|
PDE3A
PDE3 is a phosphodiesterase. The PDEs belong to at least eleven related gene families, which are different in their primary structure, substrate affinity, responses to effectors, and regulation mechanism. Most of the PDE families are composed of more than one gene. PDE3 is clinically significant because of its role in regulating heart muscle, vascular smooth muscle and platelet aggregation. PDE3 inhibitors have been developed as pharmaceuticals, but their use is limited by arrhythmic effects and they can increase mortality in some applications. Function PDE3 enzymes are involved in regulation of cardiac and vascular smooth muscle contractility. Molecules that inhibit PDE3 were originally investigated for the treatment of heart failure, but, because of unwanted arrhythmic side-effects, they are not studied for that indication any longer. Nonetheless, the PDE3 inhibitor milrinone is approved for use in heart failure in intravenous form. Both PDE3A and PDE3B are expressed in vas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDE3 Litil
PDE3 is a phosphodiesterase. The PDEs belong to at least eleven related gene families, which are different in their primary structure, substrate affinity, responses to effectors, and regulation mechanism. Most of the PDE families are composed of more than one gene. PDE3 is clinically significant because of its role in regulating heart muscle, vascular smooth muscle and platelet aggregation. PDE3 inhibitors have been developed as pharmaceuticals, but their use is limited by arrhythmic effects and they can increase mortality in some applications. Function PDE3 enzymes are involved in regulation of cardiac and vascular smooth muscle contractility. Molecules that inhibit PDE3 were originally investigated for the treatment of heart failure, but, because of unwanted arrhythmic side-effects, they are not studied for that indication any longer. Nonetheless, the PDE3 inhibitor milrinone is approved for use in heart failure in intravenous form. Both PDE3A and PDE3B are expressed in vas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipocytes
Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Adipocytes are derived from mesenchymal stem cells which give rise to adipocytes through adipogenesis. In cell culture, adipocyte progenitors can also form osteoblasts, myocytes and other cell types. There are two types of adipose tissue, white adipose tissue (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT), which are also known as white and brown fat, respectively, and comprise two types of fat cells. Structure White fat cells White fat cells contain a single large lipid droplet surrounded by a layer of cytoplasm, and are known as unilocular. The nucleus is flattened and pushed to the periphery. A typical fat cell is 0.1 mm in diameter with some being twice that size, and others half that size. However, these numerical estimates of fat cell size depend largely on the measurement method and the location of the adipose tissue. The fat stored is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
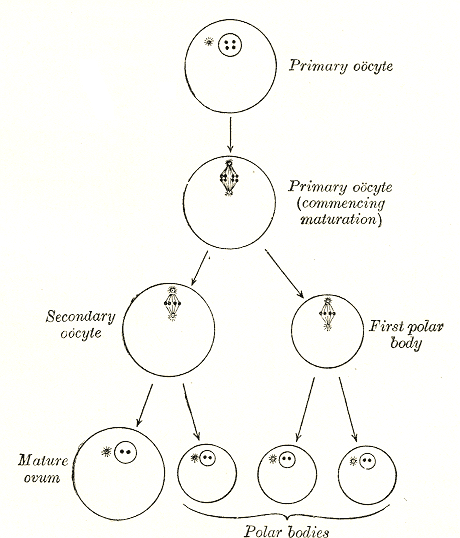
Oocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Formation The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation. Characteristics Cytoplasm Oocytes are rich in cytoplasm, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development. Nucleus During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelets
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby initiating a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm that are derived from the megakaryocytes of the bone marrow or lung, which then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site of interrupted endothelium. They gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secrete chemical messengers: ''activatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Smooth Muscle
Vascular smooth muscle is the type of smooth muscle that makes up most of the walls of blood vessels. Structure Vascular smooth muscle refers to the particular type of smooth muscle found within, and composing the majority of the wall of blood vessels. Nerve supply Vascular smooth muscle is innervated primarily by the sympathetic nervous system through adrenergic receptors (adrenoceptors). The three types present are: alpha-1, alpha-2 and beta-2 adrenergic receptors, . The main endogenous agonist of these cell receptors is norepinephrine (NE). The adrenergic receptors exert opposite physiologic effects in the vascular smooth muscle under activation: * alpha-1 receptors. Under NE binding alpha-1 receptors cause vasoconstriction ( contraction of the vascular smooth muscle cells decreasing the diameter of the vessels). Thesea receptors are activated in response to shock or low blood pressure as a defensive reaction trying to restore the normal blood pressure. Antagonists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytosolic
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells (intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments. In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is surrounded by the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. The cytosol is thus a liquid matrix around the organelles. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others take place within organelles. The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and propertie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is generally measured as the concentration of the solute in a saturated solution, one in which no more solute can be dissolved. At this point, the two substances are said to be at the solubility equilibrium. For some solutes and solvents, there may be no such limit, in which case the two substances are said to be "miscible in all proportions" (or just "miscible"). The solute can be a solid, a liquid, or a gas, while the solvent is usually solid or liquid. Both may be pure substances, or may themselves be solutions. Gases are always miscible in all proportions, except in very extreme situations,J. de Swaan Arons and G. A. M. Diepen (1966): "Gas—Gas Equilibria". ''Journal of Chemical Physics'', vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoform
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have unique functions. A set of protein isoforms may be formed from alternative splicings, variable promoter usage, or other post-transcriptional modifications of a single gene; post-translational modifications are generally not considered. (For that, see Proteoforms.) Through RNA splicing mechanisms, mRNA has the ability to select different protein-coding segments ( exons) of a gene, or even different parts of exons from RNA to form different mRNA sequences. Each unique sequence produces a specific form of a protein. The discovery of isoforms could explain the discrepancy between the small number of protein coding regions genes revealed by the human genome project and the large diversity of proteins seen in an organism: different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codon
The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material ( DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA), using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries. The codons specify which amino acid will be added next during protein biosynthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. The vast majority of genes are encoded with a single scheme (see the RNA codon table). That scheme is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply ''the'' genetic code, though variant codes (such as in mitochondria) exist. History Efforts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |