Pethidine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pethidine, also known as meperidine and sold under the brand name Demerol among others, is a synthetic
 Pethidine is quickly hydrolysed in the liver to pethidinic acid and is also demethylated to norpethidine, which has half the analgesic activity of pethidine but a longer elimination half-life (8–12 hours); accumulating with regular administration, or in
Pethidine is quickly hydrolysed in the liver to pethidinic acid and is also demethylated to norpethidine, which has half the analgesic activity of pethidine but a longer elimination half-life (8–12 hours); accumulating with regular administration, or in 
opioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use ...
pain medication
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). I ...
of the phenylpiperidine Phenylpiperidines are chemical compounds with a phenyl moiety directly attached to piperidine. There are a variety of pharmacological effects associated with phenylpiperidines including morphine-like activity or other central nervous system effects ...
class. Synthesized in 1938 as a potential anticholinergic agent by the German chemist Otto Eisleb, its analgesic properties were first recognized by Otto Schaumann while working for IG Farben
Interessengemeinschaft Farbenindustrie AG (), commonly known as IG Farben (German for 'IG Dyestuffs'), was a German chemical and pharmaceutical conglomerate. Formed in 1925 from a merger of six chemical companies— BASF, Bayer, Hoechst, Agf ...
, Germany. Pethidine is the prototype of a large family of analgesics including the pethidine 4-phenylpiperidines ( piminodine, anileridine and others), the prodines (alphaprodine
Prodine (trade names Prisilidine and Nisentil) is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of pethidine (meperidine). It was developed in Germany in the late 1940s.
There are two isomers of the trans form of prodine, alphaprodine and betaprodine ...
, MPPP, ''etc.''), bemidones ( ketobemidone, etc.) and others more distant, including diphenoxylate
Diphenoxylate is a centrally active opioid drug of the phenylpiperidine series that is used as a combination drug with atropine for the treatment of diarrhea. Diphenoxylate is an opioid and acts by slowing intestinal contractions; the atropine ...
and analogues.
Pethidine is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe pain, and is delivered as a hydrochloride salt in tablets, as a syrup, or by intramuscular
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles ha ...
, subcutaneous, or intravenous injection
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutri ...
. For much of the 20th century, pethidine was the opioid of choice for many physicians; in 1975, 60% of doctors prescribed it for acute pain and 22% for chronic severe pain.
It was patented in 1937 and approved for medical use in 1943. Compared with morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. T ...
, pethidine was thought to be safer, carry a lower risk of addiction, and to be superior in treating the pain associated with biliary spasm or renal colic due to its putative anticholinergic effects. These were later discovered to be inaccurate assumptions, as it carries an equal risk of addiction, possesses no advantageous effects on biliary spasm or renal colic compared to other opioids, and due to its toxic metabolite, norpethidine, it is more toxic than other opioids—especially during long-term use. The norpethidine metabolite was found to have serotonergic effects, so pethidine could, unlike most opioids, contributed to serotonin syndrome.
Medical uses
Pethidine is the most widely used opioid in labour and delivery but has fallen out of favour in some countries such as the United States in favour of other opioids, due to its potential drug interactions (especially with serotonergics) and its neurotoxic metabolite, norpethidine. It is still commonly used in the United Kingdom and New Zealand, and was the preferred opioid in the United Kingdom for use during labour, but has been superseded somewhat by diamorphine and other strong semi-synthetic opioids (e.g. hydromorphone) to avoid serotonin interactions since the mid-2000s. Pethidine is the preferred painkiller fordiverticulitis
Diverticulitis, specifically colonic diverticulitis, is a gastrointestinal disease characterized by inflammation of abnormal pouches— diverticula—which can develop in the wall of the large intestine. Symptoms typically include lower abdomi ...
, because it decreases intestinal intraluminal pressure.
Before 2003 it was on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.
Adverse effects
The adverse effects of pethidine administration are primarily those of the opioids as a class: nausea, vomiting, dizziness, diaphoresis, urinary retention, and constipation. Due to moderate stimulant effects mediated by pethidine's dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake inhibition, sedation is less likely compared to other opioids. Unlike other opioids, it does not cause miosis because of its anticholinergic properties. Overdose can cause muscle flaccidity, respiratory depression, obtundation,psychosis
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavi ...
, cold and clammy skin, hypotension, and coma. A narcotic antagonist such as naloxone
Naloxone, sold under the brand names Narcan (4 mg) and Kloxxado (8 mg) among others, is a medication used to reverse or reduce the effects of opioids. It is commonly used to counter decreased breathing in opioid overdose. Effects begin withi ...
is indicated to reverse respiratory depression and other effects of pethidine. Serotonin syndrome has occurred in patients receiving concurrent antidepressant therapy with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or monoamine oxidase inhibitors, or other medication types (see Interactions below). Convulsive seizures sometimes observed in patients receiving parenteral pethidine on a chronic basis have been attributed to accumulation in plasma of the metabolite norpethidine (normeperidine). Fatalities have occurred following either oral or intravenous pethidine overdose.
Interactions
Pethidine has serious interactions that can be dangerous with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (e.g., furazolidone, isocarboxazid, moclobemide, phenelzine, procarbazine, selegiline, tranylcypromine). Such patients may suffer agitation, delirium, headache, convulsions, and/orhyperthermia
Hyperthermia, also known simply as overheating, is a condition in which an individual's body temperature is elevated beyond normal due to failed thermoregulation. The person's body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. When extrem ...
. Fatal interactions have been reported including the death of Libby Zion. Seizures may develop when tramadol
Tramadol, sold under the brand name Ultram among others, is an opioid pain medication used to treat moderate to moderately severe pain. When taken by mouth in an immediate-release formulation, the onset of pain relief usually begins within an ...
is given intravenously following, or with, pethidine. It can interact as well with SSRIs
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
SSRIs increase the extracellu ...
and other antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medication used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and to help manage addictions. Common Side effect, side-effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weig ...
s, antiparkinson agents, migraine therapy, stimulants
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and inv ...
and other agents causing serotonin syndrome. It is thought to be caused by an increase in cerebral serotonin concentrations. It is probable that pethidine can also interact with a number of other medications, including muscle relaxants, benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, ...
s, and ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
.
Mechanism of action
Likemorphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. T ...
, pethidine exerts its analgesic effects by acting as an agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ag ...
at the μ-opioid receptor
The μ-opioid receptors (MOR) are a class of opioid receptors with a high affinity for enkephalins and beta-endorphin, but a low affinity for dynorphins. They are also referred to as μ(''mu'')-opioid peptide (MOP) receptors. The prototypical ...
.
Pethidine is often employed in the treatment of postanesthetic shivering. The pharmacologic mechanism of this antishivering effect is not fully understood, but it may involve the stimulation of κ-opioid receptor
The κ-opioid receptor or kappa opioid receptor, abbreviated KOR or KOP, is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''OPRK1'' gene. The KOR is coupled to the G protein Gi/G0 and is one of four related receptors that bind ...
s.
Pethidine has structural similarities to atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically given ...
and other tropane alkaloids and may have some of their effects and side effects. In addition to these opioidergic and anticholinergic effects, it has local anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of pain sensation. In the context of surgery, a local anesthetic creates an absence of pain in a specific location of the body without a loss of consciousness, as opposed to a general a ...
activity related to its interactions with sodium ion channels.
Pethidine's apparent ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology a ...
'' efficacy as an antispasmodic agent is due to its local anesthetic effects. It does not have antispasmodic effects ''in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and p ...
''. Pethidine also has stimulant effects mediated by its inhibition of the dopamine transporter (DAT) and norepinephrine transporter (NET). Because of its DAT inhibitory action, pethidine will substitute for cocaine in animals trained to discriminate cocaine from saline.
Several analogs of pethidine such as 4-fluoropethidine have been synthesized that are potent inhibitors of the reuptake of the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline" (from Latin '' ad ...
via DAT and NET. It has also been associated with cases of serotonin syndrome, suggesting some interaction with serotonergic neurons, but the relationship has not been definitively demonstrated.
It is more lipid-soluble than morphine, resulting in a faster onset of action. Its duration of clinical effect is 120–150 minutes, although it is typically administered at 4– to 6-hour intervals. Pethidine has been shown to be less effective than morphine, diamorphine
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a potent opioid mainly used as a recreational drug for its euphoric effects. Medical grade diamorphine is used as a pure hydrochloride salt. Various white and brown ...
, or hydromorphone at easing severe pain, or pain associated with movement or coughing.
Like other opioid drugs, pethidine has the potential to cause physical dependence
Physical dependence is a physical condition caused by chronic use of a tolerance-forming drug, in which abrupt or gradual drug withdrawal causes unpleasant physical symptoms. Physical dependence can develop from low-dose therapeutic use of certai ...
or addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to engage in certain behaviors, one of which is the usage of a drug, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use o ...
. It may be more likely to be abused than other prescription opioids, perhaps because of its rapid onset of action. A study which compared 75 mg pethidine administered via intravenous injection
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutri ...
(IV) and 100 mg administered orally (PO) to 10 mg oxycodone (IV) and 10 mg (PO), 10 mg morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. T ...
(IV) and 20 mg (PO), 2 mg hydromorphone (IV) and 4 mg (PO), and placebo
A placebo ( ) is a substance or treatment which is designed to have no therapeutic value. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like Saline (medicine), saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
In general ...
(C) in the subject's self-reported subjective effects such as 'drug-liking' (how many of the subjects enjoyed or not, the experience; if yes, what was the most enjoyable part and why?, etc.) and how eagerly did subject 'want to re-experience it', and after IV doses were administered, pethidine 75 mg second-highest rates of 'drug-liking', after morphine 10 mg. Descriptive adjectives for morphine by subjects were: “more sedating”, “more relaxing” and in comparison to the others, many subjects described that the experience was “more intense”. Pethidine followed, then hydromorphone, oxycodone and last was placebo. Upon oral administration, preference went from (greatest>least): oxycodone 10 mg>morphine 20 mg>hydromorphone 4 mg>pethidine 100 mg>placebo. The especially severe side effects unique to pethidine among opioids—serotonin syndrome, seizures, delirium, dysphoria, tremor—are primarily or entirely due to the action of its metabolite, norpethidine.
Pharmacokinetics
 Pethidine is quickly hydrolysed in the liver to pethidinic acid and is also demethylated to norpethidine, which has half the analgesic activity of pethidine but a longer elimination half-life (8–12 hours); accumulating with regular administration, or in
Pethidine is quickly hydrolysed in the liver to pethidinic acid and is also demethylated to norpethidine, which has half the analgesic activity of pethidine but a longer elimination half-life (8–12 hours); accumulating with regular administration, or in kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
. Norpethidine is toxic and has convulsant and hallucinogenic effects. The toxic effects mediated by the metabolites cannot be countered with opioid receptor antagonists such as naloxone or naltrexone, and are probably primarily due to norpethidine's anticholinergic activity probably due to its structural similarity to atropine, though its pharmacology has not been thoroughly explored. The neurotoxicity of pethidine's metabolites is a unique feature of pethidine compared to other opioids. Pethidine's metabolites are further conjugated with glucuronic acid
Glucuronic acid (from Greek γλεῦκος "''wine, must''" and οὖρον "''urine''") is a uronic acid that was first isolated from urine (hence the name). It is found in many gums such as gum arabic (c. 18%), xanthan, and kombucha tea ...
and excreted into the urine.

Recreational use
Trends
In data from the U.S. Drug Abuse Warning Network, mentions of hazardous or harmful use of pethidine declined between 1997 and 2002, in contrast to increases forfentanyl
Fentanyl, also spelled fentanil, is a very potent synthetic opioid used as a pain medication. Together with other drugs, fentanyl is used for anesthesia. It is also used illicitly as a recreational drug, sometimes mixed with heroin, cocain ...
, hydromorphone, morphine, and oxycodone. The number of dosage units of pethidine reported lost or stolen in the U.S. increased 16.2% between 2000 and 2003, from 32,447 to 37,687.
This article uses the terms "hazardous use", "harmful use", and "dependence" in accordance with ''Lexicon of alcohol and drug'' terms, published by the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
(WHO) in 1994. In WHO usage, the first two terms replace the term "abuse" and the third term replaces the term "addiction".
Synthesis
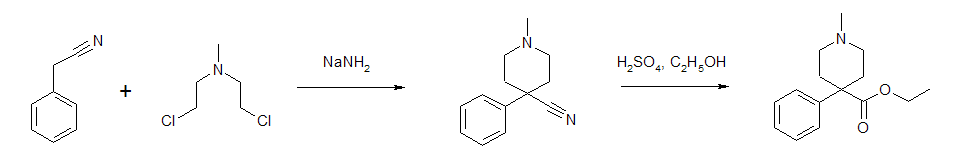
Pethidine can be produced in a two-step synthesis. The first step is reaction of benzyl cyanide and chlormethine in the presence of sodium amide to form a piperidine ring. Thenitrile
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a functional group. The prefix '' cyano-'' is used interchangeably with the term ''nitrile'' in industrial literature. Nitriles are found in many useful compounds, including me ...
is then converted to an ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ...
.
:Control
Pethidine is in Schedule II of the Controlled Substances Act 1970 of the United States as a Narcotic with ACSCN 9230 with a 6250 kilo aggregate manufacturing quota as of 2014. The free base conversion ratio for salts includes 0.87 for the hydrochloride and 0.84 for the hydrobromide. The A, B, and C intermediates in production of pethidine are also controlled, with ACSCN being 9232 for A (with a 6 gram quota) and 9233 being B (quota of 11 grams) and 9234 being C (6 gram quota). It is listed under the Single Convention for the Control of Narcotic Substances 1961 and is controlled in most countries in the same fashion as is morphine.Society and culture
InRaymond Chandler
Raymond Thornton Chandler (July 23, 1888 – March 26, 1959) was an American-British novelist and screenwriter. In 1932, at the age of forty-four, Chandler became a detective fiction writer after losing his job as an oil company executive durin ...
's novel '' The Long Goodbye'' (1953), in response to "How is Mrs. Wade?", police Lieutenant Bernie Ohls answers, "Too relaxed. She must have grabbed some pills. There's a dozen kinds up there -- even demerol. That's bad stuff."
Harold Shipman once got addicted to pethidine.
Danish writer Tove Ditlevsen suffered a lifelong addiction to pethidine since her husband, a dodgy doctor, had injected her a dose as a painkiller.
Pethidine is referenced by its brand name Demerol in the song "Morphine" by singer Michael Jackson
Michael Joseph Jackson (August 29, 1958 – June 25, 2009) was an American singer, songwriter, dancer, and philanthropist. Dubbed the " King of Pop", he is regarded as one of the most significant cultural figures of the 20th century. Over ...
on his 1997 album '' Blood on the Dance Floor: HIStory in the Mix''. Pethidine was one of several prescription drugs which Michael Jackson was addicted to at the time and the singer describes this in the lyrics of the song with phrases such as "Relax/This won't hurt you" and "Yesterday you had his trust/Today he's taking twice as much".
Pethidine is referenced in the television show ''Broadchurch
''Broadchurch'' is a British crime drama television series broadcast on ITV for three series between 2013 and 2017. It was created by Chris Chibnall, who acted as an executive producer and wrote all 24 episodes and produced by Kudos in asso ...
'', season 2, episode 3, as it was given to the character Beth after she has her baby.
In the 1987 Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry ( Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 22 scheduled languages of India. Malayalam wa ...
movie, ''Amrutham Gamaya
''Amrutham Gamaya'' , (translation: ''Path to immortality'') is a 1987 Indian Malayalam-language drama film directed by Hariharan, written by M. T. Vasudevan Nair and produced by P. K. R. Pillai. It features Mohanlal in the lead role, along ...
'', Mohanlal
Mohanlal Viswanathan (born 21 May 1960), known mononymously as Mohanlal, is an Indian actor, film producer, playback singer, film distributor, and director who predominantly works in Malayalam cinema besides also having sporadically app ...
's character, Dr. P.K. Haridas injects pethidine in himself and gets addicted to it.
A doctor in the TV show '' Call the Midwife'' becomes addicted to pethidine.
In William Gibson
William Ford Gibson (born March 17, 1948) is an American-Canadian speculative fiction writer and essayist widely credited with pioneering the science fiction subgenre known as ''cyberpunk''. Beginning his writing career in the late 1970s, hi ...
's book '' Neuromancer'', one of the characters say '"A mixture of cocaine and meperidine, yes." The Armenian went back to the conversation he was having with the Sanyo. "Demerol, they used to call that," said the Finn.'
South Carolina-based modern rock group Crossfade mentions Demerol in the lyrics of their 2004 song, "Dead Skin".
In the episode " The Fight" of the TV show ''Parks and Recreation
''Parks and Recreation'' (also known as ''Parks and Rec'') is an American political satire mockumentary sitcom television series created by Greg Daniels and Michael Schur. The series aired on NBC from April 9, 2009, to February 24, 2015, for 125 ...
'', some characters become intoxicated on a mixed drink called Snake Juice. The character Ann (Rashida Jones), who is a nurse, asks, "What the hell is in Snake Juice? Demerol?"
In David Foster Wallace's book '' Infinite Jest'', one of the main characters, Don Gately, is a Demerol addict in recovery.
See also
* Libby Zion Law (a case involving phenelzine and pethidine)References
{{Navboxes , title =Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms ...
, titlestyle = background:#ccccff
, list1 =
{{Glycine receptor modulators
{{Ion channel modulators
{{Ionotropic glutamate receptor modulators
{{Monoamine reuptake inhibitors
{{Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor modulators
{{Opioid receptor modulators
Analgesics
Convulsants
Ethyl esters
Euphoriants
Glycine receptor antagonists
Kappa-opioid receptor agonists
Local anesthetics
Mu-opioid receptor agonists
Muscarinic antagonists
NMDA receptor antagonists
4-Phenylpiperidines
Serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitors
Sodium channel blockers
Synthetic opioids
German inventions of the Nazi period