|
Peranema
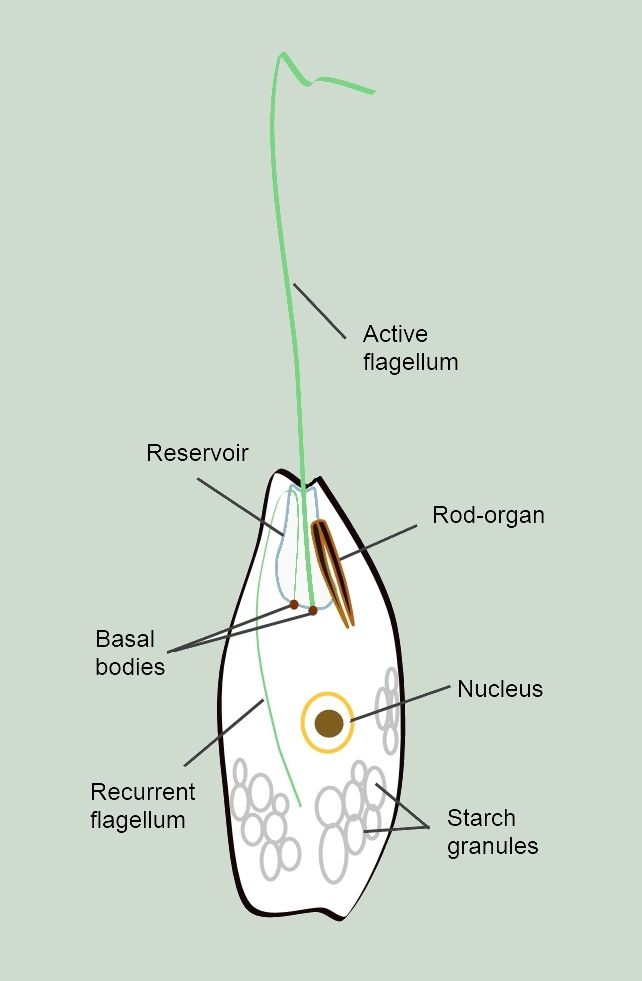
''Peranema'' is a genus of free-living phagotrophic euglenids (Euglenida; Euglenozoa; Excavata). There are more than 20 nominal species, varying in size between 8 and 200 micrometers. ''Peranema'' cells are gliding flagellates found in freshwater lakes, ponds and ditches, and are often abundant at the bottom of stagnant pools rich in decaying organic material. Although they belong to the class Euglenoidea, and are morphologically similar to the green ''Euglena'', ''Peranema'' have no chloroplasts, and do not conduct autotrophy. Instead, they capture live prey, such as yeast, bacteria and other flagellates, consuming them with the help of a rigid feeding apparatus called a "rod-organ." Unlike the green euglenids, they lack both an eyespot (stigma), and the paraflagellar body (photoreceptor) that is normally coupled with that organelle. However, while ''Peranema'' lack a localized photoreceptor, they do possess the light-sensitive protein rhodopsin, and respond to changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peranema Diagram 2
''Peranema'' is a genus of free-living phagotrophic euglenids (Euglenida; Euglenozoa; Excavata). There are more than 20 nominal species, varying in size between 8 and 200 micrometers. ''Peranema'' cells are gliding flagellates found in freshwater lakes, ponds and ditches, and are often abundant at the bottom of stagnant pools rich in decaying organic material. Although they belong to the class Euglenoidea, and are morphologically similar to the green ''Euglena'', ''Peranema'' have no chloroplasts, and do not conduct autotrophy. Instead, they capture live prey, such as yeast, bacteria and other flagellates, consuming them with the help of a rigid feeding apparatus called a "rod-organ." Unlike the green euglenids, they lack both an Eyespot apparatus, eyespot (stigma), and the Eyespot apparatus, paraflagellar body (photoreceptor) that is normally coupled with that organelle. However, while ''Peranema'' lack a localized photoreceptor, they do possess the light-sensitive protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euglenozoa
Euglenozoa are a large group of flagellate Discoba. They include a variety of common free-living species, as well as a few important parasites, some of which infect humans. Euglenozoa are represented by three major clades, i.e., Kinetoplastea, Diplonema and Symbiontida. Euglenozoa are unicellular, mostly around in size, although some euglenids get up to long. Structure Most euglenozoa have two flagella, which are inserted parallel to one another in an apical or subapical pocket. In some these are associated with a cytostome or mouth, used to ingest bacteria or other small organisms. This is supported by one of three sets of microtubules that arise from the flagellar bases; the other two support the dorsal and ventral surfaces of the cell. Some other euglenozoa feed through absorption, and many euglenids possess chloroplasts, the only eukaryotes outside Diaphoretickes to do so without performing kleptoplasty, and so obtain energy through photosynthesis. These chloroplasts are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euglenoidea
Euglenids (euglenoids, or euglenophytes, formally Euglenida/Euglenoida, ICZN, or Euglenophyceae, ICBN) are one of the best-known groups of flagellates, which are excavate eukaryotes of the phylum Euglenophyta and their cell structure is typical of that group. They are commonly found in freshwater, especially when it is rich in organic materials, with a few marine and endosymbiotic members. Many euglenids feed by phagocytosis, or strictly by diffusion. A monophyletic group consisting of the mixotrophic Rapaza viridis (1 species) and the two groups Eutreptiales (24 species) and Euglenales (983 species) have chloroplasts and produce their own food through photosynthesis. This group is known to contain the carbohydrate paramylon. Euglenids split from other Euglenozoa more than a billion years ago. The plastids in all extant photosynthetic species is the result from secondary endosymbiosis between a phagotrophic eukaryovorous euglenid and a Pyramimonas-related green alga. Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euglena
''Euglena'' is a genus of Unicellular organism, single cell flagellate eukaryotes. It is the best known and most widely studied member of the class Euglenoidea, a diverse group containing some 54 genera and at least 200 species. Species of ''Euglena'' are found in fresh water and salt water. They are often abundant in quiet inland waters where they may bloom in numbers sufficient to color the surface of ponds and ditches green (''E. viridis'') or red (''Euglena sanguinea, E. sanguinea''). The species ''Euglena gracilis'' has been used extensively in the laboratory as a model organism. Most species of ''Euglena'' have photosynthesizing chloroplasts within the body of the cell, which enable them to feed by autotrophy, like plants. However, they can also take nourishment heterotrophically, like animals. Since ''Euglena'' have features of both animals and plants, early taxonomists, working within the Linnaean taxonomy, Linnaean two-kingdom system of biological classificati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euglenales
Euglenids (euglenoids, or euglenophytes, formally Euglenida/Euglenoida, ICZN, or Euglenophyceae, ICBN) are one of the best-known groups of flagellates, which are excavate eukaryotes of the phylum Euglenophyta and their cell structure is typical of that group. They are commonly found in freshwater, especially when it is rich in organic materials, with a few marine and endosymbiotic members. Many euglenids feed by phagocytosis, or strictly by diffusion. A monophyletic group consisting of the mixotrophic Rapaza viridis (1 species) and the two groups Eutreptiales (24 species) and Euglenales (983 species) have chloroplasts and produce their own food through photosynthesis. This group is known to contain the carbohydrate paramylon. Euglenids split from other Euglenozoa more than a billion years ago. The plastids in all extant photosynthetic species is the result from secondary endosymbiosis between a phagotrophic eukaryovorous euglenid and a Pyramimonas-related green alga. Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euglenid
Euglenids (euglenoids, or euglenophytes, formally Euglenida/Euglenoida, ICZN, or Euglenophyceae, ICBN) are one of the best-known groups of flagellates, which are excavate eukaryotes of the phylum Euglenophyta and their cell structure is typical of that group. They are commonly found in freshwater, especially when it is rich in organic materials, with a few marine and endosymbiotic members. Many euglenids feed by phagocytosis, or strictly by diffusion. A monophyletic group consisting of the mixotrophic Rapaza viridis (1 species) and the two groups Eutreptiales (24 species) and Euglenales (983 species) have chloroplasts and produce their own food through photosynthesis. This group is known to contain the carbohydrate paramylon. Euglenids split from other Euglenozoa more than a billion years ago. The plastids in all extant photosynthetic species is the result from secondary endosymbiosis between a phagotrophic eukaryovorous euglenid and a Pyramimonas-related green alga. Structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Klebs
Georg Albrecht Klebs (23 October 1857 – 15 October 1918) was a German botanist from Neidenburg (Nidzica), Prussia. His brother was the historian Elimar Klebs. Life Klebs studied chemistry, philosophy, and art history at the University of Königsberg and became an assistant to Anton de Bary at the University of Strassburg. After his military service, Klebs became an assistant to Julius Sachs at the University of Würzburg and Wilhelm Pfeffer at the University of Tübingen. He became a professor at the University of Basel in 1887, the University of Halle in 1898, and the University of Heidelberg in 1907, where he founded today's botanical garden, the Botanischer Garten der Universität Heidelberg. Klebs received a Croonian Lectureship in 1910. From 1910 to 1912 he travelled through Siberia, Japan, Java, India, the Caucasus, and southern Russia. In 1913 he participated in an expedition to Egypt. He died in Heidelberg from influenza during the 1918 influenza pandemic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astasia
Astasis is a lack of motor coordination marked by an inability to stand, walk or even sit without assistance due to disruption of muscle coordination. The term ''astasia'' is interchangeable with ''astasis'' and is most commonly referred to as ''astasia'' in the literature describing it. Astasis is the inability to stand or sit up without assistance in the absence of motor weakness or sensory loss (although the inclusion of 'the lack of motor weakness' has been debated by some physicians). It is categorized more as a symptom than an actual disease, as it describes a disruption of muscle coordination resulting in this deficit. The disturbance differs from cerebellar ataxia in that with astasis the gait can be relatively normal, with balance significantly impaired during transition from a seated to standing position. This balance impairment is similar to patients with vestibulocerebellar syndrome, which is a progressive neurological disease with many symptoms and effects. Astasis ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Code Of Zoological Nomenclature
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is a widely accepted convention in zoology that rules the formal scientific naming of organisms treated as animals. It is also informally known as the ICZN Code, for its publisher, the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (which shares the acronym "ICZN"). The rules principally regulate: * How names are correctly established in the frame of binominal nomenclature * Which name must be used in case of name conflicts * How scientific literature must cite names Zoological nomenclature is independent of other systems of nomenclature, for example botanical nomenclature. This implies that animals can have the same generic names as plants (e.g. there is a genus ''Abronia'' in both animals and plants). The rules and recommendations have one fundamental aim: to provide the maximum universality and continuity in the naming of all animals, except where taxonomic judgment dictates otherwise. The code is meant to guid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoplasm
Protoplasm (; ) is the living part of a cell that is surrounded by a plasma membrane. It is a mixture of small molecules such as ions, monosaccharides, amino acid, and macromolecules such as proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, etc. In some definitions, it is a general term for the cytoplasm (e.g., Mohl, 1846), but for others, it also includes the nucleoplasm (e.g., Strasburger, 1882). For Sharp (1921), "According to the older usage the extra-nuclear portion of the protoplast 'the entire cell, excluding the cell wall''was called "protoplasm," but the nucleus also is composed of protoplasm, or living substance in its broader sense. The current consensus is to avoid this ambiguity by employing Strasburger's '(1882)''terms cytoplasm Albert_von_Kölliker.html"_;"title="'coined_by_Albert_von_Kölliker">Kölliker_(1863),_originally_as_synonym_for_protoplasm''and_nucleoplasm_([''term_coined_by_Edouard_Van_Beneden.html" ;"title="Albert von Kölliker">Kölliker (1863), originally as syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytopharynx
A cytostome (from ''cyto-'', cell and ''stome-'', mouth) or cell mouth is a part of a cell specialized for phagocytosis, usually in the form of a microtubule-supported funnel or groove. Food is directed into the cytostome, and sealed into vacuoles. Only certain groups of protozoa, such as the Ciliophora and Excavata, have cytostomes. An example is ''Balantidium coli'', a ciliate. In other protozoa, and in cells from multicellular organisms, phagocytosis takes place at any point on the cell or feeding takes place by absorption. Structure The cytostome forms an invagination on the cell surface and is typically directed towards the nucleus of the cell.Okuda, Kendi, et al. "The cytostome of Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes is associated with the flagellar complex." Experimental parasitology 92.4 (1999): 223-231. The cytostome is often labeled as the entire invagination, but in fact the cytostome only constitutes the opening of the invagination at the surface of the cell. The rest o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |