|
Pûˋage Island
Pûˋage Island is a small rocky island southwest of Cape Dûˋcouverte. Charted in 1951 by the French Antarctic Expedition and named by them for its position, which seems to command access to the Curzon Islands for parties arriving from Port Martin, ''pûˋage'' being French for toll booth. See also * List of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic islands References Islands of Adûˋlie Land {{AdûˋlieLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
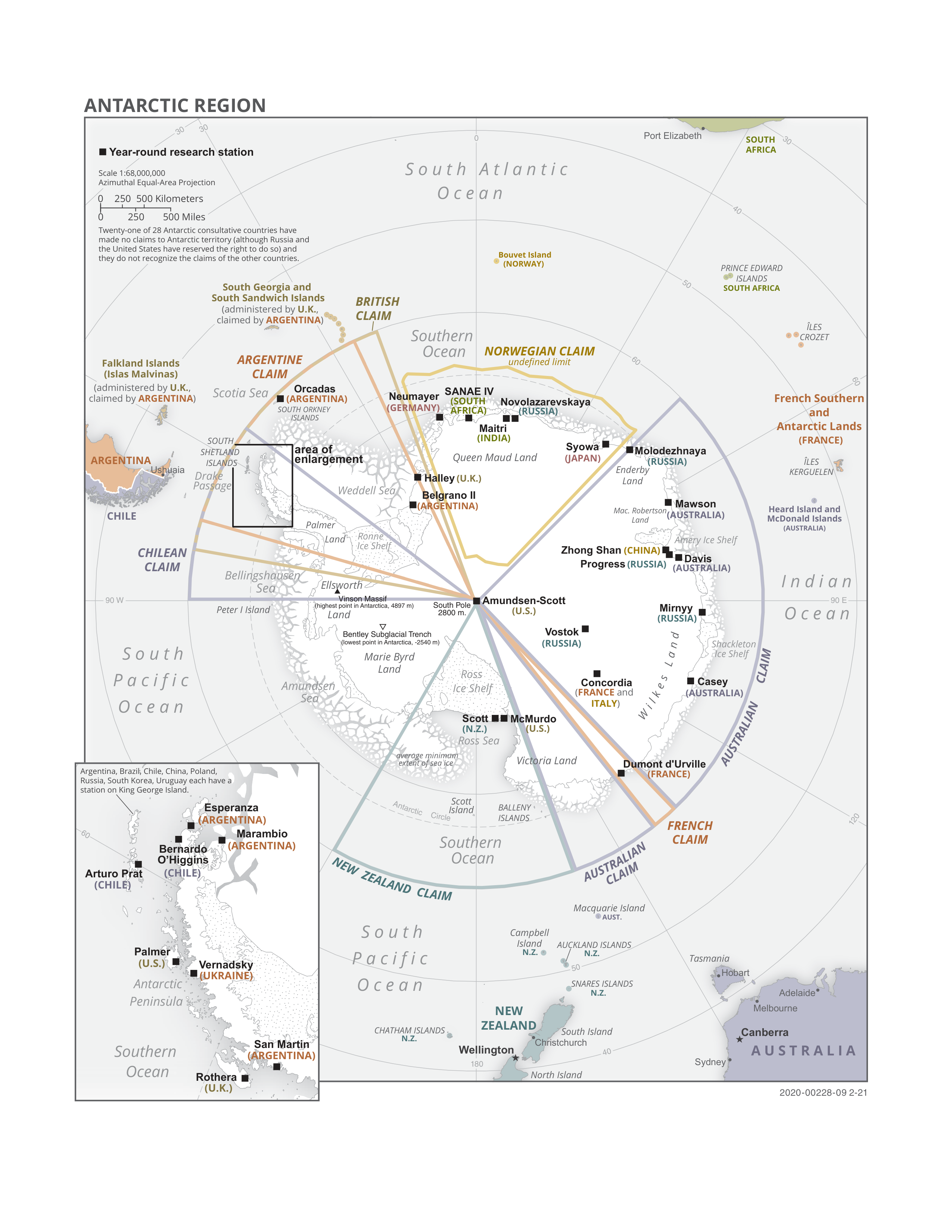
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Treaty System
russian: link=no, ÅŃŰŃÅýŃî ŃÅÝ ÅŧîůîŤîšŤÅç es, link=no, Tratado AntûÀrtico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty System , type = Condominium , date_drafted = , date_signed = December 1, 1959"Antarctic Treaty" in ''The New EncyclopûÎdia Britannica''. Chicago: EncyclopûÎdia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 439. , location_signed = Washington, D.C., United States , date_sealed = , date_effective = June 23, 1961 , condition_effective = Ratification of all 12 signatories , date_expiration = , signatories = 12 , parties = 55 , depositor = Federal government of the United States , languages = English, French, Russian, and Spanish , wikisource = Antarctic Treaty The Antarctic Treaty an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Dûˋcouverte
Cape Dûˋcouverte or Cape Discovery () is the point of rocks which marks the northwest extremity of the Curzon Islands along the Adûˋlie Coast. It was discovered on 21 January 1840, by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1837ã40, under Captain Jules Dumont d'Urville Jules Sûˋbastien Cûˋsar Dumont d'Urville (; 23 May 1790 ã 8 May 1842) was a French explorer and naval officer who explored the south and western Pacific, Australia, New Zealand, and Antarctica. As a botanist and cartographer, he gave his nam ... who gave the name "Cap de la Decouverte" (cape of the discovery). It was the first rocky point of the coast seen by members of the expedition. References Headlands of Adûˋlie Land {{AdûˋlieLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Antarctic Expedition
The French Antarctic Expedition is any of several French expeditions in Antarctica. First expedition In 1772, Yves-Joseph de Kerguelen-Trûˋmarec and the naturalist Jean Guillaume Bruguiû´re sailed to the Antarctic region in search of the fabled Terra Australis. Kerguelen-Trûˋmarec took possession of various Antarctic territories for France, including what would later be called the Kerguelen Islands. In Kerguelen-Trûˋmarec's report to King Louis XV, he greatly overestimated the value of the Kerguelen Islands. The King sent him on a second expedition to Kerguelen in late 1773. When it became clear that these islands were desolate, useless, and not the Terra Australis, he was sent to prison. Second expedition In 1837, during an 1837ã1840 expedition across the deep southern hemisphere, Captain Jules Dumont d'Urville sailed his ship ''Astrolabe'' along a coastal area of Antarctica which he later named Adûˋlie Land, in honor of his wife. During the Antarctic part of this expedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curzon Islands
The Curzon Islands are a small group of rocky islands lying close off Cape Dûˋcouverte, Adûˋlie Coast. They were probably sighted in January 1840 by a French expedition under Captain Jules Dumont d'Urville, though not identified as islands on d'Urville's maps. The islands were roughly charted in 1912 by Captain J.K. Davis of the Australasian Antarctic Expedition ship ''Aurora'' and named by Mawson for Lord Curzon, the President of the Royal Geographical Society, 1911ã14. The islands were mapped in detail by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1950ã52. Important Bird Area A 359 ha site comprising the island group and the intervening marine area has been designated an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because it supports about 13,000 breeding pairs of Adûˋlie penguins, mainly on Retour Island, the largest of the group. South polar skuas and Wilson's storm-petrels also breed in the islands. The closest permanent station is the French Dumont d'Urville ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Martin
Port Martin, or Port-Martin, is an abandoned French research base at Cape Margerie on the coast of Adûˋlie Land, Antarctica, as well as the name of the adjacent anchorage. History The site was discovered in 1950 by the French Antarctic Expedition under Andrûˋ-Franck Liotard and a landing made on 18 January 1950. The base was established by Liotard and a team of 11 men who raised the main building with several annexes to house scientific activities. It was named for expeditioner J. A. Martin, originally second-in-command of the expedition, who had died en route to the Antarctic. On 6 January 1951 the base team was relieved by 17-member team under the leadership of Michel Barrûˋ. Over the following year they enlarged the main building while continuing the research program. They, in turn, were relieved on 4 January 1952 while a smaller team of four, led by Mario Marret, built a secondary base on Petrel Island, some to the west in the Gûˋologie Archipelago. On the night of 23ã ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |