|
Postcolonial Literature
Postcolonial literature is the literature by people from formerly colonized countries. It exists on all continents except Antarctica. Postcolonial literature often addresses the problems and consequences of the decolonization of a country, especially questions relating to the political and cultural independence of formerly subjugated people, and themes such as racialism and colonialism. A range of literary theory has evolved around the subject. It addresses the role of literature in perpetuating and challenging what postcolonial critic Edward Said refers to as cultural imperialism. Migrant literature and postcolonial literature show some considerable overlap. However, not all migration takes place in a colonial setting, and not all postcolonial literature deals with migration. A question of current debate is the extent to which postcolonial theory also speaks to migration literature in non-colonial settings. Terminology The significance of the prefix "post-" in "postcolonial" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include oral literature, much of which has been transcribed. Literature is a method of recording, preserving, and transmitting knowledge and entertainment, and can also have a social, psychological, spiritual, or political role. Literature, as an art form, can also include works in various non-fiction genres, such as biography, diaries, memoir, letters, and the essay. Within its broad definition, literature includes non-fictional books, articles or other printed information on a particular subject.''OED'' Etymologically, the term derives from Latin ''literatura/litteratura'' "learning, a writing, grammar," originally "writing formed with letters," from ''litera/littera'' "letter". In spite of this, the term has also been applied to spoken or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
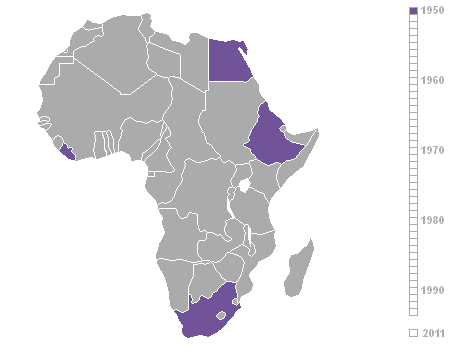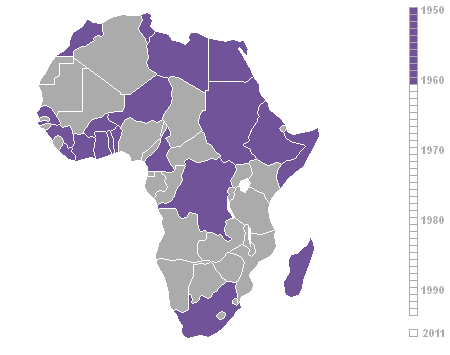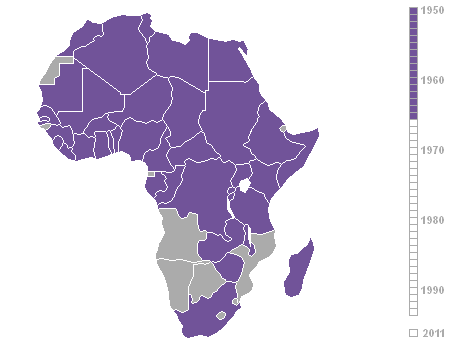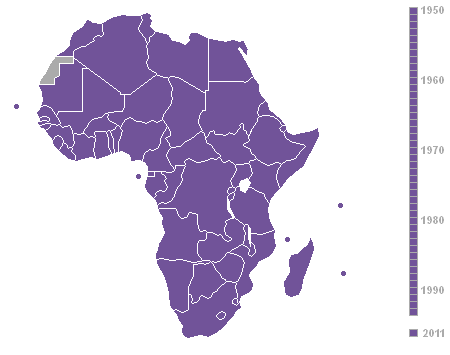
Decolonization Of Africa
The decolonisation of Africa was a process that took place in the mid-to-late 1950s to 1975 during the Cold War, with radical government changes on the continent as colonial governments made the transition to independent states. The process was often marred with violence, political turmoil, widespread unrest, and organised revolts in both northern and sub-Saharan countries including the Algerian War in French Algeria, the Angolan War of Independence in Portuguese Angola, the Congo Crisis in the Belgian Congo, the Mau Mau Uprising in British Kenya, the Zanzibar Revolution in the Sultanate of Zanzibar, and the Nigerian Civil War in the secessionist state of Biafra. Background The "Scramble for Africa" between 1870 and 1914 was a significant period of European imperialism in Africa that ended with almost all of Africa, and its natural resources, being controlled as colonies by a small number of European states. Racing to secure as much land as possible while avoiding conflict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Literature
Australian literature is the written or literary work produced in the area or by the people of the Commonwealth of Australia and its preceding colonies. During its early Western history, Australia was a collection of British colonies; as such, its recognised literary tradition begins with and is linked to the broader tradition of English literature. However, the narrative art of Australian writers has, since 1788, introduced the character of a new continent into literature—exploring such themes as Aboriginality, ''mateship'', egalitarianism, democracy, national identity, migration, Australia's unique location and geography, the complexities of urban living, and " the beauty and the terror" of life in the Australian bush. Overview Australian writers who have obtained international renown include the Nobel-winning author Patrick White, as well as authors Christina Stead, David Malouf, Peter Carey, Bradley Trevor Greive, Thomas Keneally, Colleen McCullough, Nevil Shute and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-structuralism
Post-structuralism is a term for philosophical and literary forms of theory that both build upon and reject ideas established by structuralism, the intellectual project that preceded it. Though post-structuralists all present different critiques of structuralism, common themes among them include the rejection of the self-sufficiency of structuralism, as well as an interrogation of the binary oppositions that constitute its structures. Accordingly, post-structuralism discards the idea of interpreting media (or the world) within pre-established, socially constructed structures.Bensmaïa, Réda. 2005. "Poststructuralism." Pp. 92–93 in The Columbia History of Twentieth-Century French Thought', edited by L. Kritzman. Columbia University Press. Poster, Mark. 1988. "Introduction: Theory and the problem of Context." pp. 5–6 i''Critical theory and poststructuralism: in search of a context'' Merquior, José G. 1987. ''Foucault'', (Fontana Modern Masters series). University of Californi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Canon
The Western canon is the body of high culture literature, music, philosophy, and works of art that are highly valued in the West; works that have achieved the status of classics. However, not all these works originate in the Western world, and such works are also valued throughout the globe. It is "a certain Western intellectual tradition that goes from, say, Socrates to Wittgenstein in philosophy, and from Homer to James Joyce in literature". Literary canon Classic book A classic is a book, or any other work of art, accepted as being exemplary or noteworthy. In the second century Roman miscellany '' Attic Nights'', Aulus Gellius refers to a writer as "classicus... scriptor, non proletarius" ("A distinguished, not a commonplace writer"). Such classification began with the Greeks' ''ranking'' their cultural works, with the word '' canon'' (ancient Greek κανών, kanṓn: "measuring rod, standard"). Moreover, early Christian Church Fathers used ''canon'' to rank the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental aspects, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations amongst member states. Numerous organisations are associated with and operate within the Commonwealth. The Commonwealth dates back to the first half of the 20th century with the decolonisation of the British Empire through increased self-governance of its territories. It was originally created as the British Commonwealth of Nations through the Balfour Declaration at the 1926 Imperial Conference, and formalised by the United Kingdom through the Statute of Westminster in 1931. The current Commonwealth of Nations was formally constituted by the London Declaration in 1949, which modernised the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global South
The concept of Global North and Global South (or North–South divide in a global context) is used to describe a grouping of countries along socio-economic and political characteristics. The Global South is a term often used to identify regions within Latin America, Asia, Africa, and Oceania. It is one of a family of terms, including "Third World" and "Periphery", that denote regions outside Europe and North America. Most, though not all, of these countries are low-income and often politically or culturally marginalized on one side of the divide, while on the other side are the countries of the Global North (often equated with developed countries). As such, the term does not inherently refer to a geographical south; for example, most of the Global South is geographically within the Northern Hemisphere. The term as used by governmental and developmental organizations was first introduced as a more open and value-free alternative to "Third World" and similarly potentially "valui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neocolonialism
Neocolonialism is the continuation or reimposition of imperialist rule by a state (usually, a former colonial power) over another nominally independent state (usually, a former colony). Neocolonialism takes the form of economic imperialism, globalization, cultural imperialism and conditional aid to influence or control a developing country instead of the previous colonial methods of direct military control or indirect political control (hegemony). Neocolonialism differs from standard globalisation and development aid in that it typically results in a relationship of dependence, subservience, or financial obligation towards the neocolonialist nation. This may result in an undue degree of political control or spiraling debt obligations, functionally imitating the relationship of traditional colonialism. Neocolonialism frequently affects all levels of society, creating neo-colonial systems that disadvantage local communities, such as neo-colonial science. Coined by the Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a Megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with Deserts of Australia, deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approximately Early human migrations#Nearby Oceania, 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |