|
Paṭṭiṉappālai
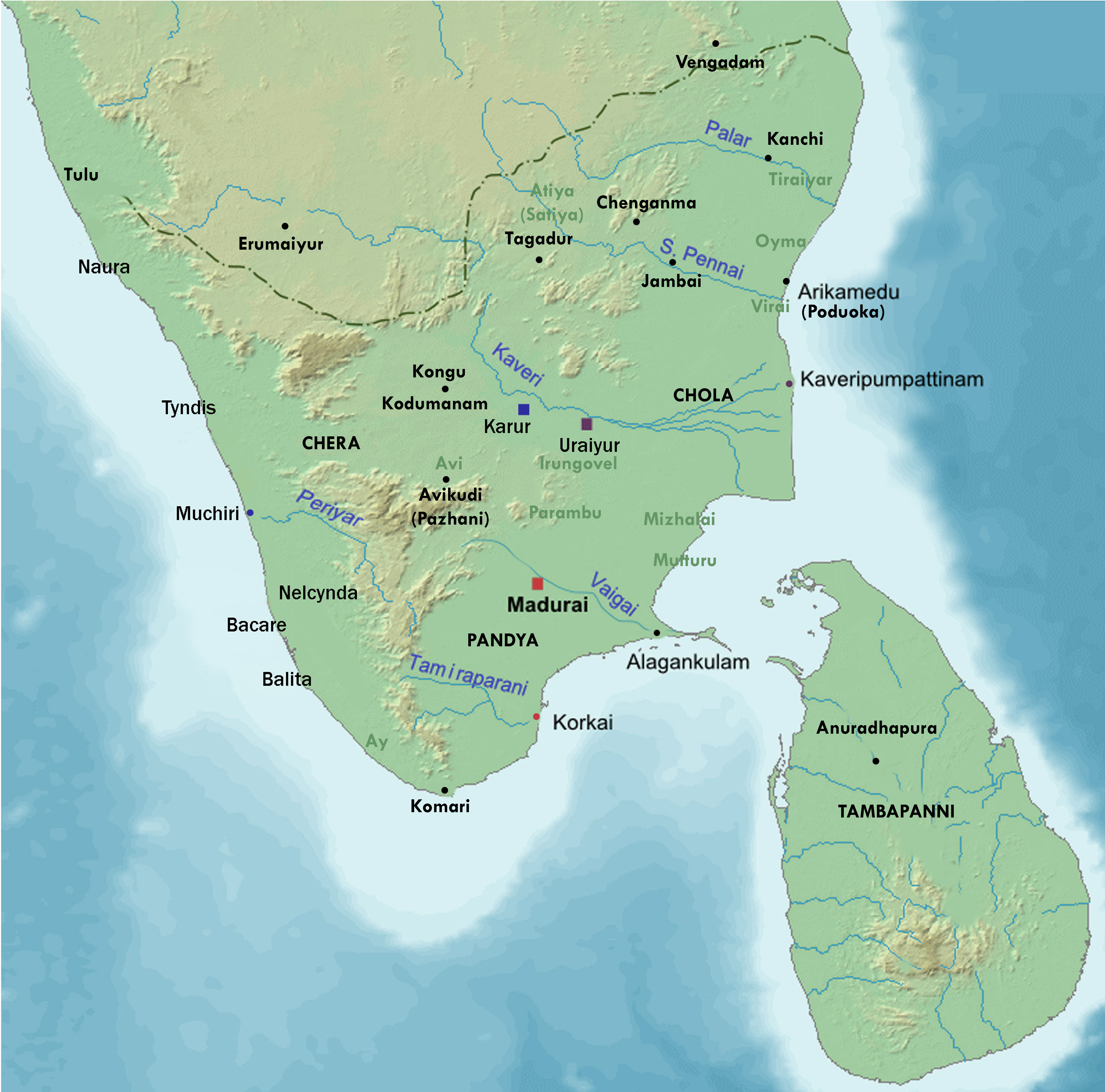
__NOTOC__ ''Paṭṭiṉappālai'' ( ta, பட்டினப் பாலை) is a Tamil poem in the ancient Sangam literature. It contains 301 lines, of which 296 lines are about the port city of Kaveripoompattinam, the early Chola kingdom and the Chola king Karikalan. The remaining 5 lines are on the proposed separation by a man who wants to move there and the separation pain of his wife who would miss her husband's love. Of the 301 lines, 153 are in the ''vanci'' meter and the rest are in ''akaval''. It is sometimes referred to as ''Vancinetumpattu'', or the "long song in the vanci meter". The poem was composed by Katiyalur Uruttirankannanar, sometime around 1st century and 2nd century CE, states Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature scholar. The title ''Pattinappalai'' is combination of two words, ''pattinam'' (city) and ''palai'' (desert, metonymically "separation, love division"). The poem has a lengthy initial section on the harbor capital city of the ancient Cholas, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karikalan
Karikala ( ta, கரிகால சோழன்) was a Tamils, Tamil Chola dynasty, Chola Emperor who ruled southern India. He is credited with the construction of the flood banks of the Kaveri, river Kaveri. He is recognised as the greatest of the Early Cholas. Sources The story of Karikala is mixed with legend and anecdotal information gleaned from Sangam literature. The only sources available are the numerous mentions in Sangam poetry. The period covered by the extant literature of the Sangam is unfortunately not easy to determine with any measure of certainty. ''Paṭṭiṉappālai'', ''Poruṇarāṟṟuppaṭai'' and a number of individual poems in the ''Akanaṉūṟu'' and ''Purananuru'' have been the main source for the information that is attributed to Karikala. No authentic records of Karikala's reign have been found so far. However many rulers and petty chiefs who came after him claimed him as their ancestor and decorated themselves as belonging to the ''Cho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kadiyalur Uruttirangannanar
Kadiyalur Uruttirangannanar (3rd/4th century CE) was a Tamil poet of the Sangam period. He is credited with the composition of the ''Paṭṭiṉappālai'' and the ''Perumpāṇāṟṟuppaṭai'' in the '' Pattuppāṭṭu'' anthology and song 167 of the ''Akanaṉūṟu'' and 352 of the ''Kuṟuntokai''. According to P. T. Srinivasa Iyengar, he lived between the late 3rd and early 4th centuries CE and was a contemporary of the king of Kanchipuram Ilandiraiyan. Biography Uruttirangannanar was born in a Brahmin family in the village of Kadiyalur in the present-day Vellore district. See also * Sangam literature * List of Sangam poets Sangam refers to the assembly of the highly learned people of the ancient Tamil land, with the primary aim of advancing the literature. There were historically three Sangams. With the details of the first two Sangams remaining obscure, all the ... References * {{Authority control Tamil poets Sangam literature Tamil-language li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kedah
Kedah (), also known by its honorific Darul Aman and historically as Queda, is a state of Malaysia, located in the northwestern part of Peninsular Malaysia. The state covers a total area of over 9,000 km2, and it consists of the mainland and the Langkawi islands. The mainland has a relatively flat terrain, which is used to grow rice, while Langkawi is an archipelago, most of which are uninhabited islands. Kedah was previously known as Kadaram (; ') by the ancient and medieval Tamils, Kataha or Kalahbar (; ' or ; ') by the Arabs, and '' Syburi'' ( th, ไทรบุรี; ) by the Siamese when it was under their influence. To the north, Kedah borders the state of Perlis and shares an international boundary with the Songkhla and Yala provinces of Thailand. It borders the states of Perak to the south and Penang to the southwest. The state's capital is Alor Setar and the royal seat is in Anak Bukit. Other major towns include Sungai Petani (its largest urban area by pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Language
Tamil (; ' , ) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is an official language of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, the sovereign nations of Sri Lanka and Singapore, and the Indian territory of Puducherry. Tamil is also spoken by significant minorities in the four other South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is also spoken by the Tamil diaspora found in many countries, including Malaysia, Myanmar, South Africa, United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia and Mauritius. Tamil is also natively spoken by Sri Lankan Moors. One of 22 scheduled languages in the Constitution of India, Tamil was the first to be classified as a classical language of India. Tamil is one of the longest-surviving classical languages of India.. "Tamil is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India" (p. 7). A. K. Ramanujan described it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sangam Literature
The Sangam literature (Tamil: சங்க இலக்கியம், ''caṅka ilakkiyam'';) historically known as 'the poetry of the noble ones' (Tamil: சான்றோர் செய்யுள், ''Cāṉṟōr ceyyuḷ'') connotes the ancient Tamil literature and is the earliest known literature of South India. The Tamil tradition and legends link it to three literary gatherings around Madurai and Kapāṭapuram ( Pandyan capitals): the first over 4,440 years, the second over 3,700 years, and the third over 1,850 years before the start of the common era. Scholars consider this Tamil tradition-based chronology as ahistorical and mythical. Most scholars suggest the historical Sangam literature era spanned from c. 300 BCE to 300 CE, while others variously place this early classical Tamil literature period a bit later and more narrowly but all before 300 CE. According to Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature and history scholar, the most acceptable range for the Sangam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puhar, Mayiladuthurai
Puhar (also known as Poompuhar) is a town in the Mayiladuthurai district in the southern Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It was once a flourishing ancient port city known as Kaveri Poompattinam, which is described in Sangam literature like Silappadikaram, Manimekalai, Pattinapalai and Akananuru as the capital of the Early Chola kings in Tamilakam. Puhar is located near the mouth of the Kaveri river, on the sea coast. It is mentioned in the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea. It has now been established by marine archaeological research (conducted by the National institute of marine archaeology, Goa) that much of the town was washed away by progressive erosion and floods. In the 1960s and 1970s, archaeological research was conducted under the leadership of the noted archaeologist K. V. Soundararajan. Submerged wharves and several meter lengths of pier walls excavated in recent times have corroborated the literary references to Poompuhar. It was rebuilt several times after that. Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cholas
The Early Cholas were a Tamil kingdom of the pre and post Sangam period (600 BCE–300 CE). It was one of the three main kingdoms of South India. Their early capitals were Urayur or Tiruchirapalli and Kaveripattinam. Along with Pandyas and Cheras, Chola history goes back to the period when written records were scarce. Sources Ancient Tamil Nadu contained three monarchical states, headed by kings called ''Vendhar'' and several chieftaincies, headed by the chiefs called by the general denomination ''Vel'' or '' Velir''. Still lower at the local level there were clan chiefs called ''kizhar'' or ''mannar''. The Tamil area had an independent existence outside the control of these northern empires. The Tamil kings and chiefs were always in conflict with each other mostly over property. The royal courts were mostly places of social gathering rather than places of dispensation of authority; they were centres for distribution of resources. The names of the three dynasties, Cholas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Tamilakam Ports
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puhar, Nagapattinam
Puhar (also known as Poompuhar) is a town in the Mayiladuthurai district in the southern Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It was once a flourishing ancient port city known as Kaveri Poompattinam, which is described in Sangam literature like Silappadikaram, Manimekalai, Pattinapalai and Akananuru as the capital of the Early Chola kings in Tamilakam. Puhar is located near the mouth of the Kaveri river, on the sea coast. It is mentioned in the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea. It has now been established by marine archaeological research (conducted by the National institute of marine archaeology, Goa) that much of the town was washed away by progressive erosion and floods. In the 1960s and 1970s, archaeological research was conducted under the leadership of the noted archaeologist K. V. Soundararajan. Submerged wharves and several meter lengths of pier walls excavated in recent times have corroborated the literary references to Poompuhar. It was rebuilt several times after that. Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veda
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''. The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit literature and the oldest scriptures of Hinduism. There are four Vedas: the Rigveda, the Yajurveda, the Samaveda and the Atharvaveda. Each Veda has four subdivisions – the Samhitas (mantras and benedictions), the Aranyakas (text on rituals, ceremonies, sacrifices and symbolic-sacrifices), the Brahmanas (commentaries on rituals, ceremonies and sacrifices), and the Upanishads (texts discussing meditation, philosophy and spiritual knowledge).Gavin Flood (1996), ''An Introduction to Hinduism'', Cambridge University Press, , pp. 35–39A Bhattacharya (2006), ''Hindu Dharma: Introduction to Scriptures and Theology'', , pp. 8–14; George M. Williams (2003), Handbook of Hindu Mythology, Oxford University Press, , p. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murugan
Kartikeya ( sa, कार्त्तिकेय, Kārttikeya), also known as Skanda, Subrahmanya, Shanmukha (), and Murugan ( ta, முருகன்), is the Hindu god of war. He is the son of Parvati and Shiva, the brother of Ganesha and a god whose legends have many versions in Hinduism. Kartikeya has been an important deity in the Indian subcontinent since ancient times, worshipped as Mahasena and Kumara in North India and is predominantly worshipped in the state of Tamil Nadu and other parts of South India, Sri Lanka, Singapore, and Malaysia as Murugan. Murugan is widely regarded as the "God of the Tamil people". It has been postulated that the Tamil deity of Murugan was syncretised with the Vedic deity of Subrahmanya following the Sangam era. Both Muruga and Subrahmanya refer to Kartikeya. The iconography of Kartikeya varies significantly; he is typically represented as an ever-youthful man, riding or near an Indian peafowl, called Paravani, bearing a vel and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hero Stone
A hero stone (Vīragallu in Kannada, Naṭukal in Tamil) is a memorial commemorating the honorable death of a hero in battle. Erected between the second half of the first millennium BC and the 18th century AD, hero stones are found all over India. They often carry inscriptions and a variety of ornaments, including bas relief panels, frieze, and figures in carved stone. Usually they are in the form of a stone monument and may have an inscription at the bottom with a narrative of the battle. The earliest and oldest of such memorial Hero stones is found in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu is more than 2400 years old that is 4th Century BC. According to the historian Upinder Singh, the largest concentration of such memorial stones is found in the Indian state of Karnataka. About two thousand six hundred and fifty hero stones, the earliest in Karnataka is dated to the 5th century AD.Chapter "Memorializing death in stone", Singh (2009), p48 The custom of erecting memorial stones dates b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |