|
Park Ship
Park ships were merchant steamships constructed for Canada’s Merchant Navy during the Second World War. Park ships and Fort ships (built in Canada for operation by the British) were the Canadian equivalent of the American Liberty ships. All three shared a similar design by J.L. Thompson and Sons of Sunderland, England. Fort ships had a triple expansion steam engine and a single screw propeller. Fort ships were ships transferred to the British government and the Park ships were those employed by the Canadian government, both had the similar design. Park ships were named after local and National Parks of Canada. A few Park ships were launched as "Camp ships", named after Canada military camps, but were quickly renamed after Parks. was the first Park ship lost to enemy attack, in the Indian Ocean after a torpedo attack from U-177 in the Indian Ocean, South of Durban, South Africa. Park Steamship Company The Allied merchant fleet suffered significant losses in the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pictou Shipyard
The Pictou Shipyard is a Canadian shipbuilding site located in Pictou County, Nova Scotia, and made famous by its use as an emergency shipbuilding facility in World War II, during which it constructed twenty-four 4,700-ton Scandinavian class freighters. It was founded at its current location in 1856, as the Pictou Iron Foundry, by William Henry Davies.Sherwood, Roland H. (1945). ''Pictou Parade''. Sackville, New Brunswick: The Tribune Press. pp. 12–13. Through many business booms and busts, as well as several changes of ownership, it has continued to operate until today, when it is owned by Aecon Atlantic Industrial Inc. Early shipbuilding and repairs Although the official founding by W. H. Davies did not occur until 1856, Pictou's ship registry began in 1840.Cameron, James M. (1990). ''The Ships, Shipbuilders and Seamen of Pictou County''. Antigonish, Nova Scotia: Pictou County Historical Society. Shipbuilding and ship repair began in Pictou in various places near the town a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
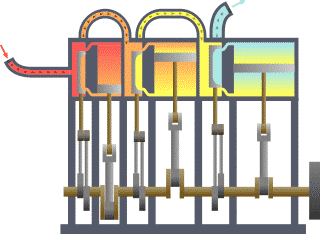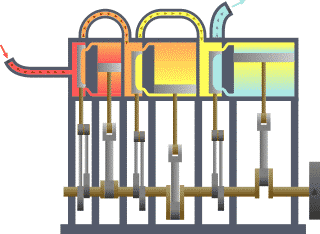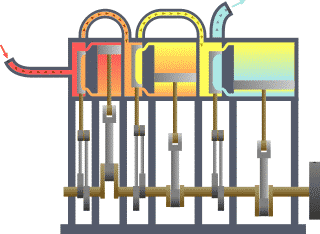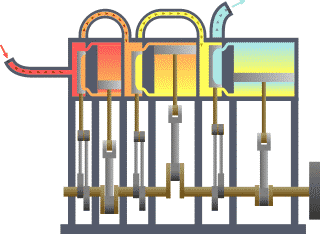
Triple Expansion Steam Engine
A compound steam engine unit is a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. A typical arrangement for a compound engine is that the steam is first expanded in a high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinder, then having given up heat and losing pressure, it exhausts directly into one or more larger-volume low-pressure ''(LP)'' cylinders. Multiple-expansion engines employ additional cylinders, of progressively lower pressure, to extract further energy from the steam. Invented in 1781, this technique was first employed on a Cornish beam engine in 1804. Around 1850, compound engines were first introduced into Lancashire textile mills. Compound systems There are many compound systems and configurations, but there are two basic types, according to how HP and LP piston strokes are phased and hence whether the HP exhaust is able to pass directly from HP to LP ( Woolf compounds) or whether pressure fluctuation necessitates an intermediate "buffer" space in the form of a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
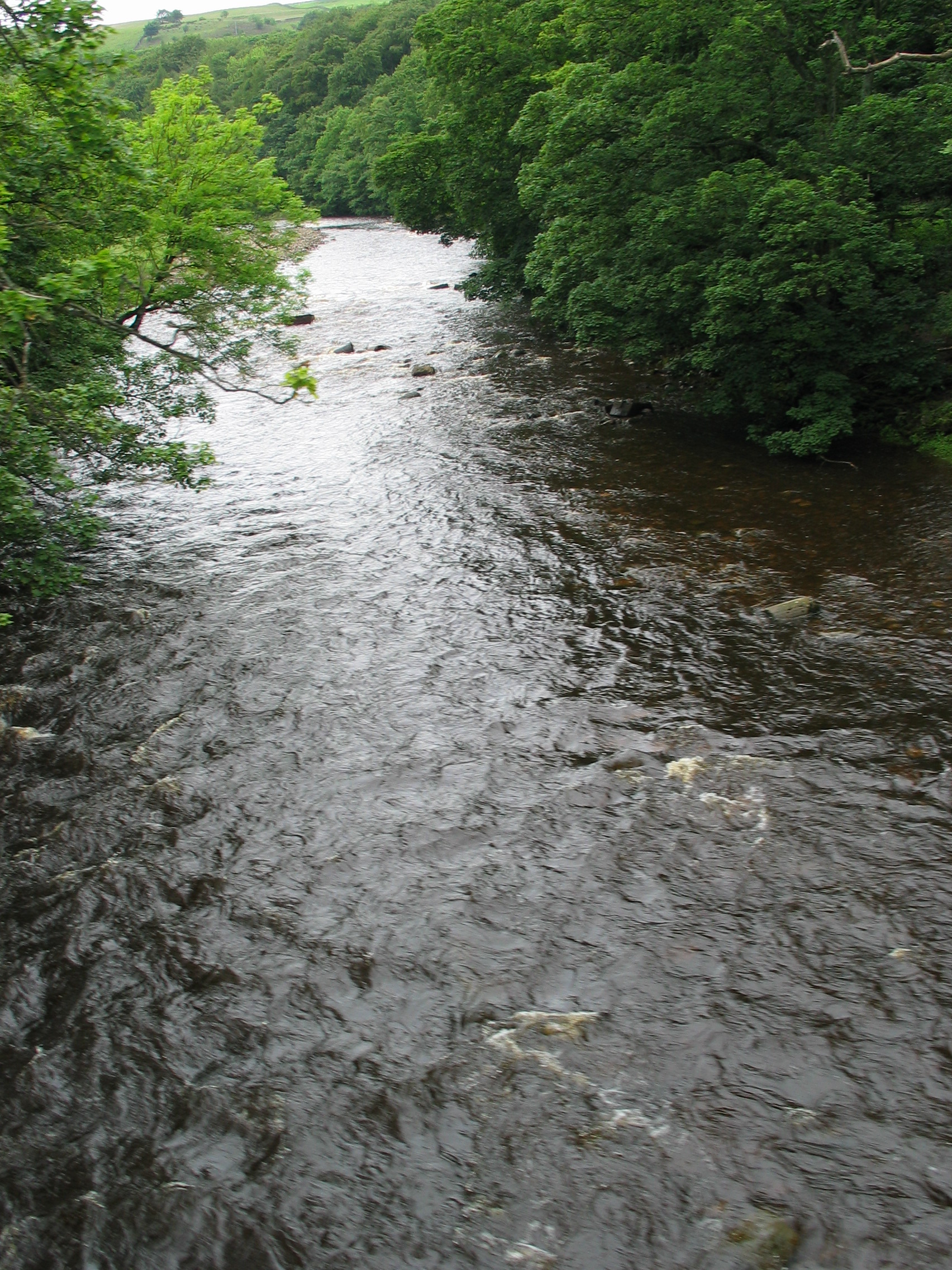
River Wear
The River Wear (, ) in North East England rises in the Pennines and flows eastwards, mostly through County Durham to the North Sea in the City of Sunderland. At long, it is one of the region's longest rivers, wends in a steep valley through the cathedral city of Durham and gives its name to Weardale in its upper reach and Wearside by its mouth. Etymology The origin behind the hydronym ''Wear'' is uncertain but is generally understood to be Celtic. The ''River Vedra'' on the Roman Map of Britain may very well be the River Wear. The name may be derived from Brittonic ''*wejr'' (<''*wẹ:drā''), which meant "a bend" (c.f ''-gwair-''). An alternative but very problematic etymology might involve ''*wẹ:d-r-'', from a lengthened form of the |
North Sands Class
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography. Etymology The word ''north'' is related to the Old High German ''nord'', both descending from the Proto-Indo-European unit *''ner-'', meaning "left; below" as north is to left when facing the rising sun. Similarly, the other cardinal directions are also related to the sun's position. The Latin word ''borealis'' comes from the Greek '' boreas'' "north wind, north", which, according to Ovid, was personified as the wind-god Boreas, the father of Calais and Zetes. ''Septentrionalis'' is from ''septentriones'', "the seven plow oxen", a name of ''Ursa Major''. The Greek ἀρκτικός (''arktikós'') is named for the same constellation, and is the source of the English word ''Arctic''. Other languages have other derivations. For example, in Lezgian, ''kefer'' can me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Materiel
Materiel (; ) refers to supplies, equipment, and weapons in military supply-chain management, and typically supplies and equipment in a commercial supply chain context. In a military context, the term ''materiel'' refers either to the specific needs (excluding manpower) of a force to complete a specific mission, or the general sense of the needs (excluding manpower) of a functioning army. An important category of materiel is commonly referred to as ordnance, especially concerning mounted guns (artillery) and the shells it consumes. Along with fuel, and munitions in general, the steady supply of ordnance is an ongoing logistic challenge in active combat zones. Materiel management consists of continuing actions relating to planning, organizing, directing, coordinating, controlling, and evaluating the application of resources to ensure the effective and economical support of military forces. It includes provisioning, cataloging, requirements determination, acquisition, distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare role ( commerce raiding) and enforcing a naval blockade against enemy shipping. The primary targets of the U-boat campaigns in both wars were the merchant convoys bringing supplies from Canada and other parts of the British Empire, and from the United States, to the United Kingdom and (during the Second World War) to the Soviet Union and the Allied territories in the Mediterranean. German submarines also destroyed Brazilian merchant ships during World War II, causing Brazil to declare war on both Germany and Italy on 22 August 1942. The term is an anglicised version of the German word ''U-Boot'' , a shortening of ''Unterseeboot'' ('under-sea-boat'), though the German term refers to any submarine. Austro-Hungarian Navy submarines were also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Atlantic
The Battle of the Atlantic, the longest continuous military campaign in World War II, ran from 1939 to the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, covering a major part of the naval history of World War II. At its core was the Allies of World War II, Allied naval Blockade of Germany (1939–1945), blockade of Germany, announced the day after the declaration of war, and Germany's subsequent counter-blockade. The campaign peaked from mid-1940 through to the end of 1943. The Battle of the Atlantic pitted U-boats and other warships of the German ''Kriegsmarine'' (Navy) and aircraft of the ''Luftwaffe'' (Air Force) against the Royal Navy, Royal Canadian Navy, United States Navy, and World War II United States Merchant Navy, Allied merchant shipping. Convoys, coming mainly from North America and predominantly going to the United Kingdom and the Soviet Union, were protected for the most part by the British and Canadian navies and air forces. These forces were aided by ships and aircraft of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. With over 60 million people, the country is the world's 23rd-most populous nation and covers an area of . South Africa has three capital cities, with the executive, judicial and legislative branches of government based in Pretoria, Bloemfontein and Cape Town respectively. The largest city is Johannesburg. About 81% of the population are Black South Africans. The remaining population consists of Africa's largest communities of European (White South Africans), Asian (Indian South Africans and Chinese South Africans), and Multiracial ( Coloured South Africans) ancestry. South Africa is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe; and to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini and it surrounds the Enclave and exclave, enclaved country of Les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |