|
Plakina Trilopha
''Plakina trilopha'' is a species of sponge in the order Homosclerophorida. It is native to the Mediterranean Sea and the Canary Islands. It was first described in 1880 by the German zoologist Franz Eilhard Schulze Franz Eilhard Schulze (22 March 1840 – 2 November 1921) was a German anatomist and zoologist born in Eldena, near Greifswald. Biography He studied at the Universities of Bonn and Rostock. In 1863, he received his doctorate from Rostock, where .... References Homoscleromorpha Fauna of the Atlantic Ocean Fauna of the Mediterranean Sea Sponges described in 1880 Taxa named by Franz Eilhard Schulze {{sponge-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Eilhard Schulze
Franz Eilhard Schulze (22 March 1840 – 2 November 1921) was a German anatomist and zoologist born in Eldena, near Greifswald. Biography He studied at the Universities of Bonn and Rostock. In 1863, he received his doctorate from Rostock, where he subsequently became a lecturer of anatomy (1864) and an associate professor of comparative anatomy (1865). In 1871 he established the zoological institute at the University of Rostock.See entry oFranz Eilhard Schulzein Catalogus Professorum Rostochiensium Later on, he served as a professor at the Universities of Graz and Berlin. In 1872, he took part in the "Pomerania" expedition to the North Sea. For several years during the 1890s, he was president of the German Zoological Society (''Deutsche Zoologische Gesellschaft''). He made contributions in his studies on the anatomy and developmental history of invertebrates, in particular, his research and publications in regards to sea-sponges. He was especially interested in a class of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
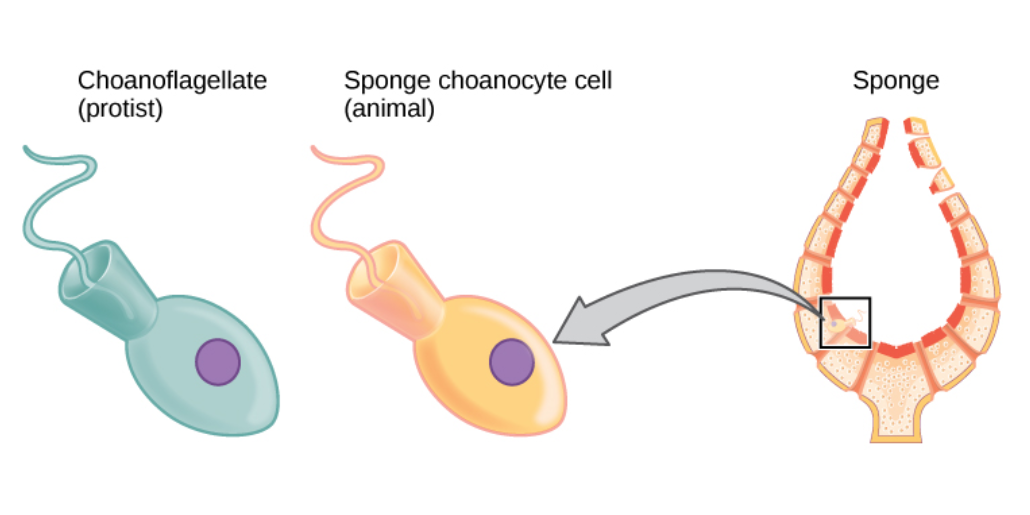
Sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homosclerophorida
Homosclerophorida is an order of marine sponges. It is the only order in the monotypic class Homoscleromorpha. The order is composed of two families: Plakinidae and Oscarellidae. Taxonomy Homoscleromorpha is phylogenetically well separated from Demospongiae. Therefore, it has been recognized as the fourth class of sponges. It has been suggested that Homoscleromorpha are more closely related to eumetazoans than to the other sponge groups, rendering sponges paraphyletic.Sperling, Pisani and Peterson 2007, cited in: The Cambrian Explosion p. 80, Erwin and Valentine 2013 This view has not been supported by later work using larger datasets and new techniques for phylogenetic inference, which tend to support sponges as monophyletic, with Homoscleromorpha grouping together with Calcarea. On the basis of molecular and morphological evidence, the two families Plakinidae and Oscarellidae have been reinstated. There are 117 species in this group divided into 9 genera. The spiculate gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant. The Sea has played a central role in the history of Western civilization. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. The Mediterranean Sea e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocco. They are the southernmost of the autonomous communities of Spain. The islands have a population of 2.2 million people and they are the most populous special territory of the European Union. The seven main islands are (from largest to smallest in area) Tenerife, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Lanzarote, La Palma, La Gomera, and El Hierro. The archipelago includes many smaller islands and islets, including La Graciosa, Alegranza, Isla de Lobos, Montaña Clara, Roque del Oeste, and Roque del Este. It also includes a number of rocks, including those of Salmor, Fasnia, Bonanza, Garachico, and Anaga. In ancient times, the island chain was often referred to as "the Fortunate Isles". The Canary Islands are the southernmost region of Spain, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Description
A species description is a formal description of a newly discovered species, usually in the form of a scientific paper. Its purpose is to give a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have been described previously or are related. In order for species to be validly described, they need to follow guidelines established over time. Zoological naming requires adherence to the ICZN code, plants, the ICN, viruses ICTV, and so on. The species description often contains photographs or other illustrations of type material along with a note on where they are deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million species have been identified and described, out of some 8.7 million that may actually exist. Millions more have become extinct throughout the existence of life on Earth. Naming process A name of a new species becomes valid (available in zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homoscleromorpha
Homosclerophorida is an order of marine sponges. It is the only order in the monotypic class Homoscleromorpha. The order is composed of two families: Plakinidae and Oscarellidae. Taxonomy Homoscleromorpha is phylogenetically well separated from Demospongiae. Therefore, it has been recognized as the fourth class of sponges. It has been suggested that Homoscleromorpha are more closely related to eumetazoans than to the other sponge groups, rendering sponges paraphyletic.Sperling, Pisani and Peterson 2007, cited in: The Cambrian Explosion p. 80, Erwin and Valentine 2013 This view has not been supported by later work using larger datasets and new techniques for phylogenetic inference, which tend to support sponges as monophyletic, with Homoscleromorpha grouping together with Calcarea. On the basis of molecular and morphological evidence, the two families Plakinidae and Oscarellidae have been reinstated. There are 117 species in this group divided into 9 genera. The spiculate gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of The Atlantic Ocean
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is ''funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoologists and paleontologists use ''fauna'' to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics. Etymology ''Fauna'' comes from the name Fauna, a Roman goddess of earth and fertility, the Roman god Faunus, and the related forest spirits called Fauns. All three words are cognates of the name of the Greek god Pan, and ''panis'' is the Greek equivalent of fauna. ''Fauna'' is also the word for a book that catalogues the animals in such a manner. The term was first used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of The Mediterranean Sea
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is ''funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoologists and paleontologists use ''fauna'' to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics. Etymology ''Fauna'' comes from the name Fauna, a Roman goddess of earth and fertility, the Roman god Faunus, and the related forest spirits called Fauns. All three words are cognates of the name of the Greek god Pan, and ''panis'' is the Greek equivalent of fauna. ''Fauna'' is also the word for a book that catalogues the animals in such a manner. The term was first used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sponges Described In 1880
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, heter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |