|
PRKG1
cGMP-dependent protein kinase 1, alpha isozyme is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKG1'' gene. Interactions PRKG1 has been shown to interact with: * GTF2I, * ITPR1, * MRVI1, * RGS2, and * TNNT1 Slow skeletal muscle troponin T (sTnT) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TNNT1'' gene. The TNNT1 gene is located at 19q13.4 in the human chromosomal genome, encoding the slow twitch skeletal muscle isoform of troponin T (ssTnT). ss .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * EC 2.7.11 {{gene-10-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GTF2I
General transcription factor II-I is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GTF2I'' gene. Function This gene encodes a multifunctional phosphoprotein, TFII-I, with roles in transcription and signal transduction. Haploinsuffiency (deletion of one copy) of the GTF2I gene is noted in Williams-Beuren syndrome, a multisystem developmental disorder caused by the deletion of contiguous genes at chromosome 7q11.23. It is duplicated in the 7q11.23 duplication syndrome. The exon(s) encoding 5' UTR has not been fully defined, but this gene is known to contain at least 34 exons, and its alternative splicing generates 4 transcript variants in humans. A single gain-of-function point mutation in GTF2I is also found in certain Thymomas. Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in GTF2I is correlated to autoimmune disorders. Interactions GTF2I has been shown to interact with: * Bruton's tyrosine kinase, * HDAC3, * Histone deacetylase 2, * MAPK3, * Myc, * PRKG1, * Serum response fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITPR1
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ITPR1'' gene. Interactions ITPR1 has been shown to interact with: * AHCYL1, * CA8, * EPB41L1 * FKBP1A, * MRVI1, * PRKG1, * RHOA, and * TRPC4. See also * Inositol triphosphate * Inositol triphosphate receptor Inositol trisphosphate receptor (InsP3R) is a membrane glycoprotein complex acting as a Ca2+ channel activated by inositol trisphosphate (InsP3). InsP3R is very diverse among organisms, and is necessary for the control of cellular and physiol ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 15 {{Ion channels, g1 Ion channels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRVI1
Protein MRVI1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MRVI1'' gene. Function This gene is similar to a mouse putative tumor suppressor gene that is frequently disrupted by mouse AIDS-related virus (MRV). The encoded protein, which is found in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum, is similar to Jaw1, a lymphoid-restricted protein whose expression is downregulated during myeloid differentiation. Therefore, this gene may be a myeloid leukemia