|
Philoponus
John Philoponus (Greek: ; ; c. 490 – c. 570), also known as John the Grammarian or John of Alexandria, was a Byzantine Greek philologist, Aristotelian commentator, Christian theologian and an author of a considerable number of philosophical treatises and theological works. He was born in Alexandria. A rigorous, sometimes polemical writer and an original thinker who was controversial in his own time, John Philoponus broke from the Aristotelian–Neoplatonic tradition, questioning methodology and eventually leading to empiricism in the natural sciences. He was one of the first to propose a "theory of impetus" similar to the modern concept of inertia over Aristotelian dynamics. Later in life Philoponus turned to Christian apologetics, arguing against the eternity of the world, a theory which formed the basis of pagan attacks on the Christian doctrine of Creation. He also wrote on Christology and was posthumously condemned as a heretic by the Church in 680–81 because of what was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonius Hermiae
Ammonius Hermiae (; grc-gre, Ἀμμώνιος ὁ Ἑρμείου, Ammōnios ho Hermeiou, Ammonius, son of Hermias; – between 517 and 526) was a Greek philosopher from Alexandria in the eastern Roman empire during Late Antiquity. A Neoplatonist, he was the son of the philosophers Hermias and Aedesia, the brother of Heliodorus of Alexandria and the grandson of Syrianus. Ammonius was a pupil of Proclus in Roman Athens, and taught at Alexandria for most of his life, having obtained a public chair in the 470s. According to Olympiodorus of Thebes's ''Commentaries'' on Plato's ''Gorgias'' and ''Phaedo'' texts, Ammonius gave lectures on the works of Plato, Aristotle, and Porphyry of Tyre, and wrote commentaries on Aristotelian works and three lost commentaries on Platonic texts. He is also the author of a text on the astrolabe published in the ''Catalogus Codicum Astrologorum Graecorum'', and lectured on astronomy and geometry. Ammonius taught numerous Neoplatonists, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
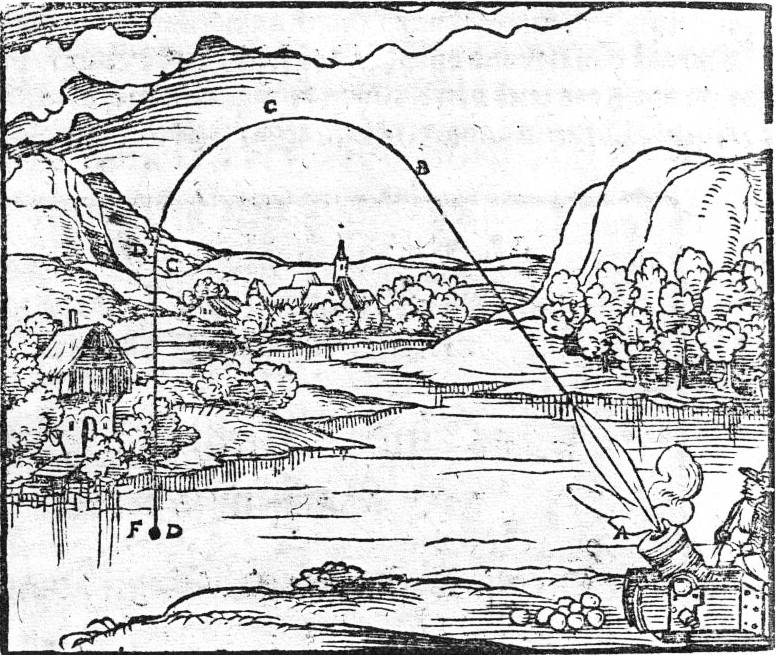
Theory Of Impetus
The theory of impetus was an auxiliary or secondary theory of Aristotelian dynamics, put forth initially to explain projectile motion against gravity. It was introduced by John Philoponus in the 6th century, and elaborated by Nur ad-Din al-Bitruji at the end of the 12th century. The theory was modified by Avicenna in the 11th century and Abu'l-Barakāt al-Baghdādī in the 12th century, before it was later established in Western scientific thought by Jean Buridan in the 14th century. It is the intellectual precursor to the concepts of inertia, momentum and acceleration in classical mechanics. Aristotelian theory Aristotelian physics is the form of Natural sciences, natural science described in the works of the Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher Aristotle (384–322 BC). In his work ''Physics (Aristotle), Physics'', Aristotle intended to establish general principles of change that govern all natural bodies, both living and inanimate, celestial and terrestrial – includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of philosophy within the Lyceum and the wider Aristotelian tradition. His writings cover many subjects including physics, biology, zoology, metaphysics, logic, ethics, aesthetics, poetry, theatre, music, rhetoric, psychology, linguistics, economics, politics, meteorology, geology, and government. Aristotle provided a complex synthesis of the various philosophies existing prior to him. It was above all from his teachings that the West inherited its intellectual lexicon, as well as problems and methods of inquiry. As a result, his philosophy has exerted a unique influence on almost every form of knowledge in the West and it continues to be a subject of contemporary philosophical discussion. Little is known about his life. Aristotle was born in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was born in the city of Pisa, then part of the Duchy of Florence. Galileo has been called the "father" of observational astronomy, modern physics, the scientific method, and modern science. Galileo studied speed and velocity, gravity and free fall, the principle of relativity, inertia, projectile motion and also worked in applied science and technology, describing the properties of pendulums and "hydrostatic balances". He invented the thermoscope and various military compasses, and used the telescope for scientific observations of celestial objects. His contributions to observational astronomy include telescopic confirmation of the phases of Venus, observation of the four largest satellites of Jupiter, observation of Saturn's rings, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Buridan
Jean Buridan (; Latin: ''Johannes Buridanus''; – ) was an influential 14th-century French people, French Philosophy, philosopher. Buridan was a teacher in the Faculty (division)#Faculty of Art, faculty of arts at the University of Paris for his entire career who focused in particular on logic and the works of Aristotle. Buridan sowed the seeds of the Copernican Revolution in Europe. He developed the concept of Theory of impetus, impetus, the first step toward the modern concept of inertia and an important development in the History of science in the Middle Ages, history of medieval science. His name is most familiar through the thought experiment known as Buridan's ass, but the thought experiment does not appear in his extant writings. Life Education and career Buridan was born sometime before 1301, perhaps at or near the town of Béthune in Picardy, France,Zupko 2015, §1 or perhaps elsewhere in the diocese of Arras. He received his education in Paris, first at the Collège d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Kindi
Abū Yūsuf Yaʻqūb ibn ʼIsḥāq aṣ-Ṣabbāḥ al-Kindī (; ar, أبو يوسف يعقوب بن إسحاق الصبّاح الكندي; la, Alkindus; c. 801–873 AD) was an Arab Muslim philosopher, polymath, mathematician, physician and music theorist. Al-Kindi was the first of the Islamic peripatetic philosophers, and is hailed as the "father of Arab philosophy". Al-Kindi was born in Kufa and educated in Baghdad. He became a prominent figure in the House of Wisdom, and a number of Abbasid Caliphs appointed him to oversee the translation of Greek scientific and philosophical texts into the Arabic language. This contact with "the philosophy of the ancients" (as Hellenistic philosophy was often referred to by Muslim scholars) had a profound effect on him, as he synthesized, adapted and promoted Hellenistic and Peripatetic philosophy in the Muslim world. He subsequently wrote hundreds of original treatises of his own on a range of subjects ranging from metaphysics, ethi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Of Mopsuestia
Theodore of Mopsuestia (c. 350 – 428) was a Christian theologian, and Bishop of Mopsuestia (as Theodore II) from 392 to 428 AD. He is also known as Theodore of Antioch, from the place of his birth and presbyterate. He is the best known representative of the middle Antioch School of hermeneutics. Life and work Theodore was born at Antioch, where his father held an official position and the family was wealthy (Chrysostom, ''ad Th. Laps.'' ii). Theodore's cousin, Paeanius, to whom several of John Chrysostom's letters are addressed, held an important post of civil government; his brother Polychronius became bishop of the metropolitan see of Apamea. Theodore first appears as the early companion and friend of Chrysostom, his fellow-townsman, his equal in rank, and but two or three years his senior in age. Together with their common friend Maximus, who was later bishop of Isaurian Seleucia, Chrysostom and Theodore attended the lectures of the Greek-speaking teacher of rhet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyry (philosopher)
Porphyry of Tyre (; grc-gre, Πορφύριος, ''Porphýrios''; ar, فُرْفُورِيُوس, ''Furfūriyūs''; – ) was a Neoplatonic philosopher born in Tyre, Roman Phoenicia during Roman rule. He edited and published ''The Enneads'', the only collection of the work of Plotinus, his teacher. His commentary on Euclid's ''Elements'' was used as a source by Pappus of Alexandria. He wrote original works in the Greek language on a wide variety of topics, ranging from music theory to Homer to vegetarianism. His ''Isagoge'', or ''Introduction'', an introduction to logic and philosophy, was the standard textbook on logic throughout the Middle Ages in its Latin and Arabic translations. Porphyry was, and still is, also well-known for his anti-Christian polemics. Through works such as ''Philosophy from Oracles'' and ''Against the Christians'' (which was banned by Constantine the Great), he was involved in a controversy with early Christians. Biography The ''Suda'' (a 10th- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severus Of Antioch
Severus the Great of Antioch (Greek: Σεβῆρος; syr, ܣܘܝܪܝܘܣ ܕܐܢܛܝܘܟܝܐ), also known as Severus of Gaza or Crown of Syrians (Syriac: ܬܓܐ ܕܣܘܪܝܥܝܐ; Tagha d'Suryoye; Arabic: تاج السوريين; Taj al-Suriyyun), was the Patriarch of Antioch, and head of the Syriac Orthodox Church, from 512 until his death in 538. He is venerated as a saint in the Oriental Orthodox Church, and his feast day is 8 February. Biography Early life and education Severus was born in the city of Sozopolis in Pisidia in c. 459,Barsoum (2003), p. 92 or c. 465, into an affluent Christian family, however, later Miaphysite sources would assert that his parents were pagan.Witakowski (2004), pp. 115-116 His father was a senator in the city,Chapman (1911) and his paternal grandfather, also named Severus, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commentaries On Aristotle
Commentaries on Aristotle refers to the great mass of literature produced, especially in the ancient and medieval world, to explain and clarify the works of Aristotle. The pupils of Aristotle were the first to comment on his writings, a tradition which was continued by the Peripatetic school throughout the Hellenistic period and the Roman era. The Neoplatonists of the late Roman empire wrote many commentaries on Aristotle, attempting to incorporate him into their philosophy. Although Ancient Greek commentaries are considered the most useful, commentaries continued to be written by the Christian scholars of the Byzantine Empire and by the many Islamic philosophers and Western scholastics who had inherited his texts. Greek commentators The first pupils of Aristotle commentated on his writings, but often with a view to expand his work. Thus Theophrastus invented five moods of syllogism in the first figure, in addition to the four invented by Aristotle, and stated with additional accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Pico Della Mirandola
Giovanni Pico della Mirandola (24 February 1463 – 17 November 1494) was an Italian Renaissance nobleman and philosopher. He is famed for the events of 1486, when, at the age of 23, he proposed to defend 900 theses on religion, philosophy, natural philosophy, and magic against all comers, for which he wrote the ''Oration on the Dignity of Man'', which has been called the "Manifesto of the Renaissance", and a key text of Renaissance humanism and of what has been called the "Hermetic Reformation". He was the founder of the tradition of Christian Kabbalah, a key tenet of early modern Western esotericism. The ''900 Theses'' was the first printed book to be universally banned by the Church.Hanegraaff p. 54 Pico is sometimes seen as a proto-Protestant, because his 900 theses anticipated many Protestant views. Biography Family Giovanni was born at Mirandola, near Modena, the youngest son of Gianfrancesco I Pico, Lord of Mirandola and Count of Concordia, by his wife Giulia, daugh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_-_BEIC_6329210.jpg)