|
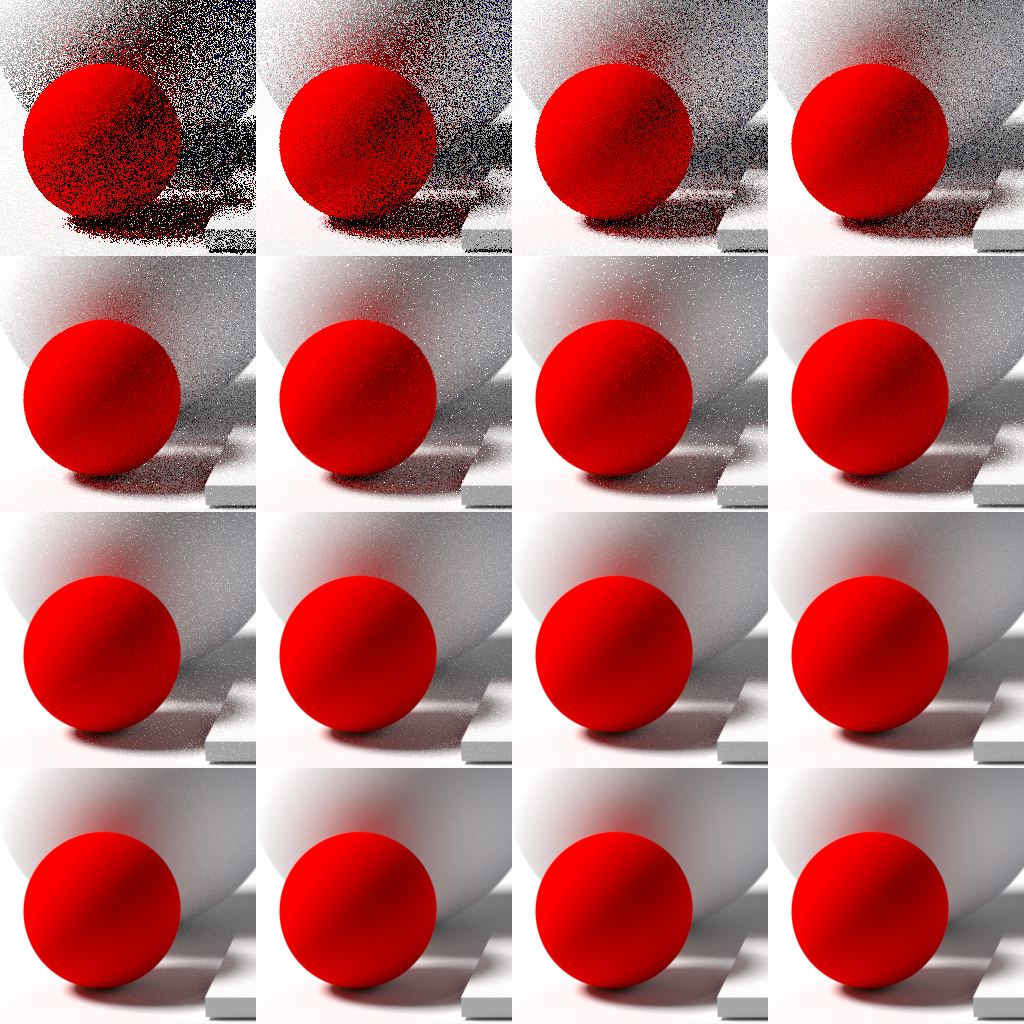
Path Tracing
Path tracing is a computer graphics Monte Carlo method of rendering images of three-dimensional scenes such that the global illumination is faithful to reality. Fundamentally, the algorithm is integrating over all the illuminance arriving to a single point on the surface of an object. This illuminance is then reduced by a surface reflectance function (BRDF) to determine how much of it will go towards the viewpoint camera. This integration procedure is repeated for every pixel in the output image. When combined with physically accurate models of surfaces, accurate models of real light sources (light bulbs), and optically correct cameras, path tracing can produce still images that are indistinguishable from photographs. Path tracing naturally simulates many effects that have to be specifically added to other methods (conventional ray tracing or scanline rendering), such as soft shadows, depth of field, motion blur, caustics, ambient occlusion, and indirect lighting. Implementa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Path Tracing
Path tracing is a computer graphics Monte Carlo method of rendering images of three-dimensional scenes such that the global illumination is faithful to reality. Fundamentally, the algorithm is integrating over all the illuminance arriving to a single point on the surface of an object. This illuminance is then reduced by a surface reflectance function (BRDF) to determine how much of it will go towards the viewpoint camera. This integration procedure is repeated for every pixel in the output image. When combined with physically accurate models of surfaces, accurate models of real light sources (light bulbs), and optically correct cameras, path tracing can produce still images that are indistinguishable from photographs. Path tracing naturally simulates many effects that have to be specifically added to other methods (conventional ray tracing or scanline rendering), such as soft shadows, depth of field, motion blur, caustics, ambient occlusion, and indirect lighting. Implementa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volumetric Path Tracing
Volumetric path tracing is a method for rendering images in computer graphics which was first introduced by Lafortune and Willems. This method enhances the rendering of the lighting in a scene by extending the path tracing method with the effect of light scattering. It is used for photorealistic effects of participating media like fire, explosions, smoke, clouds, fog or soft shadows. Like in the path tracing method, a ray gets followed backwards, beginning from the eye, until reaching the light source. In volumetric path tracing, scattering events can occur along with ray tracing. When a light ray hits a surface, a certain amount gets scattered into the media. Description The algorithm is based on the volumetric rendering equation, which extends the rendering equation with a scattering term. It is composed of an absorption, out-scattering, emission and an in-scattering part. The absorption and out-scattering together form the extinction term. The in-scattering is the most expensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenCL
OpenCL (Open Computing Language) is a framework for writing programs that execute across heterogeneous platforms consisting of central processing units (CPUs), graphics processing units (GPUs), digital signal processors (DSPs), field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) and other processors or hardware accelerators. OpenCL specifies programming languages (based on C99, C++14 and C++17) for programming these devices and application programming interfaces (APIs) to control the platform and execute programs on the compute devices. OpenCL provides a standard interface for parallel computing using task- and data-based parallelism. OpenCL is an open standard maintained by the non-profit technology consortium Khronos Group. Conformant implementations are available from Altera, AMD, ARM, Creative, IBM, Imagination, Intel, Nvidia, Qualcomm, Samsung, Vivante, Xilinx, and ZiiLABS. Overview OpenCL views a computing system as consisting of a number of ''compute devices'', which migh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CUDA
CUDA (or Compute Unified Device Architecture) is a parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API) that allows software to use certain types of graphics processing units (GPUs) for general purpose processing, an approach called general-purpose computing on GPUs (GPGPU). CUDA is a software layer that gives direct access to the GPU's virtual instruction set and parallel computational elements, for the execution of compute kernels. CUDA is designed to work with programming languages such as C, C++, and Fortran. This accessibility makes it easier for specialists in parallel programming to use GPU resources, in contrast to prior APIs like Direct3D and OpenGL, which required advanced skills in graphics programming. CUDA-powered GPUs also support programming frameworks such as OpenMP, OpenACC and OpenCL; and HIP by compiling such code to CUDA. CUDA was created by Nvidia. When it was first introduced, the name was an acronym for Compute Unified Device Architectur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPGPU
General-purpose computing on graphics processing units (GPGPU, or less often GPGP) is the use of a graphics processing unit (GPU), which typically handles computation only for computer graphics, to perform computation in applications traditionally handled by the central processing unit (CPU). The use of multiple video cards in one computer, or large numbers of graphics chips, further parallelizes the already parallel nature of graphics processing. Essentially, a GPGPU pipeline is a kind of parallel processing between one or more GPUs and CPUs that analyzes data as if it were in image or other graphic form. While GPUs operate at lower frequencies, they typically have many times the number of cores. Thus, GPUs can process far more pictures and graphical data per second than a traditional CPU. Migrating data into graphical form and then using the GPU to scan and analyze it can create a large speedup. GPGPU pipelines were developed at the beginning of the 21st century for graphic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nvidia
Nvidia CorporationOfficially written as NVIDIA and stylized in its logo as VIDIA with the lowercase "n" the same height as the uppercase "VIDIA"; formerly stylized as VIDIA with a large italicized lowercase "n" on products from the mid 1990s to early-mid 2000s. Though unofficial, second letter capitalization of NVIDIA, i.e. nVidia, may be found within enthusiast communities and publications. ( ) is an American multinational technology company incorporated in Delaware and based in Santa Clara, California. It is a software and fabless company which designs graphics processing units (GPUs), application programming interface (APIs) for data science and high-performance computing as well as system on a chip units (SoCs) for the mobile computing and automotive market. Nvidia is a global leader in artificial intelligence hardware and software. Its professional line of GPUs are used in workstations for applications in such fields as architecture, engineering and construction, media ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonidas J
Leonidas I (; grc-gre, Λεωνίδας; died 19 September 480 BC) was a king of the Greek city-state of Sparta, and the 17th of the Agiad line, a dynasty which claimed descent from the mythological demigod Heracles. Leonidas I was son of King Anaxandridas II. He succeeded his half-brother King Cleomenes I to the throne in c. 489 BC. His co-ruler was King Leotychidas. He was succeeded by his son, King Pleistarchus. Leonidas had a notable participation in the Second Greco-Persian War, where he led the allied Greek forces to a last stand at the Battle of Thermopylae (480 BC) while attempting to defend the pass from the invading Persian army; he died at the battle and entered myth as the leader of the 300 Spartans. While the Greeks lost this battle, they were able to expel the Persian invaders in the following year. Life According to Herodotus, Leonidas' mother was not only his father's wife but also his father's niece and had been barren for so long that the ephors, the five an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Kajiya
James Kajiya is a pioneer in the field of computer graphics. He is perhaps best known for the development of the rendering equation. Kajiya received his PhD from the University of Utah in 1979, was a professor at Caltech from 1979 through 1994, and is currently a researcher at Microsoft Research. In 2002, Kajiya was elected a member of the National Academy of Engineering The National Academy of Engineering (NAE) is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Engineering is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of ... for contributions to formal and practical methods of computer image generation. References External links Biography at Microsoft Microsoft employees University of Utah alumni California Institute of Technology faculty Computer graphics professionals American computer scientists Computer graphics researchers Living people Year of birth missing (l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rendering Equation
In computer graphics, the rendering equation is an integral equation in which the equilibrium radiance leaving a point is given as the sum of emitted plus reflected radiance under a geometric optics approximation. It was simultaneously introduced into computer graphics by David Immel et al. and James Kajiya in 1986. The various realistic rendering techniques in computer graphics attempt to solve this equation. The physical basis for the rendering equation is the law of conservation of energy. Assuming that ''L'' denotes radiance, we have that at each particular position and direction, the outgoing light (Lo) is the sum of the emitted light (Le) and the reflected light. The reflected light itself is the sum from all directions of the incoming light (Li) multiplied by the surface reflection and cosine of the incident angle. Equation form The rendering equation may be written in the form :L_(\mathbf x, \omega_, \lambda, t) = L_(\mathbf x, \omega_, \lambda, t) \ + \int_\Omega f_( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolis Light Transport
Metropolis light transport (MLT) is a global illumination application of a variant of the Monte Carlo method called the Metropolis–Hastings algorithm to the rendering equation for generating images from detailed physical descriptions of three-dimensional scenes. The procedure constructs paths from the eye to a light source using bidirectional path tracing, then constructs slight modifications to the path. Some careful statistical calculation (the Metropolis algorithm) is used to compute the appropriate distribution of brightness over the image. This procedure has the advantage, relative to bidirectional path tracing, that once a path has been found from light to eye, the algorithm can then explore nearby paths; thus difficult-to-find light paths can be explored more thoroughly with the same number of simulated photons. In short, the algorithm generates a path and stores the path's 'nodes' in a list. It can then modify the path by adding extra nodes and creating a new light pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Noise
Image noise is random variation of brightness or color information in images, and is usually an aspect of electronic noise. It can be produced by the image sensor and circuitry of a Image scanner, scanner or digital camera. Image noise can also originate in film grain and in the unavoidable shot noise of an ideal photon detector. Image noise is an undesirable by-product of image capture that obscures the desired information. Typically the term “image noise” is used to refer to noise in 2D images, not 3D images. The original meaning of "noise" was "unwanted signal"; Noise (radio), unwanted electrical fluctuations in signals received by AM radios caused audible acoustic noise ("static"). By analogy, unwanted electrical fluctuations are also called "noise". Image noise can range from almost imperceptible specks on a digital photograph taken in good light, to Optical astronomy, optical and Radioastronomy, radioastronomical images that are almost entirely noise, from which a sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |