|
P22phox
p22phox Protein, also known as the human neutrophil cytochrome b light chain (CYBA), is an essential component of the membrane-associated enzyme phagocyte NADPH-oxidaseDinauer MC, Pierce EA, Bruns GA, Curnutte JT, Orkin SH. "Human neutrophil cytochrome b light chain (p22-phox). Gene structure, chromosomal location, and mutations in cytochrome-negative autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease." ''J Clin Invest.'' November 1990; 86(5): 1729-37. This enzyme uses NADH or NADPH as the electron donor for the one electron reduction of oxygen to produce superoxide anion, a reactive oxygen species (ROS),Xu Q, Yuan F, Wu J. "Polymorphisms of C242T and A640G in CYBA Gene and the risk of coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis." ''PLoS One''. 2014; 9(1): e84251 and a functionally important step for the antimicrobial activity of phagocytic cells. p22phox is also expressed in many other human cells such as endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells, including those within the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome B
Cytochrome b within both molecular and cell biology, is a protein found in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. It functions as part of the electron transport chain and is the main subunit of transmembrane cytochrome bc1 and b6f complexes. Function In the mitochondrion of eukaryotes and in aerobic prokaryotes, cytochrome b is a component of respiratory chain complex III () — also known as the bc1 complex or ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase. In plant chloroplasts and cyanobacteria, there is an analogous protein, cytochrome b6, a component of the plastoquinone-plastocyanin reductase (), also known as the b6f complex. These complexes are involved in electron transport, the pumping of protons to create a proton-motive force ( PMF). This proton gradient is used for the generation of ATP. These complexes play a vital role in cells. Structure Cytochrome b/b6 is an integral membrane protein of approximately 400 amino acid residues that probably has 8 transmembrane segments. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Oxygen Species
In chemistry, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (). Examples of ROS include peroxides, superoxide, hydroxyl radical, singlet oxygen, and alpha-oxygen. The reduction of molecular oxygen () produces superoxide (), which is the precursor to most other reactive oxygen species: :O2 + e^- -> \ ^\bullet O2- Dismutation of superoxide produces hydrogen peroxide (): :2 H+ + \ ^\bullet O2^- + \ ^\bullet O2^- -> H2O2 + O2 Hydrogen peroxide in turn may be partially reduced, thus forming hydroxide ions and hydroxyl radicals (), or fully reduced to water: :H2O2 + e^- -> HO^- + \ ^\bullet OH :2 H+ + 2 e- + H2O2 -> 2 H2O In a biological context, ROS are byproducts of the normal metabolism of oxygen. ROS have roles in cell signaling and homeostasis. ROS are intrinsic to cellular functioning, and are present at low and stationary levels in normal cells. In plants, ROS are involved in metabolic processes related to photoprotection and toleran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytic Cells
Phagocytes are cells that protect the body by ingesting harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dead or dying cells. Their name comes from the Greek ', "to eat" or "devour", and "-cyte", the suffix in biology denoting "cell", from the Greek ''kutos'', "hollow vessel". They are essential for fighting infections and for subsequent immunity. Phagocytes are important throughout the animal kingdom and are highly developed within vertebrates. One litre of human blood contains about six billion phagocytes. They were discovered in 1882 by Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov while he was studying starfish larvae.Ilya Mechnikov retrieved on November 28, 2008. Fro ''Physiology or Medicine 1901–1921'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Polymorphism
A gene is said to be polymorphic if more than one allele occupies that gene's locus within a population. In addition to having more than one allele at a specific locus, each allele must also occur in the population at a rate of at least 1% to generally be considered polymorphic. Gene polymorphisms can occur in any region of the genome. The majority of polymorphisms are silent, meaning they do not alter the function or expression of a gene. Some polymorphisms are visible. For example, in dogs the E locus can have any of five different alleles, known as E, Em, Eg, Eh, and e. Varying combinations of these alleles contribute to the pigmentation and patterns seen in dog coats. A polymorphic variant of a gene can lead to the abnormal expression or to the production of an abnormal form of the protein; this abnormality may cause or be associated with disease. For example, a polymorphic variant of the gene encoding the enzyme CYP4A11, in which thymidine replaces cytosine at the gene's nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
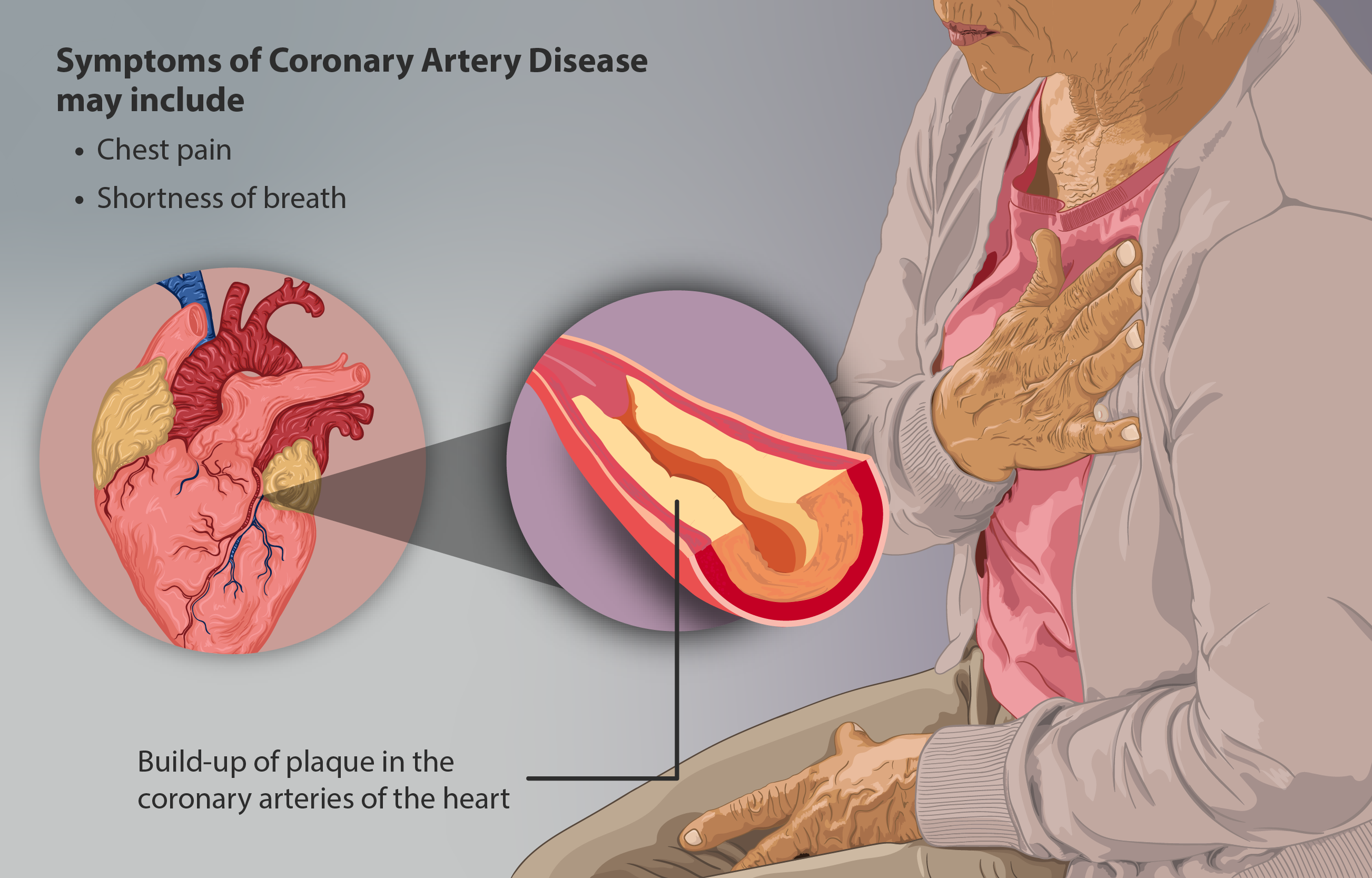
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic plaque An atheroma, or atheromatous plaque, is an abnormal and reversible accumulation of material in the inner layer of an arterial wall. The material consists of mostly macrophage cells, or debris, containing lipids, calcium and a variable amount ... in the arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Types include stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden cardiac death. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional Stress (psychological), stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycoproteins
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. Secreted extracellular proteins are often glycosylated. In proteins that have segments extending extracellularly, the extracellular segments are also often glycosylated. Glycoproteins are also often important integral membrane proteins, where they play a role in cell–cell interactions. It is important to distinguish endoplasmic reticulum-based glycosylation of the secretory system from reversible cytosolic-nuclear glycosylation. Glycoproteins of the cytosol and nucleus can be modified through the reversible addition of a single GlcNAc residue that is considered reciprocal to phosphorylation and the functions of these are likely to be an additional regulatory mechanism that controls phosphorylation-based signalling. In contrast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superoxide Anion
In chemistry, a superoxide is a Chemical compound, compound that contains the superoxide ion, which has the chemical formula . The systematic name of the anion is dioxide(1−). The reactive oxygen species, reactive oxygen ion superoxide is particularly important as the product of the one-electron redox, reduction of dioxygen , which occurs widely in nature. Molecular oxygen (dioxygen) is a diradical containing two unpaired electrons, and superoxide results from the addition of an electron which fills one of the two Degenerate energy level, degenerate molecular orbitals, leaving a charged ionic species with a single unpaired electron and a net negative charge of −1. Both dioxygen and the superoxide anion are free radicals that exhibit paramagnetism. Superoxide was historically also known as "hyperoxide". Salts Superoxide forms salts with alkali metals and alkaline earth metals. The salts caesium superoxide (), rubidium superoxide (), potassium superoxide (), and sodium su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis in which the wall of the artery develops abnormalities, called lesions. These lesions may lead to narrowing due to the buildup of atheroma, atheromatous plaque. At onset there are usually no symptoms, but if they develop, symptoms generally begin around middle age. When severe, it can result in coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, or kidney problems, depending on which Artery, arteries are affected. The exact cause is not known and is proposed to be multifactorial. Risk factors include dyslipidemia, abnormal cholesterol levels, elevated levels of inflammatory markers, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, obesity, family history, genetic, and an unhealthy diet. Atheroma, Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. The narrowing of Artery, arteries limits the flow of oxygen-rich blood to parts of the body. Diagnosis is based upon a physical exam, ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |