in oily fish may help improve inflammatory conditions such as arthritis
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In som ...
.
Health benefits

Dementia
A 1997 study published in ''Annals of Neurology
''Annals of Neurology'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal publishing articles of "broad interest in neurology, particularly those with high impact in understanding the mechanisms and treatment of diseases of the human nervous system." The journal ...
'' followed 5,386 elderly participants in Rotterdam. It found that fish consumption decreased the risk of dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affe ...
. However, the 2.1-year average follow-up was less than the three years dementia commonly affects people prior to diagnosis. Thus, the study was unclear as to whether fish consumption protected against dementia, or if dementia prevented the participants from wanting more fish.
French research published in 2002 in the ''British Medical Journal'' (BMJ
''The BMJ'' is a weekly peer-reviewed medical trade journal, published by the trade union the British Medical Association (BMA). ''The BMJ'' has editorial freedom from the BMA. It is one of the world's oldest general medical journals. Origina ...
) followed 1,674 elderly residents of southern France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
for seven years, studying their consumption of meat versus seafood and the presence of dementia symptoms. The conclusion was that people who ate fish at least once a week had a significantly lower risk of being diagnosed with dementia over a seven-year period. This study reinforced the Annals of Neurology findings. Because of the longer term, the BMJ study provided stronger evidence of a genuine protective effect. There was a possible confounding
In statistics, a confounder (also confounding variable, confounding factor, extraneous determinant or lurking variable) is a variable that influences both the dependent variable and independent variable, causing a spurious association. Con ...
factor in that individuals with higher education have both a lower risk of dementia and higher consumption of fish.
Cardiovascular health
Consuming 200–400 g of oily fish twice per week may also help prevent sudden death due tomyocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may ...
by preventing cardiac arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults ...
. The eicosapentaenoic acid
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; also icosapentaenoic acid) is an omega-3 fatty acid. In physiological literature, it is given the name 20:5(n-3). It also has the trivial name timnodonic acid. In chemical structure, EPA is a carboxylic acid with a 20-c ...
found in fish oils appears to dramatically reduce inflammation through conversion within the body to resolvins
Resolvins are specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) derived from omega-3 fatty acids, primarily eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), as well as docosapentaenoic acid (DPA) and clupanodonic acid. As autacoids similar ...
, with beneficial effects for the cardiovascular system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
and arthritis
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In som ...
.
Recommended consumption
 In 1994, the UK Committee on Medical Aspects of Food and Nutrition Policy recommended that people eat at least two portions of fish per week, one of which should be oily fish.
In 2004 the UK
In 1994, the UK Committee on Medical Aspects of Food and Nutrition Policy recommended that people eat at least two portions of fish per week, one of which should be oily fish.
In 2004 the UK Food Standards Agency
, type = Non-ministerial government department
, nativename =
, nativename_a =
, nativename_r =
, logo = Food Standards Agency.svg
, logo_width =
, logo_caption =
, seal =
, seal_width =
, seal_caption =
, picture =
, picture_width =
, ...
published advice on the recommended minimum and maximum quantities of oily fish to be eaten per week, to balance the beneficial qualities of the omega-3 fatty acids against the potential dangers of ingesting polychlorinated biphenyls
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are highly carcinogenic chemical compounds, formerly used in industrial and consumer products, whose production was banned in the United States by the Toxic Substances Control Act of 1976, Toxic Substances Contro ...
and dioxins. It reiterated the 1994 guideline of two portions of fish per week including one portion of oily fish, but advised eating no more than four portions per week, and no more than two portions for people who are pregnant, may become pregnant or who are breastfeeding.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it be ...
's (EPA) Exposure Reference Dose (RfI) for methylmercury
Methylmercury (sometimes methyl mercury) is an organometallic cation with the formula . It is the simplest organomercury compound. Methylmercury is extremely toxic, and its derivatives are the major source of organic mercury for humans. It is a ...
(MeHg) is 0.1 micrograms per kg body weight per day. The corresponding limit of blood mercury is 5.8 micrograms per liter. The restrictions apply to certain oily fish – "marlin, swordfish, shark and, to a lesser extent, tuna". The recommendations on maximum consumption of oily fish were up to four portions (1 portion = 140g, or approx 4.9 ounces) a week for men, boys, and women past childbearing age, and up to two portions a week for women of childbearing age, including pregnant and breastfeeding women, and girls. There is no recommended limit on the consumption of white fish.
The EPA and 2007 U.S. Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of com ...
guidelines sets a limit only on consumption of fatty fish with greater than one part per million of methylmercury, specifically tilefish
250px, Blue blanquillo, ''Malacanthus latovittatus''
Tilefishes are mostly small perciform marine fish comprising the family Malacanthidae. They are usually found in sandy areas, especially near coral reefs.
Commercial fisheries exist for th ...
, king mackerel
The king mackerel (''Scomberomorus cavalla'') or kingfish, is a migratory species of mackerel of the western Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Mexico. It is an important species to both the commercial and recreational fishing industries.
Description
T ...
, shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimo ...
and swordfish
Swordfish (''Xiphias gladius''), also known as broadbills in some countries, are large, highly migratory predatory fish characterized by a long, flat, pointed bill. They are a popular sport fish of the billfish category, though elusive. Swordfis ...
. There are limits, however, for nursing/pregnant women and children under the age of six. This population should completely avoid fish with high risk of mercury contamination (those listed above) and limit consumption of moderate and low-mercury fish to 12 ounces or less per week. Albacore
The albacore (''Thunnus alalunga''), known also as the longfin tuna, is a species of tuna of the order Perciformes. It is found in temperate and tropical waters across the globe in the epipelagic and mesopelagic zones. There are six distinct sto ...
tuna should be limited to six ounces or less per week.
Omega-3 content
Concerns aboutcontamination
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that spoils, corrupts, infects, makes unfit, or makes inferior a material, physical body, natural environment, workplace, etc.
Types of contamination
W ...
, diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
or supply
Supply may refer to:
*The amount of a resource that is available
**Supply (economics), the amount of a product which is available to customers
**Materiel, the goods and equipment for a military unit to fulfill its mission
*Supply, as in confidenc ...
have led to investigation of plant sources of omega-3 fatty acids, notably flax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. Textiles made from flax are known in ...
, hempseed
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a botanical class of ''Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial or medicinal use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest growing plants ...
and perilla oil
Perilla oil ( ''Deulgireum'') is an edible vegetable oil derived from perilla seeds. Having a distinct nutty aroma and taste, the oil pressed from the toasted perilla seeds is used as a flavor enhancer, condiment, and cooking oil in Korean cuisine ...
s. Lactating women who supplemented their diet with flaxseed oil showed increases in blood and breastmilk
Breast milk (sometimes spelled as breastmilk) or mother's milk is milk produced by mammary glands located in the breast of a human female. Breast milk is the primary source of nutrition for newborns, containing fat, protein, carbohydrates (lactos ...
concentration of alpha-linolenic acid
''alpha''-Linolenic acid (ALA), also known as α-Linolenic acid (from Greek ''alpha'' meaning "first" and ''linon'' meaning flax), is an ''n''−3, or omega-3, essential fatty acid. ALA is found in many seeds and oils, including flaxseed, wa ...
and eicosapentaenoic acid
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; also icosapentaenoic acid) is an omega-3 fatty acid. In physiological literature, it is given the name 20:5(n-3). It also has the trivial name timnodonic acid. In chemical structure, EPA is a carboxylic acid with a 20-c ...
but no changes to concentrations of docosahexaenoic acid
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid that is a primary structural component of the human brain, cerebral cortex, skin, and retina. In physiological literature, it is given the name 22:6(n-3). It can be synthesized from alpha-lino ...
.
See also
*Mercury in fish
The presence of mercury in fish is a health concern for people who eat them, especially for women who are or may become pregnant, nursing mothers, and young children. Fish and shellfish concentrate mercury in their bodies, often in the form of m ...
References
Further reading
* Clover, Charles. 2004. ''The End of the Line: How overfishing is changing the world and what we eat''. Ebury Press, London.External links
Achieving optimal essential fatty acid status in vegetarians: current knowledge and practical implications
(American Journal of Clinical Nutrition)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Oily Fish Biologically-based therapies Fishing industry