|
Postanesthetic Shivering
Postanesthetic shivering (PAS) is shivering after anesthesia. Description and treatment Postanesthetic shivering is one of the leading causes of discomfort in patients recovering from general anesthesia. It usually results due to the anesthetic inhibiting the body's thermoregulatory capability, although cutaneous vasodilation (triggered by post-operative pain) may also be a causative factor. First-line treatment consists of warming the patient; more persistent/severe cases may be treated with medications such as tramadol, pethidine, clonidine, and nefopam, which work by reducing the shivering threshold temperature and reducing the patient's level of discomfort. As these medications may react and/or synergize with the anesthetic agents employed during the surgery, their use is generally avoided when possible. The anesthetic ketamine can also be used to manage postanesthetic shivering. Intensity The intensity of PAS may be graded using the scale described by Crossley and Mahajan: : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise cause severe or intolerable pain in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * General anesthesia suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * Sedation suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness. * Regional and local anesthesia, which blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shivering
Shivering (also called shuddering) is a bodily function in response to cold and extreme fear in warm-blooded animals. When the core body temperature drops, the shivering reflex is triggered to maintain homeostasis. Skeletal muscles begin to shake in small movements, creating warmth by expending energy. Shivering can also be a response to fever, as a person may feel cold. During fever, the hypothalamic set point for temperature is raised. The increased set point causes the body temperature to rise (pyrexia), but also makes the patient feel cold until the new set point is reached. Severe chills with violent shivering are called rigors. Rigors occur because the patient's body is shivering in a physiological attempt to increase body temperature to the new set point. Biological basis Located in the posterior hypothalamus near the wall of the third ventricle is an area called the primary motor center for shivering. This area is normally inhibited by signals from the heat center in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise cause severe or intolerable pain in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * General anesthesia suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * Sedation suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness. * Regional and local anesthesia, which blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoregulation
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature as its own body temperature, thus avoiding the need for internal thermoregulation. The internal thermoregulation process is one aspect of homeostasis: a state of dynamic stability in an organism's internal conditions, maintained far from thermal equilibrium with its environment (the study of such processes in zoology has been called physiological ecology). If the body is unable to maintain a normal temperature and it increases significantly above normal, a condition known as hyperthermia occurs. Humans may also experience lethal hyperthermia when the wet bulb temperature is sustained above for six hours. The opposite condition, when body temperature decreases below normal levels, is known as hypothermia. It results when the homeostatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasodilation
Vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasoconstriction, which is the narrowing of blood vessels. When blood vessels dilate, the flow of blood is increased due to a decrease in vascular resistance and increase in cardiac output. Therefore, dilation of arterial blood vessels (mainly the arterioles) decreases blood pressure. The response may be intrinsic (due to local processes in the surrounding tissue) or extrinsic (due to hormones or the nervous system). In addition, the response may be localized to a specific organ (depending on the metabolic needs of a particular tissue, as during strenuous exercise), or it may be systemic (seen throughout the entire systemic circulation). Endogenous substances and drugs that cause vasodilation are termed vasodilators. Such vasoactivity is necessar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tramadol
Tramadol, sold under the brand name Ultram among others, is an opioid pain medication used to treat moderate to moderately severe pain. When taken by mouth in an immediate-release formulation, the onset of pain relief usually begins within an hour. It is also available by injection. It is available in combination with paracetamol (acetaminophen). As is typical of opioids, common side effects include constipation, itchiness, and nausea. Serious side effects may include hallucinations, seizures, increased risk of serotonin syndrome, decreased alertness, and drug addiction. A change in dosage may be recommended in those with kidney or liver problems. It is not recommended in those who are at risk of suicide or in those who are pregnant. While not recommended in women who are breastfeeding, those who take a single dose should not generally stop breastfeeding. Tramadol is converted in the liver to ''O''-desmethyltramadol (desmetramadol), an opioid with a stronger affinity to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pethidine
Pethidine, also known as meperidine and sold under the brand name Demerol among others, is a synthetic opioid pain medication of the phenylpiperidine class. Synthesized in 1938 as a potential anticholinergic agent by the German chemist Otto Eisleb, its analgesic properties were first recognized by Otto Schaumann while working for IG Farben, Germany. Pethidine is the prototype of a large family of analgesics including the pethidine 4-phenylpiperidines ( piminodine, anileridine and others), the prodines (alphaprodine, MPPP, ''etc.''), bemidones ( ketobemidone, etc.) and others more distant, including diphenoxylate and analogues. Pethidine is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe pain, and is delivered as a hydrochloride salt in tablets, as a syrup, or by intramuscular, subcutaneous, or intravenous injection. For much of the 20th century, pethidine was the opioid of choice for many physicians; in 1975, 60% of doctors prescribed it for acute pain and 22% for chronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clonidine
Clonidine, sold under the brand name Catapres among others, is an α2-adrenergic agonist medication used to treat high blood pressure, ADHD, drug withdrawal ( alcohol, opioids, or nicotine), menopausal flushing, diarrhea, spasticity, and certain pain conditions. It is used by mouth, by injection, or as a skin patch. Onset of action is typically within an hour with the effects on blood pressure lasting for up to eight hours. Common side effect include dry mouth, dizziness, headaches, hypotension, and sleepiness. Severe side effects may include hallucinations, heart arrhythmias, and confusion. If rapidly stopped, withdrawal effects may occur. Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is not recommended. Clonidine lowers blood pressure by stimulating α2 receptors in the brain, which results in relaxation of many arteries. Clonidine was patented in 1961 and came into medical use in 1966. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 75th most commonly prescri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nefopam
Nefopam, sold under the brand name Acupan among others, is a centrally acting, non-opioid painkilling medication, that is primarily used to treat moderate to severe pain. Nefopam acts in the brain and spinal cord to relieve pain via novel mechanisms: antinociceptive effects from triple monoamine reuptake inhibition, and antihyperalgesic activity through modulation of glutamatergic transmission. Medical uses Nefopam is effective for prevention of shivering during surgery or recovery from surgery. Nefopam was significantly more effective than aspirin as an analgesic in one clinical trial, although with a greater incidence of side effects such as sweating, dizziness and nausea, especially at higher doses. The estimated relative potency of nefopam to morphine indicates that 20 mg of nefopam HCl is the approximate analgesic equal of 12 mg of morphine with comparable analgesic efficacy to morphine, or oxycodone, while nefopam tends to produce fewer side effects, does not p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketamine
Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic used medically for induction and maintenance of anesthesia. It is also used as a recreational drug. It is one of the safest anesthetics, as, in contrast with opiates, ether, and propofol, it suppresses neither respiration nor heart rate. Ketamine is also simple to administer and highly tolerable compared to drugs with similar effects which are flammable, irritating, or even explosive. Ketamine is a novel compound, derived from PCP, created in pursuit of a safer anesthetic with similar characteristics. Ketamine is also used for acute pain management. At anesthetic doses, ketamine induces a state of "dissociative anesthesia", a trance-like state providing pain relief, sedation, and amnesia. The distinguishing features of ketamine anesthesia are preserved breathing and airway reflexes, stimulated heart function with increased blood pressure, and moderate bronchodilation. At lower, sub-anesthetic doses, ketamine is a promising agent fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
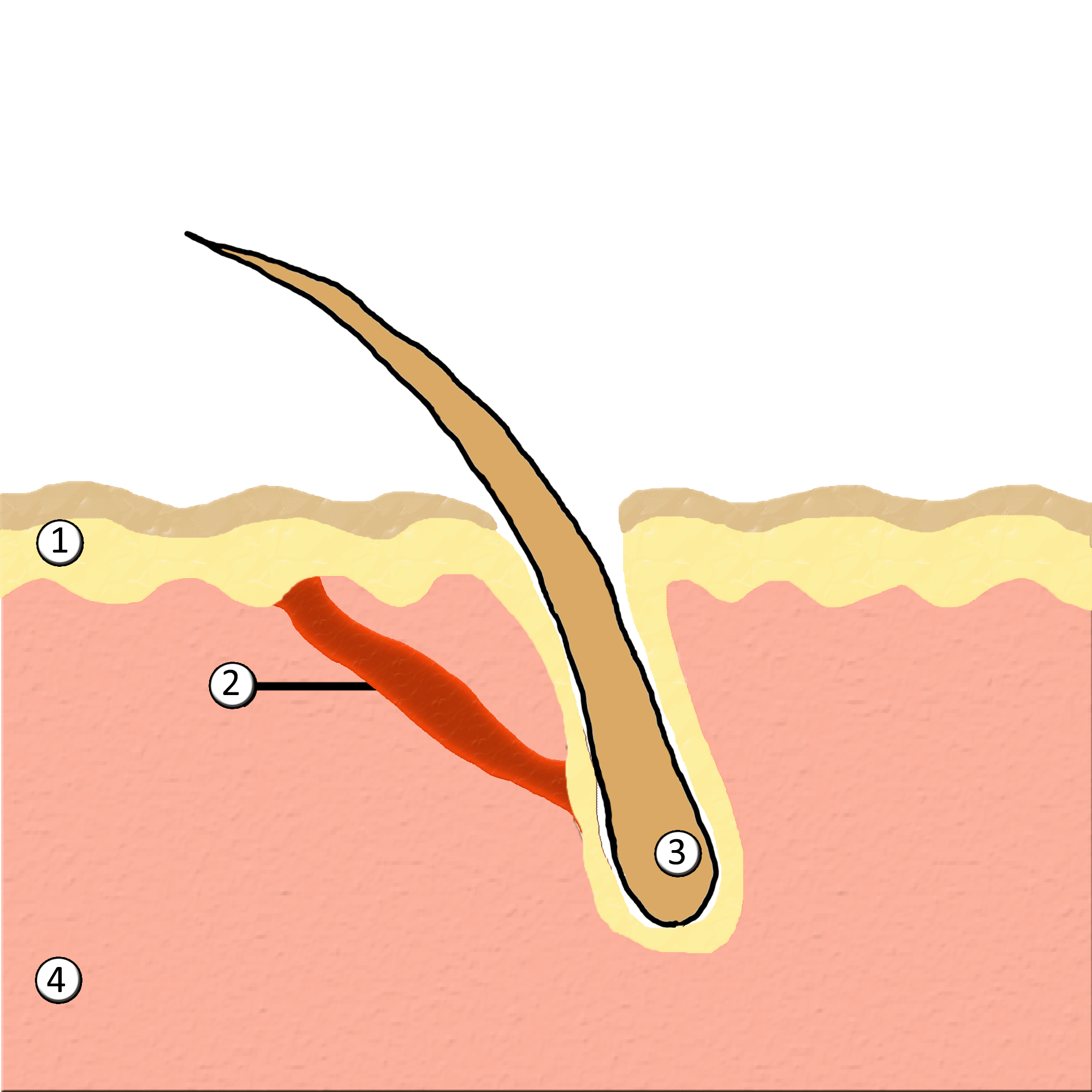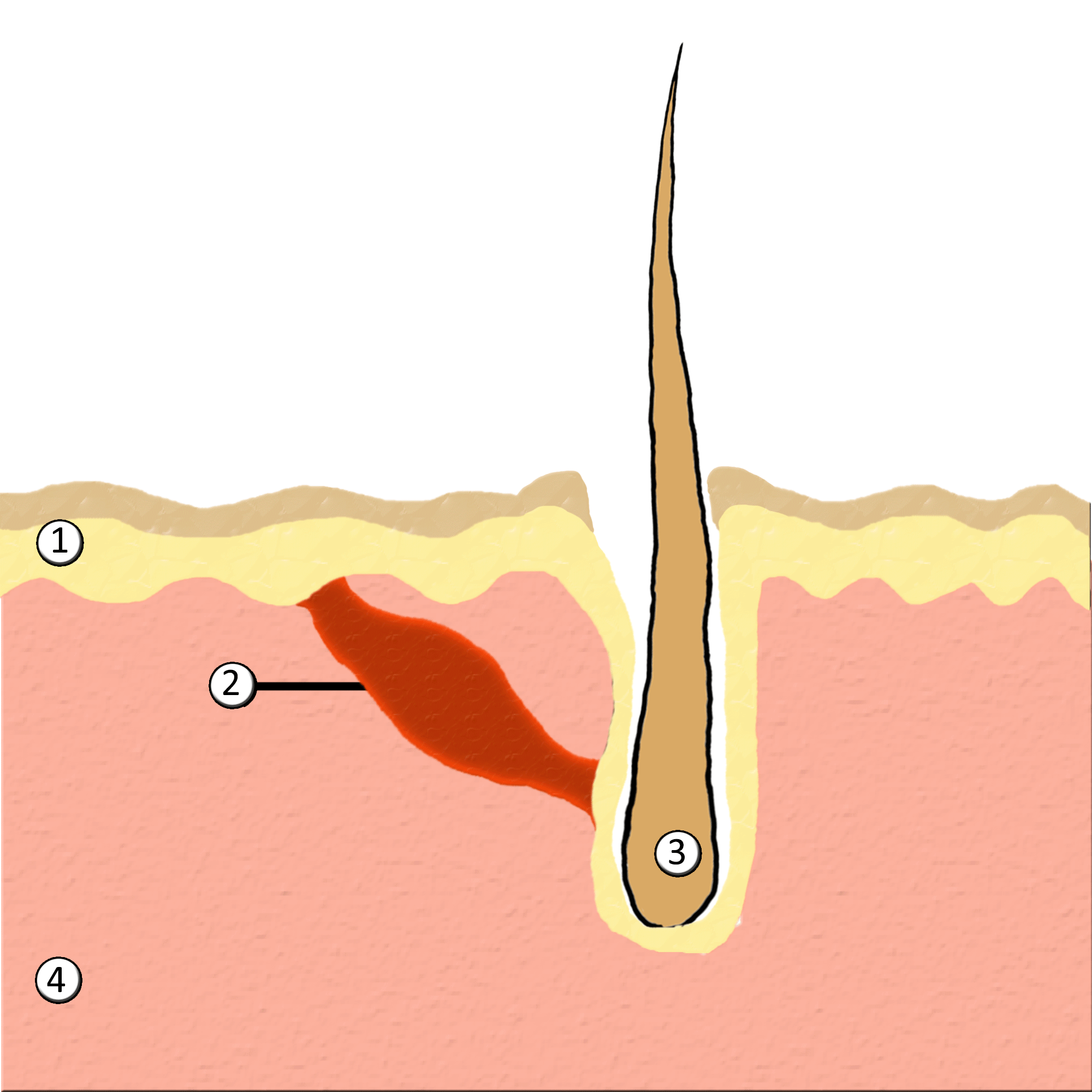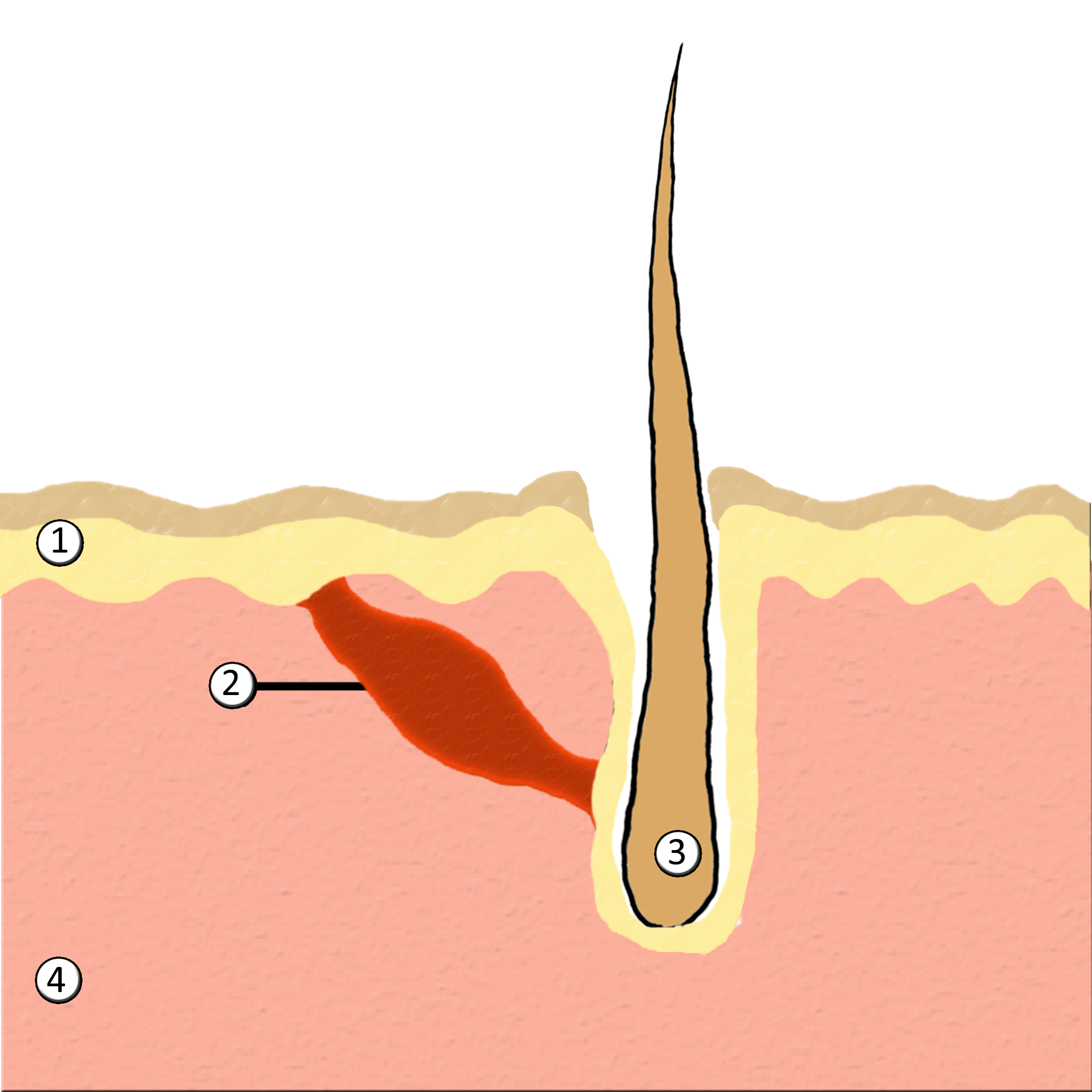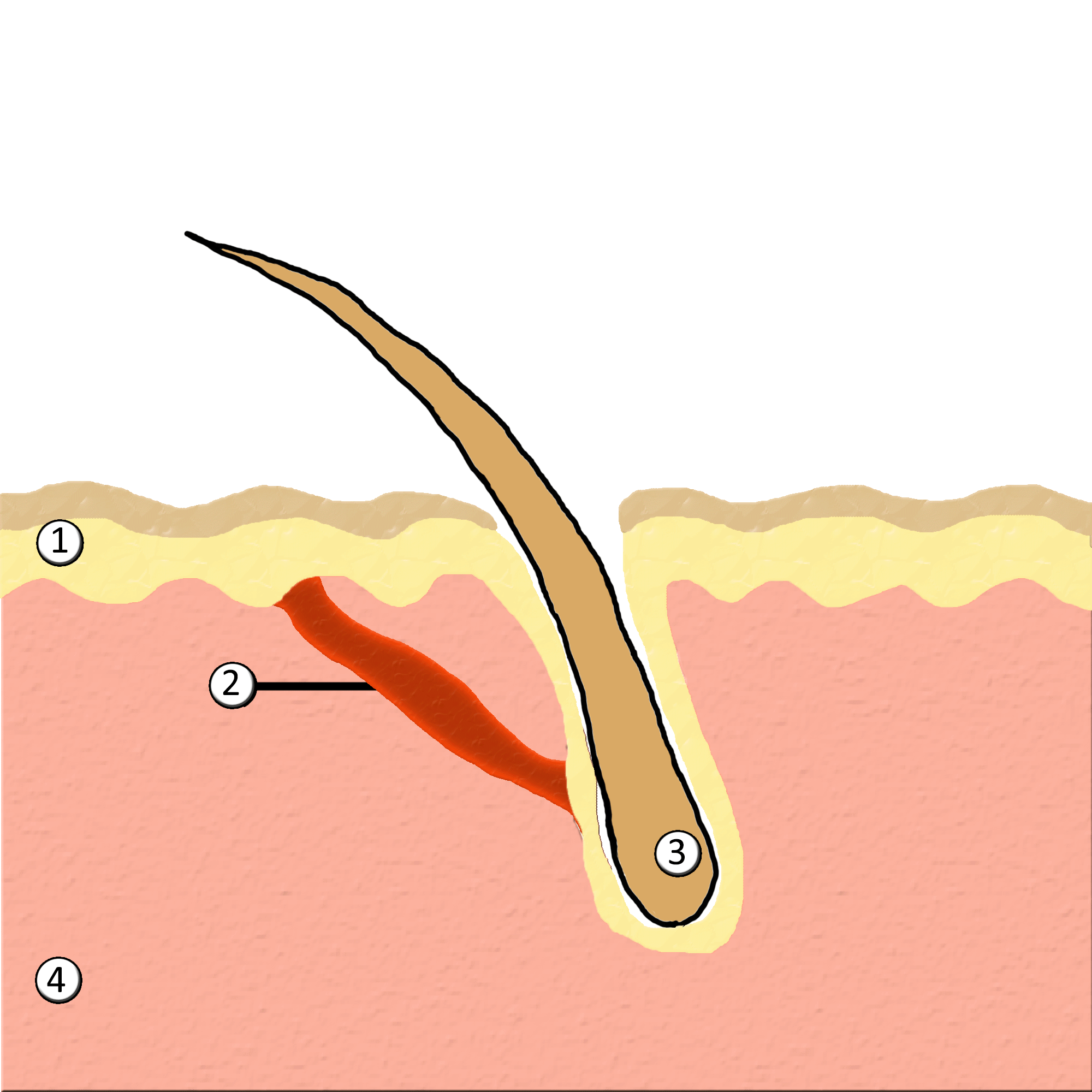
Piloerection
Goose bumps, goosebumps or goose-pimples are the bumps on a person's skin at the base of body hairs which may involuntarily develop when a person is tickled, cold or experiencing strong emotions such as fear, euphoria or sexual arousal. The formation of goose bumps in humans under stress is considered to be a vestigial reflex. Its function in other apes is to raise the body's hair, and would have made human ancestors appear larger to scare off predators or to increase the amount of air trapped in the fur to make it more insulating. The reflex of producing goose bumps is known as piloerection or the pilomotor reflex, or, more traditionally, horripilation. It occurs in many mammals; a prominent example is porcupines, which raise their quills when threatened, or sea otters when they encounter sharks or other predators. Anatomy and biology Goose bumps are created when tiny muscles at the base of each hair, known as '' arrector pili muscles'', contract and pull the hair straigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, in particular the large arteries and small arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels. The process is particularly important in controlling hemorrhage and reducing acute blood loss. When blood vessels constrict, the flow of blood is restricted or decreased, thus retaining body heat or increasing vascular resistance. This makes the skin turn paler because less blood reaches the surface, reducing the radiation of heat. On a larger level, vasoconstriction is one mechanism by which the body regulates and maintains mean arterial pressure. Medications causing vasoconstriction, also known as vasoconstrictors, are one type of medicine used to raise blood pressure. Generalized vasoconstriction usually results in an increase in systemic blood pressure, but it may also occur in specific tissues, causing a localized reduction in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |