|
Phenomenon (2006)
A phenomenon (: phenomena), sometimes spelled phaenomenon, is an observable event. The term came into its modern philosophical usage through Immanuel Kant, who contrasted it with the noumenon, which ''cannot'' be directly observed. Kant was heavily influenced by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz in this part of his philosophy, in which phenomenon and noumenon serve as interrelated technical terms. Far predating this, the ancient Greek Pyrrhonist philosopher Sextus Empiricus also used ''phenomenon'' and ''noumenon'' as interrelated technical terms. Common usage In popular usage, a ''phenomenon'' often refers to an extraordinary event. The term is most commonly used to refer to occurrences that at first defy explanation or baffle the observer. According to the ''Dictionary of Visual Discourse'':In ordinary language 'phenomenon/phenomena' refer to any occurrence worthy of note and investigation, typically an untoward or unusual event, person or fact that is of special significan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton's Cradle
The Newton's cradle is a device that demonstrates the conservation of momentum and the conservation of energy with swinging spheres. When one sphere at the end is lifted and released, it strikes the stationary spheres, transmitting a force through the stationary spheres that pushes the last sphere upward. The last sphere swings back and strikes the nearly stationary spheres, repeating the effect in the opposite direction. The device is named after 17th-century English scientist Sir Isaac Newton and designed by French scientist Edme Mariotte. It is also known as Newton's pendulum, Newton's balls, Newton's rocker or executive ball clicker (since the device makes a click each time the balls collide, which they do repeatedly in a steady rhythm). Operation When one of the end balls ("the first") is pulled sideways, the attached string makes it follow an upward arc. When it is let go, it strikes the second ball and comes to nearly a dead stop. The ball on the opposite side acquires mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motion (physics)
In physics, motion is the phenomenon in which an object changes its position with respect to time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed and frame of reference to an observer and measuring the change in position of the body relative to that frame with change in time. The branch of physics describing the motion of objects without reference to its cause is called kinematics, while the branch studying forces and their effect on motion is called dynamics. If an object is not changing relative to a given frame of reference, the object is said to be ''at rest'', ''motionless'', ''immobile'', '' stationary'', or to have a constant or time-invariant position with reference to its surroundings. Modern physics holds that, as there is no absolute frame of reference, Newton's concept of '' absolute motion'' cannot be determined. As such, everything in the universe can be considered to be in motion. Motion applies to various p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Equilibrium
In chemistry, a dynamic equilibrium exists once a reversible reaction occurs. Substances transition between the reactants and products at equal rates, meaning there is no net change. Reactants and products are formed at such a rate that the concentration of neither changes. It is a particular example of a system in a steady state. In physics, concerning thermodynamics, a closed system is in thermodynamic equilibrium when reactions occur at such rates that the composition of the mixture does not change with time. Reactions do in fact occur, sometimes vigorously, but to such an extent that changes in composition cannot be observed. Equilibrium constants can be expressed in terms of the rate constants for reversible reactions. Examples In a new bottle of soda, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the liquid phase has a particular value. If half of the liquid is poured out and the bottle is sealed, carbon dioxide will leave the liquid phase at an ever-decreasing rate, and the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Science
Natural science is one of the branches of science concerned with the description, understanding and prediction of natural phenomena, based on empirical evidence from observation and experimentation. Mechanisms such as peer review and repeatability of findings are used to try to ensure the validity of scientific advances. Natural science can be divided into two main branches: life science and physical science. Life science is alternatively known as biology, and physical science is subdivided into branches: physics, chemistry, earth science, and astronomy. These branches of natural science may be further divided into more specialized branches (also known as fields). As empirical sciences, natural sciences use tools from the formal sciences, such as mathematics and logic, converting information about nature into measurements which can be explained as clear statements of the " laws of nature". Modern natural science succeeded more classical approaches to natural philosophy, usu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pendulum
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting, equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward the equilibrium position. When released, the restoring force acting on the pendulum's mass causes it to oscillate about the equilibrium position, swinging back and forth. The time for one complete cycle, a left swing and a right swing, is called the period. The period depends on the length of the pendulum and also to a slight degree on the amplitude, the width of the pendulum's swing. From the first scientific investigations of the pendulum around 1602 by Galileo Galilei, the regular motion of pendulums was used for timekeeping and was the world's most accurate timekeeping technology until the 1930s. The pendulum clock invented by Christiaan Huygens in 1658 became the world's standard timekeeper, used in homes and offices for 270 years, and ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was born in the city of Pisa, then part of the Duchy of Florence. Galileo has been called the "father" of observational astronomy, modern physics, the scientific method, and modern science. Galileo studied speed and velocity, gravity and free fall, the principle of relativity, inertia, projectile motion and also worked in applied science and technology, describing the properties of pendulums and "hydrostatic balances". He invented the thermoscope and various military compasses, and used the telescope for scientific observations of celestial objects. His contributions to observational astronomy include telescopic confirmation of the phases of Venus, observation of the four largest satellites of Jupiter, observation of Saturn's rings, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Gravitation
Newton's law of universal gravitation is usually stated as that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.It was shown separately that separated spherically symmetrical masses attract and are attracted as if all their mass were concentrated at their centers. The publication of the law has become known as the " first great unification", as it marked the unification of the previously described phenomena of gravity on Earth with known astronomical behaviors. This is a general physical law derived from empirical observations by what Isaac Newton called inductive reasoning. It is a part of classical mechanics and was formulated in Newton's work '' Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica'' ("the ''Principia''"), first published on 5 July 1687. When Newton presented Book 1 of the unpublished text in April 1686 to the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
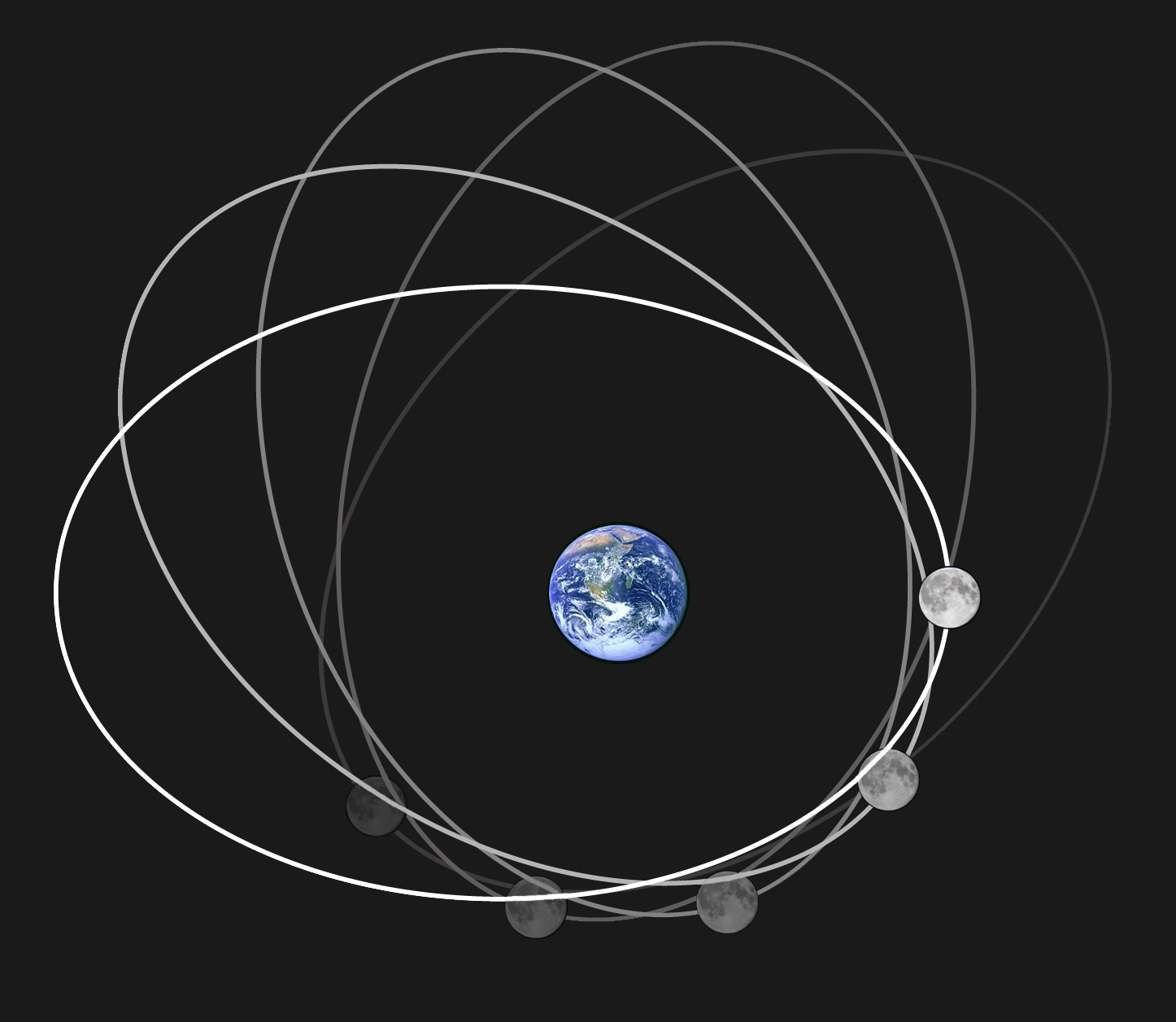
Orbit Of The Moon
The Moon orbits Earth in the prograde direction and completes one revolution relative to the Vernal Equinox and the stars in about 27.32 days (a tropical month and sidereal month) and one revolution relative to the Sun in about 29.53 days (a synodic month). Earth and the Moon orbit about their barycentre (common centre of mass), which lies about from Earth's centre (about 73% of its radius), forming a satellite system called the Earth–Moon system. On average, the distance to the Moon is about from Earth's centre, which corresponds to about 60 Earth radii or 1.282 light-seconds. With a mean orbital velocity of 1.022 km/s (0.635 miles/s, 2,286 miles/h), the Moon covers a distance approximately its diameter, or about half a degree on the celestial sphere, each hour. The Moon differs from most satellites of other planets in that its orbit is close to the ecliptic plane instead of to its primary's (in this case, Earth's) equatorial plane. The Moon's orbital plane is i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists and among the most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book (''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy''), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus. In the , Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint for centuries until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, account for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to compare the duration of events or the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change of quantities in material reality or in the conscious experience. Time is often referred to as a fourth dimension, along with three spatial dimensions. Time has long been an important subject of study in religion, philosophy, and science, but defining it in a manner applicable to all fields without circularity has consistently eluded scholars. Nevertheless, diverse fields such as business, industry, sports, the sciences, and the performing arts all incorporate some notion of time into their respective measuring systems. 108 pages. Time in physics is operationally defined as "what a clock reads". The physical nature of time is addre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |