|
Pinole Vista Shopping Center
Pinole (Spanish for "cornmeal") is a city in Contra Costa County, California, United States. The population was 18,390 at the 2010 census. History The name derives from "pinole", a Nāhuatl word for a kind of flour made from the seeds of maize, chia, and various other grasses and annual herbs. An expedition under Pedro Fages was said to have run out of provisions while exploring the area, and to have been fed pinole by a local village, and so the Spaniards named their camp "El Pinole". In 1823, Ygnacio Martínez, commandant of the Presidio of San Francisco, received a land grant of Rancho El Pinole from the Mexican government. Martinez built a hacienda in Pinole Valley at the present site of Pinole Valley Park. During the 1850s, Bernardo Fernandez, a Portuguese immigrant, started a trading facility on the shores of San Pablo Bay and eventually built the historic Fernandez Mansion, which still stands today at the end of Tennent Avenue. From these early beginnings, a sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Municipalities In California
California is a U.S. state, state located in the Western United States. It is the List of U.S. states and territories by population, most populous state and the List of U.S. states and territories by area, third largest by area after Alaska and Texas. According to the 2020 United States Census, California has 39,538,223 inhabitants and of land. California has been inhabited by numerous Indigenous peoples of California, Native American peoples since antiquity. The Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish, the Russian colonization of the Americas, Russians, and other Europeans began exploring and colonizing the area in the 16th and 17th centuries, with the Spanish establishing its first California Spanish missions in California, mission at what is now Presidio of San Diego, San Diego in 1769. After the Mexican Cession of 1848, the California Gold Rush brought worldwide attention to the area. The growth of the Cinema of the United States, movie industry in Los Angeles, high te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Information Processing Standard
The Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) of the United States are a set of publicly announced standards that the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed for use in computer systems of non-military, American government agencies and contractors. FIPS standards establish requirements for ensuring computer security and interoperability, and are intended for cases in which suitable industry standards do not already exist. Many FIPS specifications are modified versions of standards the technical communities use, such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Specific areas of FIPS standardization The U.S. government has developed various FIPS specifications to standardize a number of topics including: * Codes, e.g., FIPS county codes or codes to indicate weather conditions or emergency indications. In 1994, Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rancho El Pinole
Rancho El Pinole was a Mexican land grant along Carquinez Strait in present-day Contra Costa County, California. It was given in 1842 by Governor Juan Alvarado to Ygnacio Martinez. Rancho El Pinole extended over land that today includes most of the Franklin Ridge, Crockett, Hercules, Martinez, Oleum, Pinole, Rodeo, Selby and Tormey. History Ygnacio Martínez (1774–1848) was commandant of the Presidio of San Francisco from 1822–1827, and again from 1828–1832, and was a member of the town council in 1824 and 1827. Martinez retired in 1831. Martinez represented to the Mexican authorities in 1834, that in consideration of his military service, Governor Luís Antonio Argüello in 1823 gave him title to a tract of land known as Pinole y Cañada del Hambre. Martinez stated that he had lost his title papers. Record evidence was not found to support his claim, and he was required to petition anew, which he did in 1837. While proceedings were pending upon the Martinez petition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
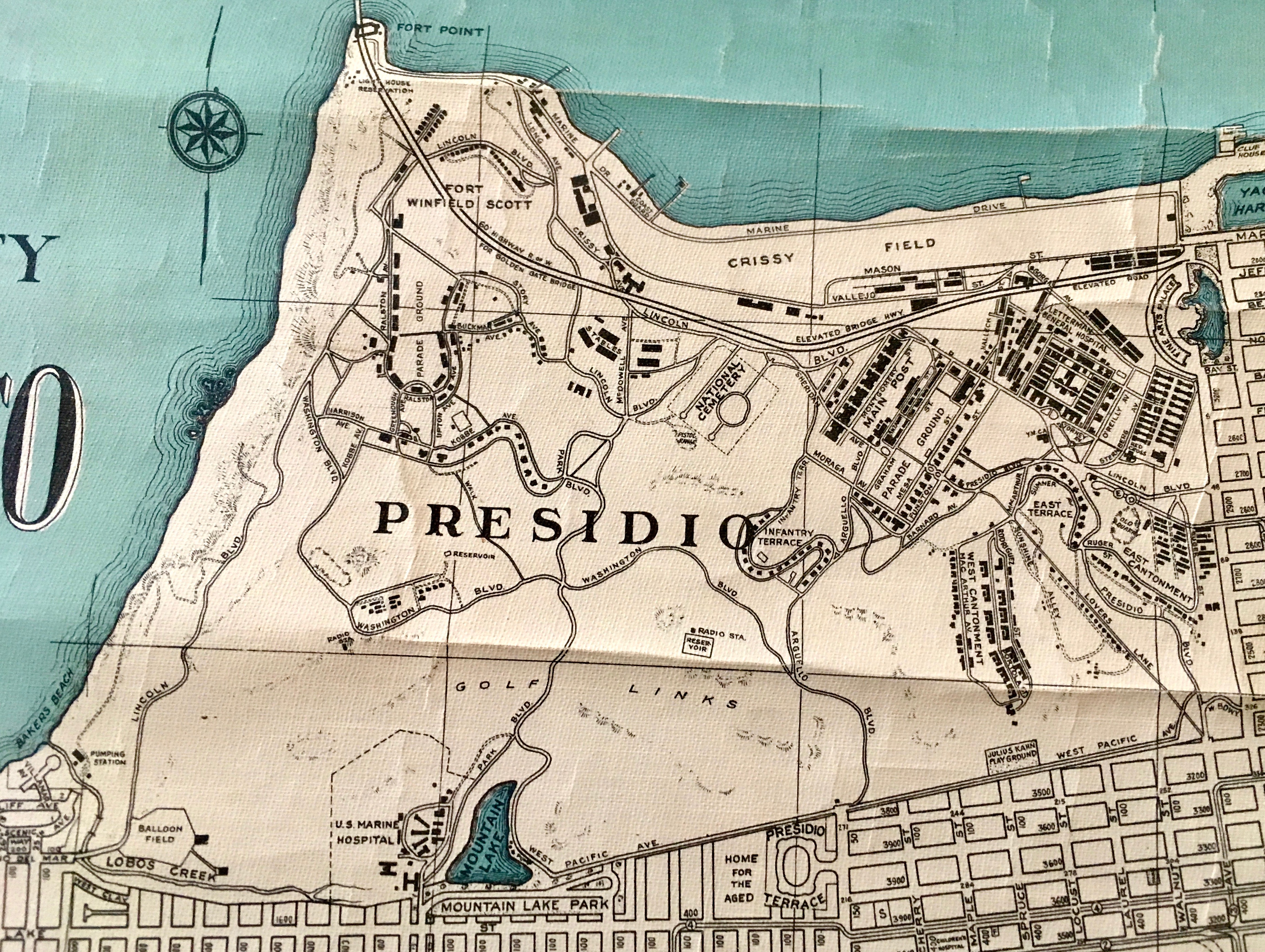
Presidio Of San Francisco
The Presidio of San Francisco (originally, El Presidio Real de San Francisco or The Royal Fortress of Saint Francis) is a park and former U.S. Army post on the northern tip of the San Francisco Peninsula in San Francisco, California, and is part of the Golden Gate National Recreation Area. It had been a fortified location since September 17, 1776, when New Spain established the presidio to gain a foothold in Alta California and the San Francisco Bay. It passed to Mexico in 1820, which in turn passed it to the United States in 1848. As part of a 1989 military reduction program under the Base Realignment and Closure ( BRAC) process, Congress voted to end the Presidio's status as an active military installation of the U.S. Army. On October 1, 1994, it was transferred to the National Park Service, ending 219 years of military use and beginning its next phase of mixed commercial and public use. In 1996, the United States Congress created the Presidio Trust to oversee and manage the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ygnacio Martínez
Ygnacio Nicanor Martínez (1774–1848) was a Californio politician, soldier, and ranchero, who served as the fourth Alcalde of San Francisco (then known as Yerba Buena). He was an important figure in the development of Contra Costa and the city of Martinez, California is named after him. Life Ygnacio Martínez was born in Mexico City, New Spain (now Mexico), and was a soldier in Alta California by 1822. In 1827, as a lieutenant stationed at the Presidio of San Francisco, Martínez met with the American explorer Jedediah Smith and helped to facilitate the continuation of Smith's northward travels toward the Columbia River. Martínez was the fourth Alcalde of Yerba Buena (now San Francisco) in 1837. In 1842, he was granted the Rancho El Pinole, which included the Alhambra Valley. A part of the rancho later became the city of Martinez. Family Martínez married Martina Arellanes in 1807, and the couple had eleven children: nine daughters and two sons. One of the daughter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedro Fages
Pedro Fages (1734–1794) was a Spanish soldier, explorer, first Lieutenant Governor of the Californias under Gaspar de Portolá. Fages claimed the governorship after Portolá's death, acting as governor in opposition to the official governor Felipe de Barri, and later served officially as fifth (1782–91) Governor of the Californias. Career Fages was born in Guissona, Spain. In 1762 he entered the light infantry in Catalonia and joined Spain's invasion of Portugal during the Seven Years' War. In May 1767 Fages, commissioned as a lieutenant in the newly formed Free Company of Volunteers of Catalonia, set sail from Cádiz along with a company of light infantry, voyaging to New Spain (Mexico). He and his men served under Domingo Elizondo in Sonora.Maynard Geiger. ''The Life and Times of Fray Junípero Serra: The Man Who Never Turned Back.'' Academy of American Franciscan History, 1959, vol. 1, p. 207. Voyage from Baja California to San Diego In 1769, Fages was selected by '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salvia Columbariae
''Salvia columbariae'' is an annual plant that is commonly called chia, chia sage, golden chia, or desert chia, because its seeds are used in the same way as those of ''Salvia hispanica'' ( chia). It grows in California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, New Mexico, Sonora, and Baja California, and was an important food for Native Americans. Some native names include ''pashiiy'' from Tongva and ''it'epeš'' from Ventureño. Description ''Salvia columbariae'' grows tall. Its stem hairs are generally short and sparse in distribution. It has oblong-ovate basal leaves that are long. The leaves are pinnately dissected and the lobes are irregularly rounded. The inflorescence is more or less scapose, meaning it has a long peduncle that comes from the ground level that has bracts. The bracts are round and awn-tipped. There are usually 1–2 cluster of flowers within the inflorescence. The calyx is long and the upper lip is unlobed but has 2 (sometimes 3) awns. The lower lip is about twice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The leafy stalk of the plant produces pollen inflorescences (or "tassels") and separate ovuliferous inflorescences called ears that when fertilized yield kernels or seeds, which are fruits. The term ''maize'' is preferred in formal, scientific, and international usage as a common name because it refers specifically to this one grain, unlike ''corn'', which has a complex variety of meanings that vary by context and geographic region. Maize has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat or rice. In addition to being consumed directly by humans (often in the form of masa), maize is also used for corn ethanol, animal feed and other maize products, such as corn starch and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahuatl
Nahuatl (; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahua peoples, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller populations in the United States. Nahuatl has been spoken in central Mexico since at least the seventh century CE. It was the language of the Aztec/ Mexica, who dominated what is now central Mexico during the Late Postclassic period of Mesoamerican history. During the centuries preceding the Spanish and Tlaxcalan conquest of the Aztec Empire, the Aztecs had expanded to incorporate a large part of central Mexico. Their influence caused the variety of Nahuatl spoken by the residents of Tenochtitlan to become a prestige language in Mesoamerica. After the conquest, when Spanish colonists and missionaries introduced the Latin alphabet, Nahuatl also became a literary language. Many chronicles, grammars, works of poetry, administrative docu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinole
Pinole, also called pinol or pinolillo, is roasted ground maize, which is then mixed with a combination of cocoa, agave, cinnamon, chia seeds, vanilla, or other spices. The resulting powder is then used as a nutrient-dense ingredient to make different foods, such as cereals, baked goods, tortillas, and beverages. The name comes from the Nahuatl word ''pinolli'', meaning cornmeal. Today, pinole is generally made by hand using wood-burning adobe ovens and a stone and pestle, and is still consumed in certain, often rural, parts of Latin America. Pinole is considered the national beverage of Nicaragua and Honduras. Nutrient content Depending on the type of pinole and the quality of its ingredients, pinole can be high in key vitamins and nutrients, including protein, amino acids, fiber, and antioxidants. Due to the large amount of fiber and the slow digestion of the maize, pinole also has a very high satiety effect, leaving those who consume it feeling full for a longer period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank Of Pinole (Pinole, CA)
The Bank of Pinole is located at 2361 San Pablo Ave. in Pinole, California. Located in Old Town Pinole The Bank of Pinole was built in 1915 by E.M. Downer, Sr. and remained as a bank till the 1960s. It is currently owned by the City of Pinole and currently does not have a tenant. It is a one-story building. With See also *National Register of Historic Places listings in Contra Costa County, California __NOTOC__ This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Contra Costa County, California. This is intended to be a complete list of the properties and districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Contra Costa ... References External links Pinole Historical Society History of Contra Costa County, California Historic districts on the National Register of Historic Places in California National Register of Historic Places in Contra Costa County, California Bank buildings on the National Register of Historic Places in California {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |