|
Pension Belhomme
The Pension Belhomme was a prison and private clinic during the French Revolution in the Rue de Charonne ( 11e arrondissement, Paris). Around 1765, the joiner Jacques Belhomme took on the construction of a building for the son of a neighbour, an aristocrat who had been mad since birth. Seeing that running an asylum was more lucrative than joinery, he opened an asylum for lunatics, old people and whoever else rich families wanted to entrust to him. A famous precursor of psychiatry, Philippe Pinel, carried out his first treatments of the insane here. Once the French Revolution had begun, Jacques Belhomme thought that his fortune was assured. Remote from the violent centre of Paris, he had noticeable advantages. In September 1793, when the Reign of Terror began, the députés encouraged the sans-culottes to imprison all suspect individuals: nobles, their wives and children, foreigners, priests, lawyers, the actors of the Comédie Française, rich people in general, in short, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquis De Sade
Donatien Alphonse François, Marquis de Sade (; 2 June 1740 – 2 December 1814), was a French nobleman, revolutionary politician, philosopher and writer famous for his literary depictions of a libertine sexuality as well as numerous accusations of sex crimes. His works include novels, short stories, plays, dialogues, and political tracts. In his lifetime some of these were published under his own name while others, which Sade denied having written, appeared anonymously. Sade is best known for his erotic works, which combined philosophical discourse with pornography, depicting sexual fantasies with an emphasis on violence, suffering, anal sex (which he calls sodomy), child rape, crime, and blasphemy against Christianity. Many of the characters in his works are teenagers or adolescents. His work is a depiction of extreme absolute freedom, unrestrained by morality, religion, or law. The words ''sadism'' and '' sadist'' are derived from his name in reference to the works of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Demolished In 1973
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commercial Buildings Completed In 1765
Commercial may refer to: * a dose of advertising conveyed through media (such as - for example - radio or television) ** Radio advertisement ** Television advertisement * (adjective for:) commerce, a system of voluntary exchange of products and services ** (adjective for:) trade, the trading of something of economic value such as goods, services, information or money * Two functional constituencies in elections for the Legislative Council of Hong Kong: **Commercial (First) **Commercial (Second) * ''Commercial'' (album), a 2009 album by Los Amigos Invisibles * Commercial broadcasting * Commercial style or early Chicago school, an American architectural style * Commercial Drive, Vancouver, a road in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada * Commercial Township, New Jersey, in Cumberland County, New Jersey See also * * Comercial (other), Spanish and Portuguese word for the same thing * Commercialism Commercialism is the application of both manufacturing and consumption towar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economist Intelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
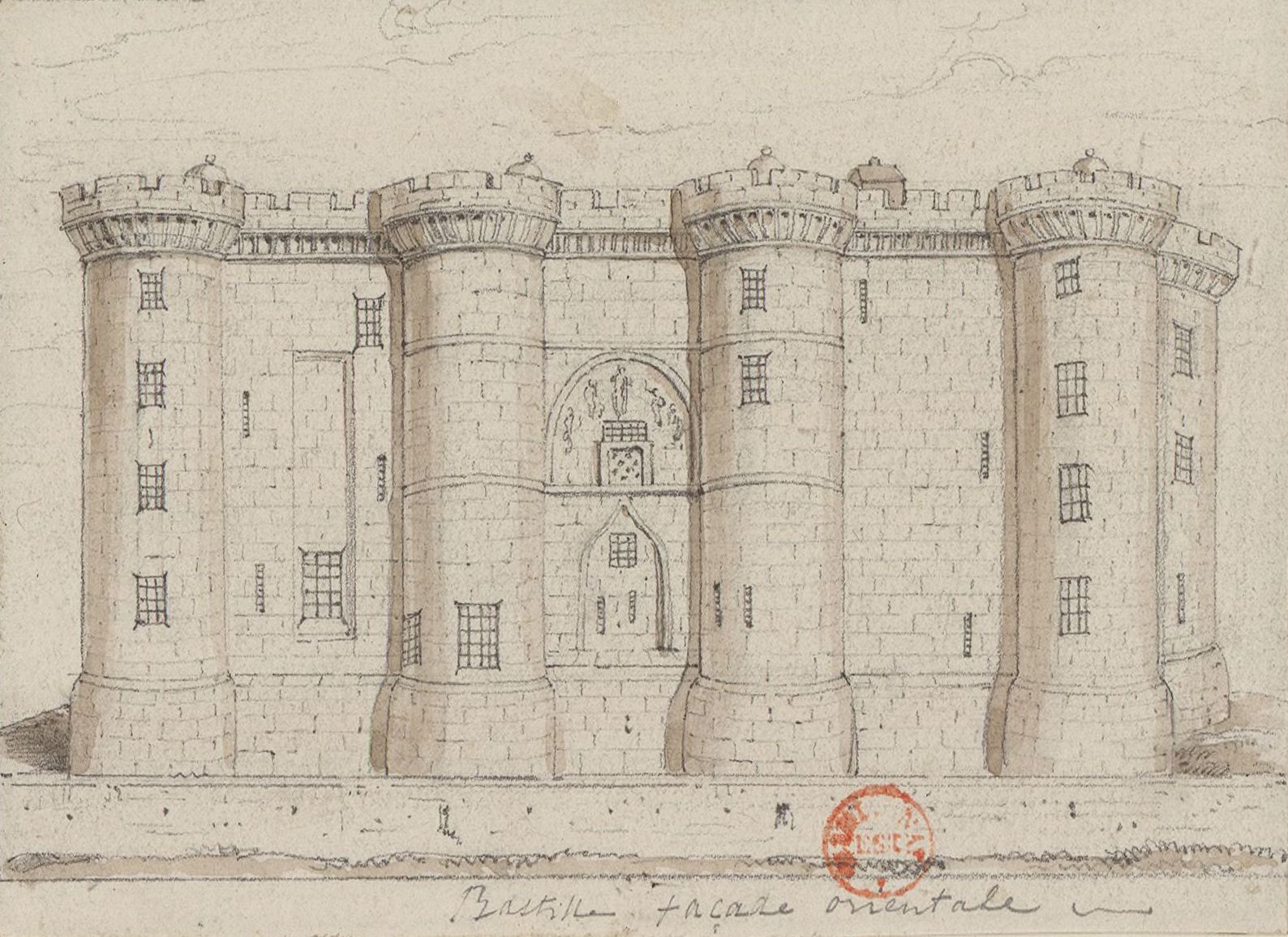
Bastille
The Bastille (, ) was a fortress in Paris, known formally as the Bastille Saint-Antoine. It played an important role in the internal conflicts of France and for most of its history was used as a state prison by the kings of France. It was stormed by a crowd on 14 July 1789, in the French Revolution, becoming an important symbol for the French Republican movement. It was later demolished and replaced by the Place de la Bastille. The castle was built to defend the eastern approach to the city from potential English attacks during the Hundred Years' War. Construction was underway by 1357, but the main construction occurred from 1370 onwards, creating a strong fortress with eight towers that protected the strategic gateway of the Porte Saint-Antoine heading out to the east. The innovative design proved influential in both France and England and was widely copied. The Bastille figured prominently in France's domestic conflicts, including the fighting between the rival factions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon-Nicholas Henri Linguet
Simon-Nicholas Henri Linguet (14 July 1736 – 27 June 1794) was a French journalist and advocate known for his conservative politics who was executed during the French Revolution. Biography Linguet was born in Reims, where his father, the assistant principal in the Collège de Beauvais of Paris, had recently been exiled by lettre de cachet for engaging in the Jansenist controversy. He attended the College de Beauvais and won the three highest prizes there in 1751. He accompanied the count palatine of Zweibrücken to Poland, and on his return to Paris he devoted himself to writing. He published partial French translations of Pedro Calderón de la Barca and Lope de Vega, and wrote parodies for the Opéra-Comique and pamphlets in favor of the Jesuits. Received at first in the ranks of the Philosophes, he soon went over to their opponents, possibly more from contempt than from conviction, the immediate occasion for his change being a quarrel with Jean le Rond d'Alembert in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Magon De La Balue
Jean-Baptiste is a male French name, originating with Saint John the Baptist, and sometimes shortened to Baptiste. The name may refer to any of the following: Persons * Charles XIV John of Sweden, born Jean-Baptiste Jules Bernadotte, was King of Sweden and King of Norway * Charles-Jean-Baptiste Bouc, businessman and political figure in Lower Canada * Felix-Jean-Baptiste-Joseph Nève, orientalist and philologist * Gui-Jean-Baptiste Target, French lawyer and politician * Hippolyte Jean-Baptiste Garneray, French painter * Jean-Baptiste (songwriter), American music record producer, singer-songwriter * Jean-Baptiste Alphonse Karr, French critic, journalist, and novelist * Jean-Baptiste Bagaza, chairman of Supreme Revolutionary Council in Burundi until 1976 and president of Burundi (1976-1987) * Jean-Baptiste Baudry, son of Guillaume Baudry, Canadian gunsmith bevear goldsmith * Jean-Baptiste Benoît Eyriès, French geographer, author and translator * Jean-Baptiste Bessières, duke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L'Anglaise Et Le Duc
''The Lady and the Duke'' (french: L'Anglaise et le Duc, lit=The Englishwoman and the Duke) is a 2001 historical romantic drama film written and directed by Éric Rohmer, based on the memoirs ''Ma vie sous la révolution'' (''Journal of My Life During the French Revolution'') by Grace Elliott Grace Dalrymple Elliott (c. 1754 – 16 May 1823) was a Scottish courtesan, writer and spy resident in Paris during the French Revolution. She was an eyewitness to events detailed in her memoirs, ''Journal of my life during the French Revo ..., a Scottish royalist caught up in the political intrigue following the French Revolution. According to a description of the film in '' The Guardian'', Rohmer's "customary verbal sparring and complex intellectual arguments are spiced by lavish sets, suspenseful plotting and the continuous threat of violence." Cast Reception The film was criticised by many viewers in France because of its uncompromising presentation of revolutionary violen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Éric Rohmer
Jean Marie Maurice Schérer or Maurice Henri Joseph Schérer, known as Éric Rohmer (; 21 March 192011 January 2010), was a French film director, film critic, journalist, novelist, screenwriter, and teacher. Rohmer was the last of the post-World War II French New Wave directors to become established. He edited the influential film journal ''Cahiers du cinéma'' from 1957 to 1963, while most of his colleagues—among them Jean-Luc Godard and François Truffaut—were making the transition from critics to filmmakers and gaining international attention. Rohmer gained international acclaim around 1969 when his film ''My Night at Maud's'' was nominated at the Academy Awards. He won the San Sebastián International Film Festival with ''Claire's Knee'' in 1971 and the Golden Lion at the Venice Film Festival for '' The Green Ray'' in 1986. Rohmer went on to receive the Venice Film Festival's Career Golden Lion in 2001. After Rohmer's death in 2010, his obituary in ''The Daily Telegrap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778) was a French Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment writer, historian, and philosopher. Known by his ''Pen name, nom de plume'' M. de Voltaire (; also ; ), he was famous for his wit, and his criticism of Christianity—especially Criticism of the Catholic Church, of the Roman Catholic Church—and of slavery. Voltaire was an advocate of freedom of speech, freedom of religion, and separation of church and state. Voltaire was a versatile and prolific writer, producing works in almost every literary form, including stageplay, plays, poems, novels, essays, histories, and scientific Exposition (narrative), expositions. He wrote more than 20,000 letters and 2,000 books and pamphlets. Voltaire was one of the first authors to become renowned and commercially successful internationally. He was an outspoken advocate of civil liberties and was at constant risk from the strict censorship laws of the Catholic French monarchy. His polemics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |