|
Mitsubishi Kinsei
The was a 14-cylinder, air-cooled, twin-row radial aircraft engine developed by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries in Japan in 1934 for the Imperial Japanese Navy. The Mitsubishi model designation for this engine was A8 while it was an experimental project; in service, it was known as the MK8 "Kinsei" by the Navy. In 1941 the engine was adopted by Army, receiving designation Ha-112 (later Ha-112-I, 1,300hp Army Type 1). In May 1943 it received Ha-33 unified designation code. Design and development Early Kinsei models (1 and 2) had A4 internal designation and their cylinder and detail design was based on the single-row, 9-cylinder air-cooled Pratt and Whitney R-1690 Hornet. In 1933 engine underwent a major redesign and redesignated A8. Head layout was reversed to allow exhaust exit to the rear, reducing back-pressure and allowing for a cleaner installation. Compression ratio increased from 5.3:1 to 6.0:1. These changes resulted in a significant performance uplift, compared to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Back Pressure
Back pressure (or backpressure) is a resistance or force opposing the desired flow of fluid through pipes, leading to friction loss and pressure drop. The term ''back pressure'' is a misnomer, as pressure is a scalar quantity, so it has a magnitude but no direction. The fluid is what is directed, tending to flow away from high-pressure regions and toward low-pressure regions. If the low-pressure space is more high-pressure than intended (e.g. due to obstructions or tight bends in an exhaust pipe) or the high-pressure space is more low-pressure than intended, this opposes the desired flow and reduces the discharge. Similarly, bending or other operations on a pipe (such as a stock car exhaust system with a particularly high number of twists and bends) can reduce flow rate. Explanation A common example of backpressure is that caused by the exhaust system (consisting of the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler and connecting pipes) of an automotive four-stroke engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawasaki Ki-96
The Kawasaki Ki-96 was a Japanese single seat, twin-engine heavy fighter of World War II. It was intended to replace the Kawasaki Ki-45s of the Imperial Japanese Army Air Service. However, it was not adopted and only three prototypes were built. Design and development The success of the Kawasaki Ki-45 led Kawasaki to start development of an evolved version, on Kawasaki's own authority, in August 1942. Like the Ki-45, the proposed design was a two-seat, twin-engine fighter, but larger and using more powerful engines. In December 1942 the ''Koku Hombu'' (Imperial Japanese Army Aviation Bureau) showed interest, but asked Kawasaki to complete the aircraft as single-seat fighters. The first prototype, which was converted while being produced and which retained the larger cockpit A cockpit or flight deck is the area, usually near the front of an aircraft or spacecraft, from which a Pilot in command, pilot controls the aircraft. The cockpit of an aircraft contains fligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawanishi N1K
The Kawanishi N1K ''Kyōfū'' (, "Strong Wind", Allied reporting name "Rex") is an Imperial Japanese Navy floatplane fighter. The Kawanishi N1K-J ''Shiden'' (, "Violet Lightning") was an Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service land-based version of the N1K. Assigned the reporting name "George", the N1K-J was considered by both its pilots and opponents to be one of the finest land-based fighters flown by the Japanese during World War II. The ''Shiden Kai'' possessed heavy armament, as well as surprisingly good maneuverability, due to a mercury switch that automatically extended the flaps during turns. These "combat" flaps created more lift, thereby allowing tighter turns. Unlike the Mitsubishi A6M Zero, the ''Shiden Kai'' could compete against the best late-war Allied fighters, such as the F6F Hellcat, F4U Corsair, and P-51 Mustang. Design and development Kawanishi's N1K was originally built as a single pontoon floatplane fighter to support forward offensive operations where no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawanishi H6K
The Kawanishi H6K was an Imperial Japanese Navy flying boat produced by the Kawanishi Aircraft Company and used during World War II for maritime patrol duties. The Allied reporting name for the type was Mavis; the Navy designation was . Design and development The aircraft was designed in response to a Navy requirement of 1934 for a long-range flying boat and incorporated knowledge gleaned by a Kawanishi team that visited the Short Brothers factory in the UK, at that time one of the world's leading producers of flying boats, and from building the Kawanishi H3K, a license-built, enlarged version of the Short Rangoon. The "Type S", as Kawanishi called it, was a large, four-engined monoplane with twin tails, and a hull suspended beneath the parasol wing by a network of struts. Three prototypes were constructed, each one making gradual refinements to the machine's handling both in the water and in the air, and finally fitting more powerful engines. The first of these flew on 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aichi M6A
The is a submarine-launched attack floatplane designed for the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II. It was intended to operate from I-400 class submarines whose original mission was to conduct aerial attacks against the United States. Design and development From the late 1920s, the Imperial Japanese Navy had developed a doctrine of operating floatplanes from submarines to search for targets.Layman and McLaughlin 1991, p. 176. In December 1941, Commander-in-Chief of the Japanese Combined Fleet, Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto, proposed constructing a large fleet of submarine aircraft carriers (also designated STo or ''sen-toku'' — special submarine) whose purpose was to mount aerial attacks against American coastal cities. The submarines would surface to launch their aircraft by catapult, submerge to avoid detection, then surface again to retrieve the aircrews who would ditch their planes nearby. By June 1942, the plan was to build a fleet of eighteen such submarines. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
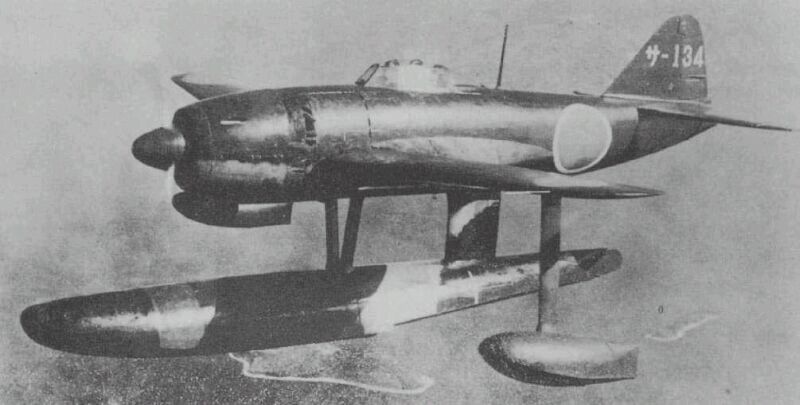
Aichi E16A
The Aichi E16A ''Zuiun'' (瑞雲 "Auspicious Cloud", Allied reporting name "Paul") was a two-seat reconnaissance seaplane operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II. Design and development The Aichi E16A originated from a 1939 specification for a replacement for the Aichi E13A, which at that time had yet to be accepted by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service (IJNAS).Francillon 1979, p. 284. Disagreements about the requirements in the 14-''Shi'' specification prevented most manufacturers from submitting designs, but in 1941 a new 16-''Shi'' specification was drafted by the IJNAS around the Aichi AM-22 design which had already been made by Aichi engineers Kishiro Matsuo and Yasuhiro Ozawa. The first AM-22, which first got the experimental designation Navy Experimental 16-Shi Reconnaissance Seaplane and later the short designation E16A1, was completed by May 1942 and was a conventional, low-wing monoplane equipped with two floats and had the unusual (for a seaplane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aichi E13A
The Aichi E13A ( Allied reporting name: "Jake") was a long-range reconnaissance seaplane used by the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) from 1941 to 1945. Numerically the most important floatplane of the IJN, it could carry a crew of three and a bombload of 250 kg (550 lb). The Navy designation was "Navy Type Zero Reconnaissance Seaplane" (零式水上偵察機). Operational history In China, it operated from seaplane tenders and cruisers. Later, it was used as a scout for the Attack on Pearl Harbor, and was encountered in combat by the United States Navy during the Battles of Coral Sea and Midway. It was in service throughout the conflict, for coastal patrols, strikes against navigation, liaison, officer transports, castaway rescues, and other missions, along with some ''kamikaze'' missions in the last days of war. One Aichi E13A was operated by Nazi Germany alongside two Arado Ar 196s out of the base at Penang. The three aircraft formed the East Asia Naval Special Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Pump (internal Combustion Engine)
The oil pump is an internal combustion engine part that circulates engine oil under pressure to the rotating bearings, the sliding pistons and the camshaft of the engine. This lubricates the bearings, allows the use of higher-capacity fluid bearings and also assists in cooling the engine. As well as its primary purpose for lubrication, pressurized oil is increasingly used as a hydraulic fluid to power small actuators. One of the first notable uses in this way was for hydraulic tappets in camshaft and valve actuation. Increasingly common recent uses may include the tensioner for a timing belt or variators for variable valve timing systems. Pumps The type of pump used varies. Gear pumps trochoid pumps and vane pumps are all commonly used. Plunger pumps have been used in the past, but these are now only used rarely, for small engines. To avoid the need for priming, the pump is always mounted low-down, either submerged or around the level of the oil in the sump. A sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Injection (engine)
In internal combustion engines, water injection, also known as anti-detonant injection (ADI), can spray water into the incoming air or fuel- air mixture, or directly into the combustion chamber to cool certain parts of the induction system where "hot points" could produce premature ignition. In jet engines it increases engine thrust at low speeds and at takeoff. Water injection was used historically to increase the power output of military aviation engines for short durations, such as dogfights or takeoff. However it has also been used in motor sports and notably in drag racing. In Otto cycle engines, the cooling effects of water injection also enables greater compression ratios by reducing engine knocking (detonation). Alternatively, this reduction in engine knocking in Otto cycle engines means that some applications gain significant performance when water injection is used in conjunction with a supercharger, turbocharger, or modifications such as aggressive ignition timing. Depe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronization Gear
A synchronization gear (also known as a gun synchronizer or interrupter gear) was a device enabling a single-engine tractor configuration aircraft to fire its forward-firing armament through the arc of its spinning propeller without bullets striking the blades. This allowed the aircraft, rather than the gun, to be aimed at the target. There were many practical problems, mostly arising from the inherently imprecise nature of an automatic gun's firing, the great (and varying) velocity of the blades of a spinning propeller, and the very high speed at which any gear synchronizing the two had to operate. In practice, all known gears worked on the principle of actively triggering each shot, in the manner of a semi-automatic weapon. Design and experimentation with gun synchronization had been underway in France and Germany in 1913–1914, following the ideas of August Euler, who seems to have been the first to suggest mounting a fixed armament firing in the direction of flight (in 191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. The current categorisation is that a turbocharger is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gasses, whereas a is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft). However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. History Prior to the invention of the turbocharger,[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


