|
Piaggio P.XIX
The Piaggio P.XIX was an Italian aircraft engine produced by Rinaldo Piaggio S.p.A. during World War II and used to power aircraft of the Regia Aeronautica. Development The engine was part of a line of 14-cylinder radial engines developed from Piaggio based on the Gnome-Rhône Mistral Major, which was itself loosely based on the Bristol Jupiter. It was derived from the earlier P.XI but with a higher compression ratio. Variants ;P.XIX R.C.45 Turbine: Geared, rated altitude ;P.XIX R.C.50: Geared Applications * CANT Z.1007ter * Macchi MC.200bis prototype * Reggiane Re.2002 The engine was also fitted experimentally to single versions of the IMAM Ro.57 and Savoia-Marchetti SM.82 The Savoia-Marchetti SM.82 ''Marsupiale'' was an Italian bomber and transport aircraft of World War II. It was a Cantilever#Aircraft, cantilever, mid-wing monoplane trimotor with a retractable, Conventional landing gear, tailwheel undercarriage. ... (serial number MM.60591). Specifications (R.C. 45 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region. Italy is also considered part of Western Europe, and shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino. It has a territorial exclave in Switzerland, Campione. Italy covers an area of , with a population of over 60 million. It is the third-most populous member state of the European Union, the sixth-most populous country in Europe, and the tenth-largest country in the continent by land area. Italy's capital and largest city is Rome. Italy was the native place of many civilizations such as the Italic peoples and the Etruscans, while due to its central geographic location in Southern Europe and the Mediterranean, the country has also historically been home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. On average, U.S. refineries produce, from a barrel of crude oil, about 19 to 20 gallons of gasoline; 11 to 13 gallons of distillate fuel (most of which is sold as diesel fuel); and 3 to 4 gallons of jet fuel. The product ratio depends on the processing in an oil refinery and the crude oil assay. A barrel of oil is defined as holding 42 US gallons, which is about 159 liters or 35 imperial gallons. The characteristic of a particular gasoline blend to resist igniting too early (which causes knocking and reduces efficiency in reciprocating engines) is measured by its octane rating, which is produced in several grades. Tetraethyl lead and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1940s Aircraft Piston Engines
Year 194 ( CXCIV) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Septimius and Septimius (or, less frequently, year 947 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 194 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Septimius Severus and Decimus Clodius Septimius Albinus Caesar become Roman Consuls. * Battle of Issus: Septimius Severus marches with his army (12 legions) to Cilicia, and defeats Pescennius Niger, Roman governor of Syria. Pescennius retreats to Antioch, and is executed by Severus' troops. * Septimius Severus besieges Byzantium (194–196); the city walls suffer extensive damage. Asia * Battle of Yan Province: Warlords Cao Cao and Lü Bu fight for control over Yan Province; the battle lasts for over 100 day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumansky M-88
The Tumansky M-88 was an air-cooled radial engine for aircraft developed in the Soviet Union shortly before World War II. Design and development The M-88 was designed to address the shortcomings of the Tumansky M-87. The improvements incorporated in the M-88 were a strengthened crankcase, crankshaft, connecting rods, waffle ribbing at the piston bottom and a two speed geared centrifugal supercharger. The M-88 retained the same bore/stroke and displacement as the M-87 while increasing power to 1,000-1,150 hp. Design work began in 1937 and by 1939 the first prototypes were being flight tested in the Polikarpov I-180 fighter prototypes. At first the M-88 was not a success, but the designers persisted and the M-88 was made into a reliable and widely produced engine. There were a number of different variants with the most numerous being the M-88B, of which 10,585 were produced at Zaporozhye and Omsk. The M-88B solved most of the mechanical failures associated with the M-87 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shvetsov ASh-82
The Shvetsov ASh-82 (M-82) is a Soviet 14-cylinder, two-row, air-cooled radial aircraft engine developed from the Shvetsov M-62. The M-62 was the result of development of the M-25, which was a licensed version of the Wright R-1820 Cyclone. Design and development Arkadiy Shvetsov re-engineered the Wright Cyclone design, through the OKB-19 design bureau he headed, for Russian aviation engine manufacturing practices and metric dimensions and fasteners, reducing the stroke, dimensions and weight. This allowed the engine to be used in light aircraft, where an American-design Twin Cyclone, of some 930 kg (2,045 lb) weight in "dry" condition could not be installed. The engine entered production in 1940 and saw service in a number of Soviet aircraft. It powered the Tupolev Tu-2 and Pe-8 bombers and the inline engine-powered LaGG-3 was adapted for the ASh-82 producing the famous Lavochkin La-5 fighter and its development, Lavochkin La-7, additionally the Lavochkin La-9 with i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratt & Whitney R-1830 Twin Wasp
The Pratt & Whitney R-1830 Twin Wasp is an American air-cooled radial aircraft engine. It displaces and its bore and stroke are both . The design traces its history to 1929 experiments at Pratt & Whitney on twin-row designs. Production began in 1932 and it was widely used during the 1930s. It was selected as the power plant for both the four-engined Consolidated B-24 Liberator heavy bomber and the twin-engined Douglas DC-3 transport, two of the most-produced aircraft. The production run of 173,618 R-1830 examples makes it the most-produced aviation engine in history. A further developed version, the R-2000, was produced starting in 1942. The R-2000 was "bored-out" to and had a number of other minor changes to improve fuel economy and allow it to run at higher power ratings on lower-octane fuel. The primary user of the R-2000 was the Douglas DC-4. Mostly retired today, the R-1830 is still used on Douglas DC-3 and various museum aircraft and warbirds seen at airshows. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakajima Sakae
The was a two-row, 14-cylinder air-cooled radial engine used in a number of combat aircraft of the Imperial Japanese Navy and Imperial Japanese Army before and during World War II. Design and development The engine was designed by Nakajima Aircraft Company with code name NAM, as a scaled-down and advanced version of the previous NAL design (Army Type 97 850 hp radial engine, Nakajima Ha5). The Imperial Japanese Army Air Force called the first of the series the Ha25 (ハ25) and later versions were designated Ha105 and Ha115, in the Hatsudoki designation system and Ha-35 in the unified designation system, while the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service designation was Nakajima NK1, with sub-types identified by Model numbers; thus Nakajima NK1 Sakae 10, 20 and 30 series. A total of 21,166 were made by Nakajima; 9,067 were manufactured by other firms. Variants ;Army Type 99 975 hp Air-cooled Radial :Long Army designation for the Nakajima NK1 radial engine named Sakae. ;Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitsubishi Kinsei
The was a 14-cylinder, air-cooled, twin-row radial aircraft engine developed by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries in Japan in 1934 for the Imperial Japanese Navy. The Mitsubishi model designation for this engine was A8 while it was an experimental project; in service, it was known as the MK8 "Kinsei" by the Navy. In 1941 the engine was adopted by Army, receiving designation Ha-112 (later Ha-112-I, 1,300hp Army Type 1). In May 1943 it received Ha-33 unified designation code. Design and development Early Kinsei models (1 and 2) had A4 internal designation and their cylinder and detail design was based on the single-row, 9-cylinder air-cooled Pratt and Whitney R-1690 Hornet. In 1933 engine underwent a major redesign and redesignated A8. Head layout was reversed to allow exhaust exit to the rear, reducing back-pressure and allowing for a cleaner installation. Compression ratio increased from 5.3:1 to 6.0:1. These changes resulted in a significant performance uplift, compared to pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnome-Rhône 14N
The Gnome-Rhône 14N was a 14-cylinder two-row air-cooled radial engine designed and manufactured by Gnome-Rhône just before the start of World War II. A development of the Gnome-Rhône 14K, the 14N was used on several French and even one German aircraft. Design and development The 14K's reliability was poor, so Gnome-Rhône carried out major redesign, using different materials for the pistons and valves, and enlarging the cooling fins to increase surface area by 39%. The 14N was introduced in 1937 and was quickly installed on several aircraft models. In 1939, minor improvements allowed Gnome-Rhône to increase the compression ratio from 6.1:1 to 6.8:1, which increased power. The 14N was further developed into the Gnome-Rhône 14R featuring a 2-stage supercharger, but this type was not widely used until after World War II as production of improved engines was restricted by the armistice with Germany. Variants ''Data from:''Aircraft engines of the World 1945, Aircraft engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiat A
Fiat Automobiles S.p.A. (, , ; originally FIAT, it, Fabbrica Italiana Automobili di Torino, lit=Italian Automobiles Factory of Turin) is an Italian automobile manufacturer, formerly part of Fiat Chrysler Automobiles, and since 2021 a subsidiary of Stellantis through its Italian division Stellantis Italy. Fiat Automobiles was formed in January 2007 when Fiat S.p.A. reorganized its automobile business, and traces its history back to 1899 when the first Fiat automobile, the Fiat 4 HP, was produced. Fiat Automobiles is the largest automobile manufacturer in Italy. During its more than century-long history, it remained the largest automobile manufacturer in Europe and the third in the world after General Motors and Ford for over 20 years, until the car industry crisis in the late 1980s. In 2013, Fiat S.p.A. was the second largest European automaker by volumes produced and the seventh in the world, while FCA was the world's eighth-largest automaker. In 1970, Fiat Automobiles employ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
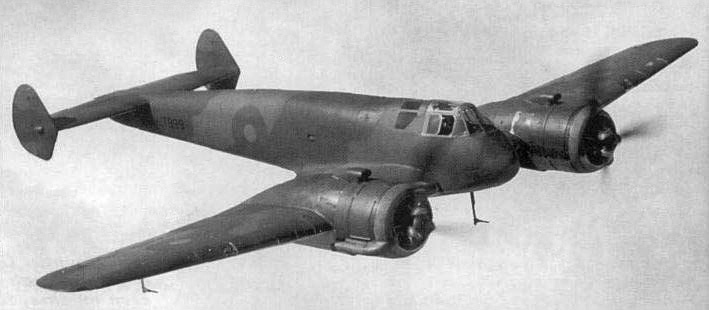
Bristol Taurus
The Taurus is a British 14-cylinder two-row radial aircraft engine, produced by the Bristol Engine Company starting in 1936. The Taurus was developed by adding cylinders to the existing single-row Aquila design and transforming it into a twin-row radial engine, creating a powerplant that produced just over 1,000 horsepower (750 kW) with very low weight. Design and development Bristol had originally intended to use the Aquila and Perseus as two of its major product lines in the 1930s, but the rapid increase in size and speed of aircraft in the 1930s demanded much larger engines than either of these. The mechanicals from both of these designs were then put into two-row configurations to develop much larger engines, the Aquila becoming the Taurus, and the Perseus becoming the Hercules. The Taurus was a sleeve valve design, resulting in an extraordinarily uncluttered exterior and very low mechanical noise. It offered high power with a relatively low weight, starting from 1,0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |