|
Port Martin
Port Martin, or Port-Martin, is an abandoned French research base at Cape Margerie on the coast of Ad├®lie Land, Antarctica, as well as the name of the adjacent anchorage. History The site was discovered in 1950 by the French Antarctic Expedition under Andr├®-Franck Liotard and a landing made on 18 January 1950. The base was established by Liotard and a team of 11 men who raised the main building with several annexes to house scientific activities. It was named for expeditioner J. A. Martin, originally second-in-command of the expedition, who had died en route to the Antarctic. On 6 January 1951 the base team was relieved by 17-member team under the leadership of Michel Barr├®. Over the following year they enlarged the main building while continuing the research program. They, in turn, were relieved on 4 January 1952 while a smaller team of four, led by Mario Marret, built a secondary base on Petrel Island, some to the west in the G├®ologie Archipelago. On the night of 23Ō ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Treaty System
russian: link=no, ąöąŠą│ąŠą▓ąŠčĆ ąŠą▒ ąÉąĮčéą░čĆą║čéąĖą║ąĄ es, link=no, Tratado Ant├Īrtico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty System , type = Condominium , date_drafted = , date_signed = December 1, 1959"Antarctic Treaty" in ''The New Encyclop├”dia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclop├”dia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 439. , location_signed = Washington, D.C., United States , date_sealed = , date_effective = June 23, 1961 , condition_effective = Ratification of all 12 signatories , date_expiration = , signatories = 12 , parties = 55 , depositor = Federal government of the United States , languages = English, French, Russian, and Spanish , wikisource = Antarctic Treaty The Antarctic Treaty an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Specially Protected Areas
An Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) is an area on the continent of Antarctica, or on nearby islands, which is protected by scientists and several different international bodies. The protected areas were established in 1961 under the Antarctic Treaty System, which governs all the land and water south of 60 latitude and protects against human development. A permit is required for entry into any ASPA site. The ASPA sites are protected by the governments of Australia, New Zealand, United States, United Kingdom, Chile, France, Argentina, Poland, Russia, Norway, Japan, India, Italy, and Republic of Korea. There are currently 72 sites. List of ASPA sites See also *Antarctic Specially Managed Area An Antarctic Specially Managed Area (ASMA) is a protected area on the continent of Antarctica, or on its adjacent islands. ASMAs are managed by the governments of Brazil, Poland, Ecuador, Peru, United States, New Ze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1952 Disestablishments In Antarctica
Year 195 ( CXCV) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scrapula and Clemens (or, less frequently, year 948 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 195 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Septimius Severus has the Roman Senate deify the previous emperor Commodus, in an attempt to gain favor with the family of Marcus Aurelius. * King Vologases V and other eastern princes support the claims of Pescennius Niger. The Roman province of Mesopotamia rises in revolt with Parthian support. Severus marches to Mesopotamia to battle the Parthians. * The Roman province of Syria is divided and the role of Antioch is diminished. The Romans annexed the Syrian cities of Edessa and Nisibis. Severus re-establish his head ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1950 Establishments In Antarctica
Year 195 ( CXCV) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scrapula and Clemens (or, less frequently, year 948 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 195 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Septimius Severus has the Roman Senate deify the previous emperor Commodus, in an attempt to gain favor with the family of Marcus Aurelius. * King Vologases V and other eastern princes support the claims of Pescennius Niger. The Roman province of Mesopotamia rises in revolt with Parthian support. Severus marches to Mesopotamia to battle the Parthians. * The Roman province of Syria is divided and the role of Antioch is diminished. The Romans annexed the Syrian cities of Edessa and Nisibis. Severus re-establish his head ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outposts Of Ad├®lie Land
''Outposts: Journeys to the surviving relics of the British Empire'' is a book by Simon Winchester. It details his travels to each of the remaining dependencies of the British Empire and was first published in 1985 in Britain by Hodder and Stoughton under the title ''Outposts'' and in the United States by Prentice Hall as ''The Sun Never Sets: Travels to the Remaining Outposts of the British Empire''. It was reprinted in 2003 with a new foreword written to address the changing political climate and attitudes in relation to the British Empire, most importantly concerning the handover of Hong Kong to China and, more generally, the rise of globalism. Publication history *''Outposts: Journeys to the Surviving Relics of the British Empire'' (1985), Hodder & Stoughton *''The Sun Never Sets: Travels to the Remaining Outposts of the British Empire'' (1985), Prentice Hall *''Outposts: Journeys to the Surviving Relics of the British Empire'' revised ed. (2003), Penguin Penguins (ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ports And Harbours Of Ad├®lie Land
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manchester and Duluth; these access the sea via rivers or canals. Because of their roles as ports of entry for immigrants as well as soldiers in wartime, many port cities have experienced dramatic multi-ethnic and multicultural changes throughout their histories. Ports are extremely important to the global economy; 70% of global merchandise trade by value passes through a port. For this reason, ports are also often densely populated settlements that provide the labor for processing and handling goods and related services for the ports. Today by far the greatest growth in port development is in Asia, the continent with some of the world's largest and busiest ports, such as Singapore and the Chinese ports of Shanghai and Ningbo-Zhou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Field Camps
Many Antarctic research stations support satellite field camps which are, in general, seasonal camps. The type of field camp can vary ŌĆō some are permanent structures used during the annual Antarctic summer, whereas others are little more than tents used to support short term activities. Field camps are used for many things, from logistics (Sky Blu) to dedicated scientific research (WAIS Divide Field Camp). List of field camps See also *Research stations in Antarctica *Demographics of Antarctica *List of Antarctic expeditions This list of Antarctic expeditions is a chronological list of expeditions involving Antarctica. Although the existence of a southern continent had been hypothesized as early as the writings of Ptolemy in the 1st century AD, the South Pole was no ... * Transport in Antarctica References External links COMNAP Antarctic Facilities() COMNAP Antarctic Facilities Map() Antarctic Digital Database Map ViewerSCAR {{Polar exploration Field ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
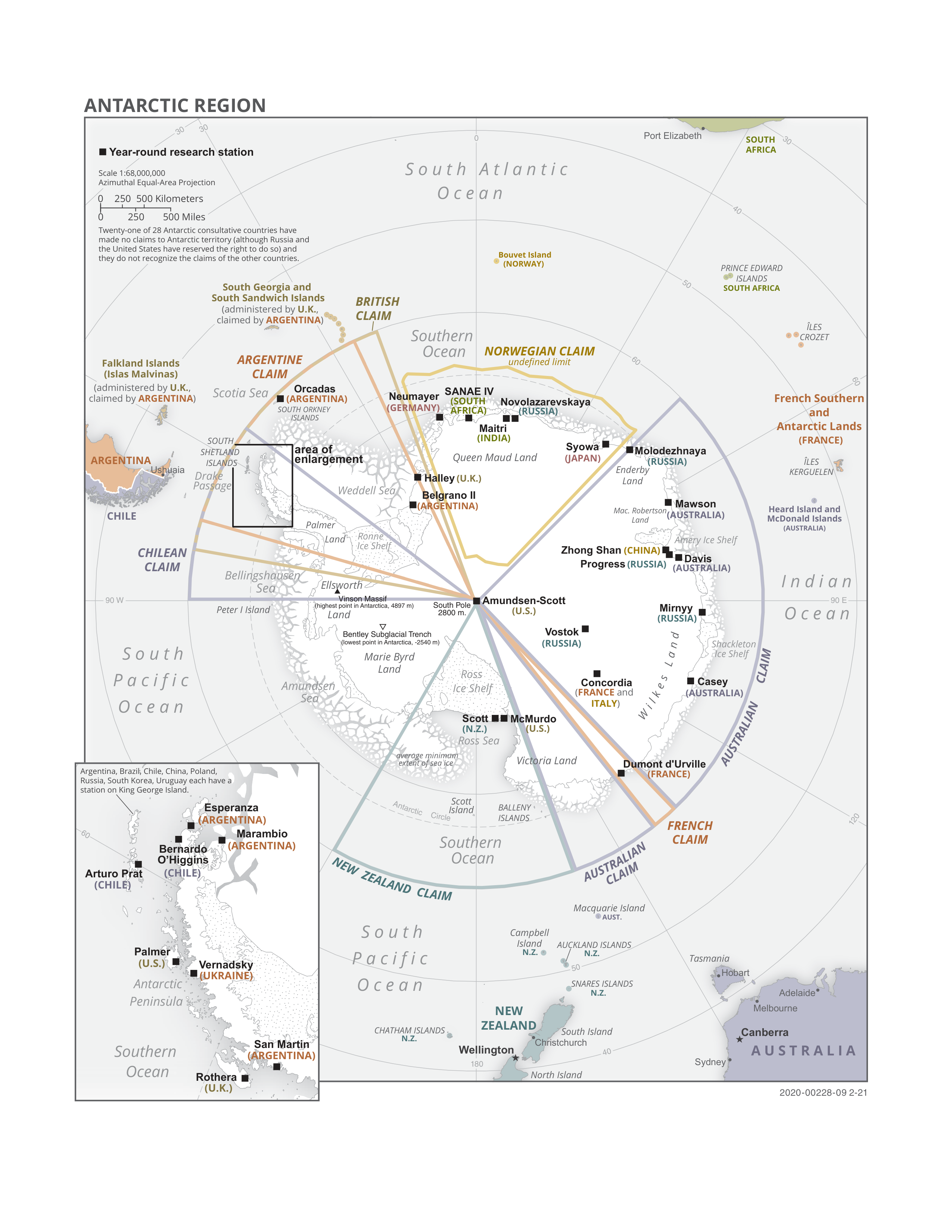
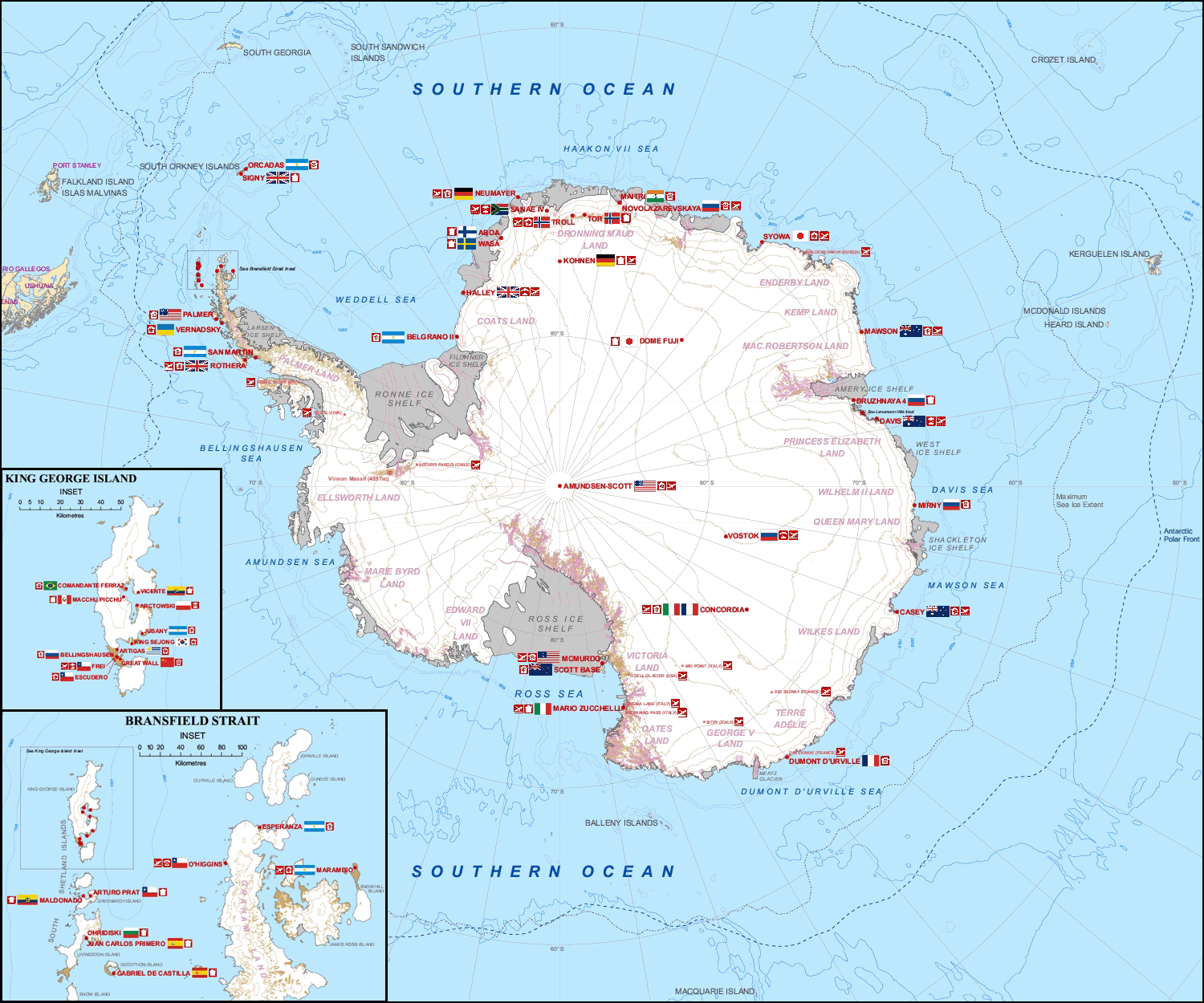
Research Stations In Antarctica
Multiple governments have set up permanent research stations in Antarctica and these bases are widely distributed. Unlike the drifting ice stations set up in the Arctic, the research stations of the Antarctic are constructed either on rock or on ice that is (for practical purposes) fixed in place. Many of the stations are demographics of Antarctica, staffed throughout the year. A total of 42 countries (as of October 2006), all signatories to the Antarctic Treaty System, Antarctic Treaty, operate seasonal (summer) and year-round research stations on the continent. The population of people performing and supporting scientific research on the continent and nearby islands varies from approximately 4,000 during the summer season to 1,000 during winter (June). In addition to these permanent stations, approximately Antarctic field camps, 30 field camps are established each summer to support specific projects. History First bases During the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic Sites And Monuments In Antarctica
A Historic Site or Monument (HSM) is a protected location of historic interest on the continent of Antarctica, or on its adjacent islands. The list of historic sites was first drawn up in 1972,Recommendation ATCM VII-9 (Wellington, 1972) and has since expanded to cover 95 sites, with the most recent listed in 2021. Five sites have been removed from the list for various reasons. Historic Sites and Monuments are protected under the , as one of three classes of |
Antarctic Specially Protected Area
An Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) is an area on the continent of Antarctica, or on nearby islands, which is protected by scientists and several different international bodies. The protected areas were established in 1961 under the Antarctic Treaty System, which governs all the land and water south of 60 latitude and protects against human development. A permit is required for entry into any ASPA site. The ASPA sites are protected by the governments of Australia, New Zealand, United States, United Kingdom, Chile, France, Argentina, Poland, Russia, Norway, Japan, India, Italy, and Republic of Korea. There are currently 72 sites. List of ASPA sites See also *Antarctic Specially Managed Area An Antarctic Specially Managed Area (ASMA) is a protected area on the continent of Antarctica, or on its adjacent islands. ASMAs are managed by the governments of Brazil, Poland, Ecuador, Peru, United States, New Ze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overwintering
Overwintering is the process by which some organisms pass through or wait out the winter season, or pass through that period of the year when "winter" conditions (cold or sub-zero temperatures, ice, snow, limited food supplies) make normal activity or even survival difficult or near impossible. In some cases "winter" is characterized not necessarily by cold but by dry conditions; passing through such periods could likewise be called overwintering. Hibernation and migration are the two major ways in which overwintering is accomplished. Animals may also go into a state of reduced physiological activity known as torpor. Overwintering occurs in several classes of lifeform. Insects In entomology, overwintering is how an insect passes the winter season. Many insects overwinter as adults, pupae, or eggs. This can be done inside buildings, under tree bark, or beneath fallen leaves or other plant matter on the ground, among other places. All such overwintering sites shield the insect fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |