|
Panamanian Dry Forests
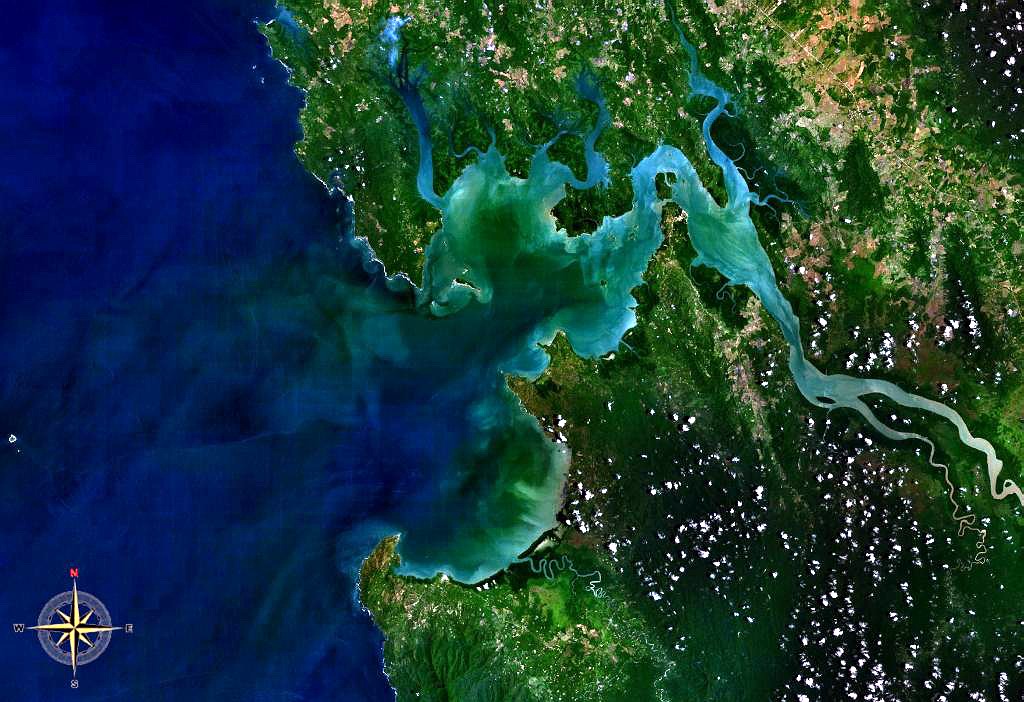
The Panamanian dry forests ecoregion (WWF ID: NT0224) covers low-lying dry forests around the coast of the Gulf of Panama on the Pacific Ocean side of Panama. It is one of the most heavily degraded ecoregions in Central America, having been heavily converted to agriculture. However, it is also important for its high biodiversity, high rates of endemic species, and its importance as a biological corridor between the moist forests inland and the mangroves on the coast. Location and description The Gulf of Panama has minor gulfs around its rim. The largest sector of this ecoregion is around the Gulf of Parita on the west. There are smaller sectors in the north on Panama Bay (around Panama City), and the Bay of San Miguel on the east. Most of the region is lowlands, with an average elevation of . The western sector is surrounded on the interior side by the Isthmian-Pacific moist forests ecoregion, the eastern sectors by the Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests ecoregion. There is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Las Minas District
Las Minas District is a district (''distrito'') of Herrera Province in Panama. The population according to the 2000 census was 7,945. The district covers a total area of 437 km². The capital lies at the city of Las Minas. Administrative divisions Las Minas District is divided administratively into the following '' corregimientos'': *Las Minas (capital) * Chepo * Chumical *El Toro El Toro, Spanish for "the bull", may refer to: Geography * El Toro (Mallorca), a neighbourhood in the municipality of Calvià on the island of Mallorca * El Toro, Castellón, a town in Castellón, Spain * El Toro (Jujuy), a rural municipality and ... * Leones * Quebrada del Rosario * Quebrada El Ciprián References Districts of Panama Herrera Province {{Herrera-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of San Miguel
The Bay of San Miguel () is a bay of the Gulf of Panama, located on the Pacific coast of Darién Province in eastern Panama. The bay is located at . It is fed by the Tuira River The Tuira River is located in the Darién Province of eastern Panama. It flows into the Bay of San Miguel at the province capital of La Palma. It is the largest river in Panama, and one of its tributaries, the Chucunaque River, is the longest .... At its southern end is Cape Garachiné (also known as Point Garachina), and at its northern end is Punta San Lorenzo (a.k.a. Cape Gardo). See also * San Miguel San Miguel, Panama Landforms of Darién Province Gulf of Panama Panamanian coasts of the Pacific Ocean {{Darién-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
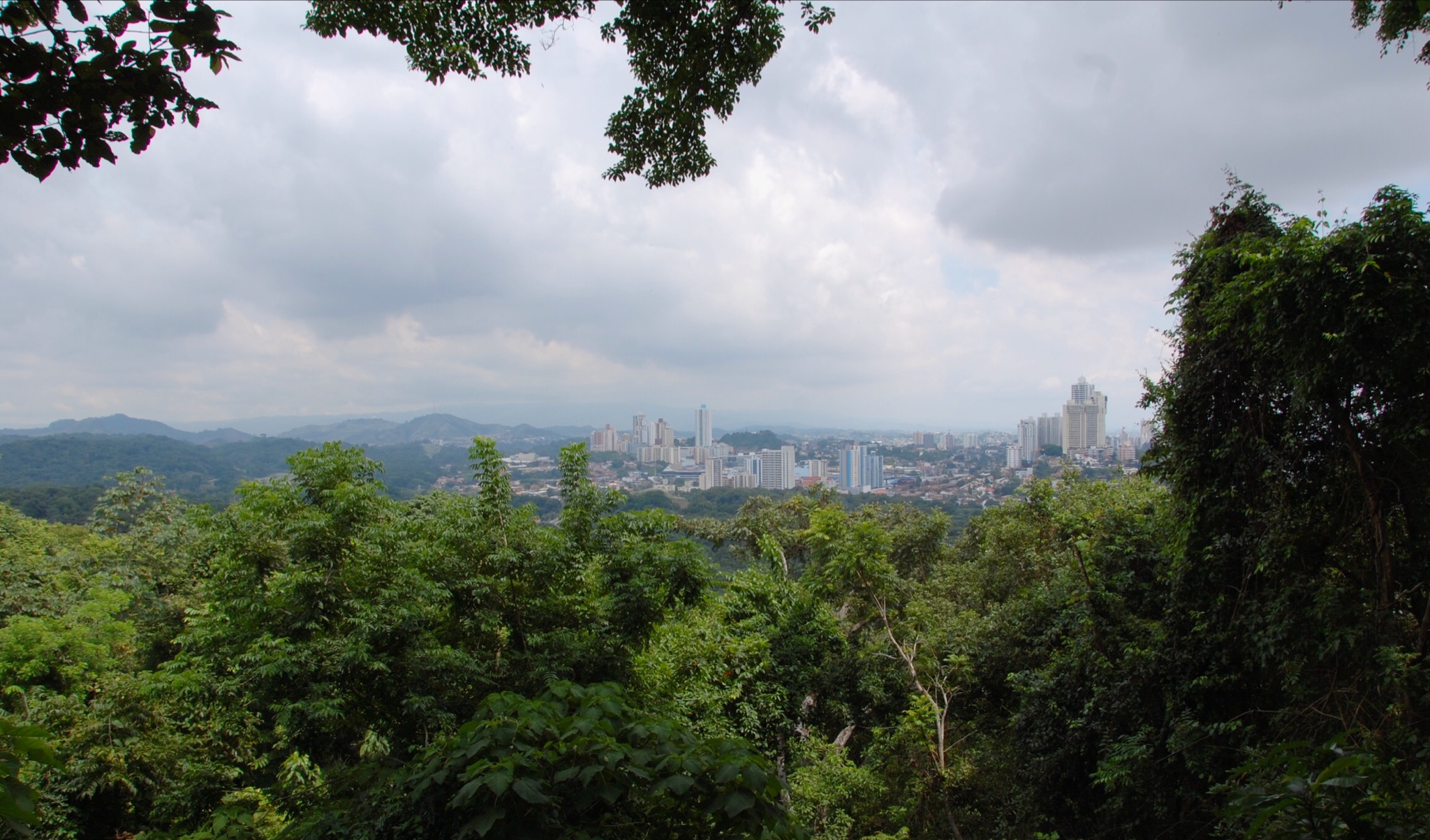
Metropolitan Natural Park
Metropolitan Natural Park (Parque Natural Metropolitano) is a park in Panama City, Panama Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Cos .... It is the only wildlife refuge in the city. Wildlife found in the park include bird species and Geoffroy's tamarin. The park was first proposed in 1974 and was inaugurated on June 5, 1988. References Parks in Panama Protected areas established in 1988 Tourist attractions in Panama City Panama City {{Panama-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarigua National Park
Sarigua National Park (''Parque Nacional Sarigua'') is a national park situated on the Azuero Peninsula in the Herrera Province of Panama, approximately from Panama City Panama City ( es, Ciudad de Panamá, links=no; ), also known as Panama (or Panamá in Spanish), is the capital and largest city of Panama. It has an urban population of 880,691, with over 1.5 million in its metropolitan area. The city is locat .... The park consists of an ancient archaeological site and was once a dry tropical rainforest. As a result of deforestation, it is now a desert. References Herrera Province {{Herrera-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parque Natural Metropolitano - Mirador Con Vista Hacia El Cerro Ancon Y La Calzada De Amador - Panoramio
*
*
{{dab, surname ...
Parque is the Galician, Portuguese and Spanish word for "park", and may refer to: * Parque (TransMilenio), a metro station in Bogotá, Colombia * Parque (Lisbon Metro), in Portugal * Parque (Santurce), a subbarrio in San Juan, Puerto Rico * Jim Parque, a baseball player See also * Parquetry, a type of flooring * Park (other) A park is an area of land with a recreational or other specific purpose. Park or Parks may also refer to: Places United Kingdom * Park (Reading ward), an electoral ward of the Borough of Reading, Berkshire, England * Park (Sefton ward), an el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Savanna Climate With Dry-winter Characteristics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to as the tropical zone and the torrid zone (see geographical zone). In terms of climate, the tropics receive sunlight that is more direct than the rest of Earth and are generally hotter and wetter as they aren't affected as much by the solar seasons. The word "tropical" sometimes refers to this sort of climate in the zone rather than to the geographical zone itself. The tropical zone includes deserts and snow-capped mountains, which are not tropical in the climatic sense. The tropics are distinguished from the other climatic and biomatic regions of Earth, which are the middle latitudes and the polar regions on either side of the equatorial zone. The tropics constitute 40% of Earth's surface area and contain 36% of Earth's landmass. , the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Savanna Climate
Tropical savanna climate or tropical wet and dry climate is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification categories ''Aw'' (for a dry winter) and ''As'' (for a dry summer). The driest month has less than of precipitation and also less than 100-\left (\frac \right)mm of precipitation. This latter fact is in a direct contrast to a tropical monsoon climate, whose driest month sees less than of precipitation but has ''more'' than 100-\left (\frac \right) of precipitation. In essence, a tropical savanna climate tends to either see less overall rainfall than a tropical monsoon climate or have more pronounced dry season(s). In tropical savanna climates, the dry season can become severe, and often drought conditions prevail during the course of the year. Tropical savanna climates often feature tree-studded grasslands due to its dryness, rather than thick jungle. It is this widespread occurrence of tall, coarse grass (called savanna) which has led to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panama City
Panama City ( es, Ciudad de Panamá, links=no; ), also known as Panama (or Panamá in Spanish), is the capital and largest city of Panama. It has an urban population of 880,691, with over 1.5 million in its metropolitan area. The city is located at the Pacific entrance of the Panama Canal, in the province of Panama. The city is the political and administrative center of the country, as well as a hub for banking and commerce. The city of Panama was founded on 15 August 1519, by Spanish conquistador Pedro Arias Dávila. The city was the starting point for expeditions that conquered the Inca Empire in Peru. It was a stopover point on one of the most important trade routes in the American continent, leading to the fairs of Nombre de Dios and Portobelo, through which passed most of the gold and silver that Spain mined from the Americas. On 28 January 1671, the original city was destroyed by a fire when the privateer Henry Morgan sacked and set fire to it. The city was formally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Costa Rica to the west, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Its capital and largest city is Panama City, whose metropolitan area is home to nearly half the country's million people. Panama was inhabited by indigenous tribes before Spanish colonists arrived in the 16th century. It broke away from Spain in 1821 and joined the Republic of Gran Colombia, a union of Nueva Granada, Ecuador, and Venezuela. After Gran Colombia dissolved in 1831, Panama and Nueva Granada eventually became the Republic of Colombia. With the backing of the United States, Panama seceded from Colombia in 1903, allowing the construction of the Panama Canal to be completed by the United States Army Corps of En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_(14597444780).jpg)