tumor suppressor gene. Several alternatively spliced transcripts have been found for this gene, however, the full-length nature of some variants has not been determined. Of the two characterized variants which encode different isoforms, one initiates translation at a non-AUG start site. Interactions MRVI1 has been shown to interact with ITPR1 and PRKG1 cGMP-dependent protein kinase 1, alpha isozyme is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKG1'' gene. Interactions PRKG1 has been shown to interact with: * GTF2I, * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RGS2
Regulator of G-protein signaling 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RGS2'' gene. It is part of a larger family of RGS proteins that control signalling through G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR). Function RGS2 is thought to have protective effects against myocardial hypertrophy as well as atrial arrhythmias. Increased stimulation of Gs coupled β1-adrenergic receptors and Gq coupled α1-adrenergic receptors in the heart can result in cardiac hypertrophy. In the case of Gq protein coupled receptor (GqPCR) mediated hypertrophy, Gαq will activate the intracellular affectors phospholipase Cβ and rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor to stimulate cell processes which lead to cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. RGS2 functions as a GTPase Activating Protein (GAP) which acts to increase the natural GTPase activity of the Gα subunit. By increasing the GTPase activity of the Gα subunit, RGS2 promotes GTP hydrolysis back to GDP, thus converting the Gα subunit back to its ina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNNT1
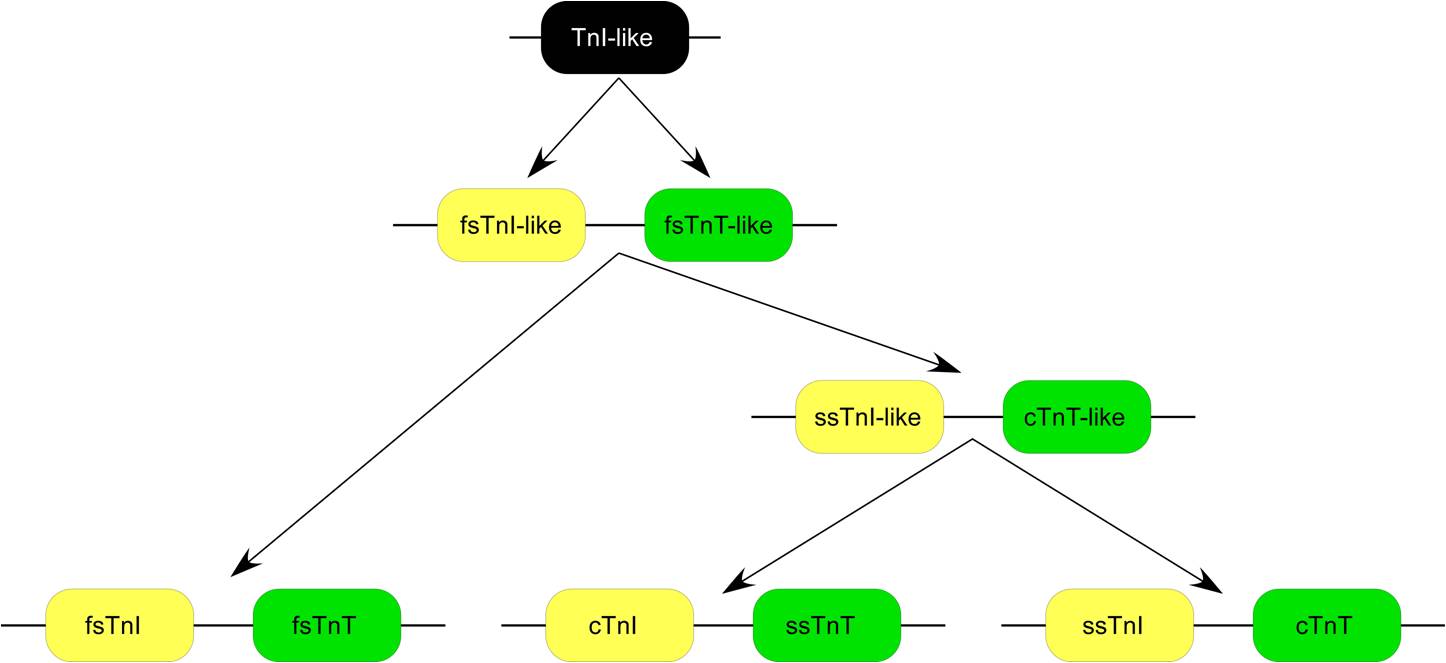
Slow skeletal muscle troponin T (sTnT) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TNNT1'' gene. The TNNT1 gene is located at 19q13.4 in the human chromosomal genome, encoding the slow twitch skeletal muscle isoform of troponin T (ssTnT). ssTnT is an ~32-kDa protein consisting of 262 amino acids (including the first methionine) with an isoelectric point (pI) of 5.95. It is the tropomyosin binding and thin filament anchoring subunit of the troponin complex in the sarcomeres of slow twitch skeletal muscle fibers. TNNT1 gene is specifically expressed in slow skeletal muscle of vertebrates, with one exception that dry land toad (Bufo) cardiac muscle expresses ssTnT other than cardiac TnT. Evolution Three homologous genes have evolved in vertebrates, encoding three muscle type specific isoforms of TnT. Each of the TnT isoform genes is linked to one of the three troponin I isoform genes encoding the inhibitory subunit of the troponin complex, in chromosomal DNA to form three g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |