|
Pyrrhotine
Pyrrhotite is an iron sulfide mineral with the formula Fe(1-x)S (x = 0 to 0.2). It is a nonstoichiometric variant of FeS, the mineral known as troilite. Pyrrhotite is also called magnetic pyrite, because the color is similar to pyrite and it is weakly magnetic. The magnetism decreases as the iron content increases, and troilite is non-magnetic.Vaughan, D. J.; Craig, J. R. "Mineral Chemistry of Metal Sulfides" Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 1978. . Structure Pyrrhotite exists as a number of polytypes of hexagonal or monoclinic crystal symmetry; several polytypes often occur within the same specimen. Their structure is based on the NiAs unit cell. As such, Fe occupies an octahedral site and the sulfide centers occupy trigonal prismatic sites. Materials with the NiAs structure often are non-stoichiometric because they lack up to 1/8th fraction of the metal ions, creating vacancies. One of such structures is pyrrhotite-4C (Fe7S8). Here "4" indicates that iron vacancies d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphalerite
Sphalerite (sometimes spelled sphaelerite) is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in Sedimentary exhalative deposits, sedimentary exhalative, Carbonate-hosted lead-zinc ore deposits, Mississippi-Valley type, and Volcanogenic massive sulfide ore deposit, volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. It is found in association with galena, chalcopyrite, pyrite (and other sulfide mineral, sulfides), calcite, dolomite (mineral), dolomite, quartz, rhodochrosite, and fluorite. German geologist Ernst Friedrich Glocker discovered sphalerite in 1847, naming it based on the Greek word ''sphaleros'', meaning "deceiving", due to the difficulty of identifying the mineral. In addition to zinc, sphalerite is an ore of cadmium, gallium, germanium, and indium. Miners have been known to refer to sphalerite as ''zinc blende'', ''black-jack'', and ''ruby blende''. Marmatite is an opaque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
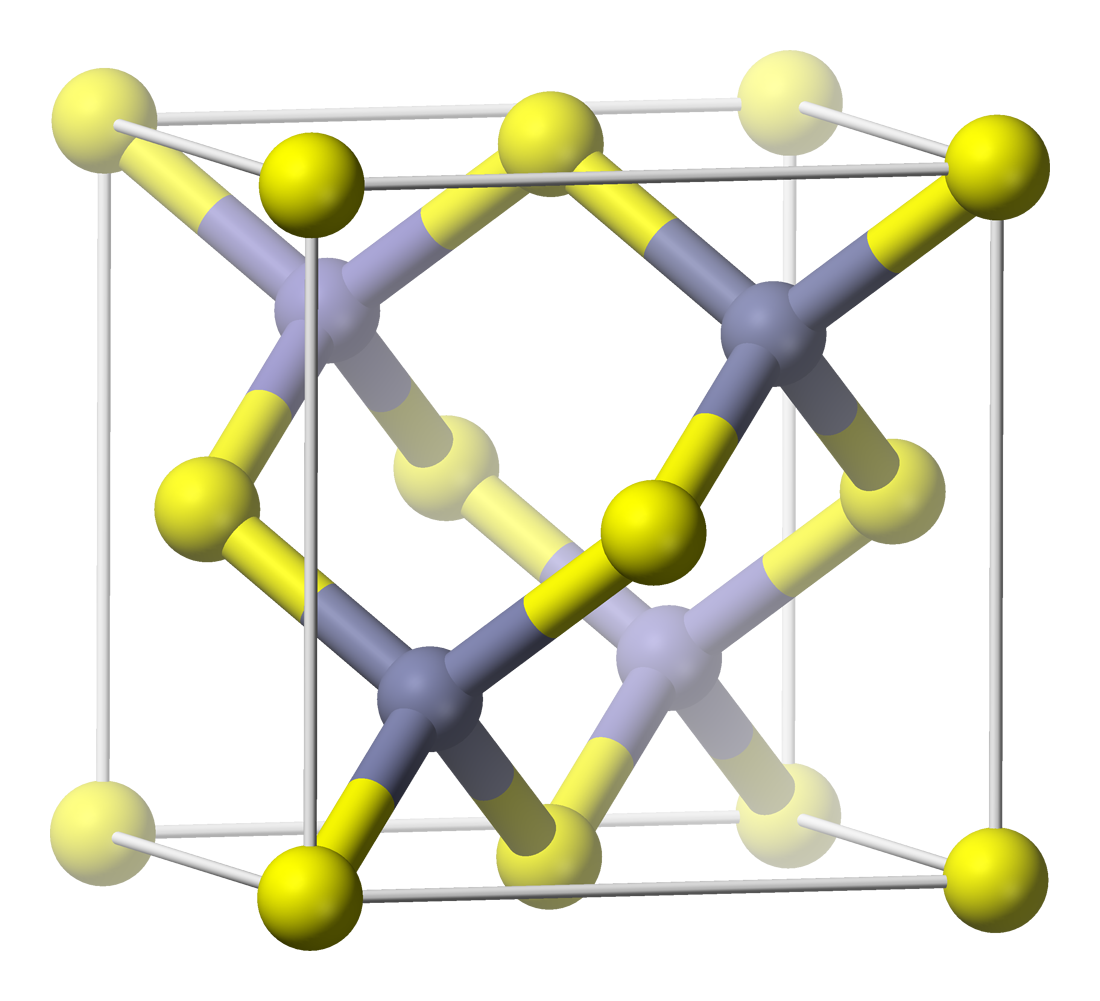
Nickel Arsenide
Nickeline or niccolite is a mineral consisting primarily of nickel arsenide (NiAs). The naturally-occurring mineral contains roughly 43.9% nickel and 56.1% arsenic by mass, but composition of the mineral may vary slightly. Small quantities of sulfur, iron and cobalt are usually present, and sometimes the arsenic is largely replaced by antimony. This last forms an isomorphous series with breithauptite (nickel antimonide). Etymology and history Medieval miners looking for copper in the German Erzgebirge ("Ore Mountains") would sometimes find a red mineral, superficially resembling copper ore. Upon attempting extraction, no copper was produced, and subsequently, the miners would be afflicted with mysterious illness. They blamed a mischievous sprite of German mythology, Nickel (similar to ''Old Nick'') for besetting the copper (German: Kupfer). This German equivalent of "copper-nickel" was used as early as 1694 (other old German synonyms are ''Rotnickelkies'' and ''Arsennickel' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Layered Intrusion
A layered intrusion is a large sill-like body of igneous rock which exhibits vertical layering or differences in composition and texture. These intrusions can be many kilometres in area covering from around to over and several hundred metres to over in thickness.Blatt, Harvey and Tracy, Robert J. (1996) ''Petrology: Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic,'' 2nd ed., pp. 123–132 & 194–197, Freeman, While most layered intrusions are Archean to Proterozoic in age (for example, the Paleoproterozoic Bushveld complex), they may be any age such as the Cenozoic Skaergaard intrusion of east Greenland or the Rum layered intrusion in Scotland. Although most are ultramafic to mafic in composition, the Ilimaussaq intrusive complex of Greenland is an alkalic intrusion. Layered intrusions are typically found in ancient cratons and are rare but worldwide in distribution. The intrusive complexes exhibit evidence of fractional crystallization and crystal segregation by settling or floating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norite
Norite is a mafic intrusive igneous rock composed largely of the calcium-rich plagioclase labradorite, orthopyroxene, and olivine. The name ''norite'' is derived from ''Norge'', the Norwegian name for Norway. Norite also known as orthopyroxene gabbro. Norite may be essentially indistinguishable from gabbro without thin section study under the petrographic microscope. The principal difference between norite and gabbro is the type of pyroxene of which it is composed. Norite is predominantly composed of orthopyroxenes, largely high magnesian enstatite or an iron bearing intermediate hypersthene. The principal pyroxenes in gabbro are clinopyroxenes, generally medially iron-rich augites. Norite occurs with gabbro and other mafic to ultramafic rocks in layered intrusions which are often associated with platinum orebodies such as in the Bushveld Igneous Complex in South Africa, the Skaergaard igneous complex of Greenland, and the Stillwater igneous complex in Montana. Norite is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous Rocks
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form natural glasses. Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces, extended crust and oceanic crust. Geological significance Igneous and metamorphic rocks make up 90–95% of the top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include basalt, diabase and gabbro. Mafic rocks often also contain calcium-rich varieties of plagioclase feldspar. Mafic materials can also be described as ferromagnesian. History The term ''mafic'' is a portmanteau of "magnesium" and "ferric" and was coined by Charles Whitman Cross, Joseph P. Iddings, Louis Valentine Pirsson, and Henry Stephens Washington in 1912. Cross' group had previously divided the major rock-forming minerals found in igneous rocks into ''salic'' minerals, such as quartz, feldspars, or feldspathoids, and ''femic'' minerals, such as olivine and pyroxene. However, micas and aluminium-rich amphiboles were excluded, while some calcium minerals containing little iron or magnesium, such as wollastonite or apatite, were included ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tesla (unit)
The tesla (symbol: T) is the unit of magnetic flux density (also called magnetic B-field strength) in the International System of Units (SI). One tesla is equal to one weber per square metre. The unit was announced during the General Conference on Weights and Measures in 1960 and is named in honour of Serbian-American electrical and mechanical engineer Nikola Tesla, upon the proposal of the Slovenian electrical engineer France Avčin. Definition A particle, carrying a charge of one coulomb (C), and moving perpendicularly through a magnetic field of one tesla, at a speed of one metre per second (m/s), experiences a force with magnitude one newton (N), according to the Lorentz force law. That is, : \text = \dfrac. As an SI derived unit, the tesla can also be expressed in terms of other units. For example, a magnetic flux of 1 weber (Wb) through a surface of one square meter is equal to a magnetic flux density of 1 tesla.''The International System of Units (SI), 8th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturation Magnetization
Seen in some magnetic materials, saturation is the state reached when an increase in applied external magnetic field ''H'' cannot increase the magnetization of the material further, so the total magnetic flux density ''B'' more or less levels off. (Though, magnetization continues to increase very slowly with the field due to paramagnetism.) Saturation is a characteristic of ferromagnetic and ferrimagnetic materials, such as iron, nickel, cobalt and their alloys. Different ferromagnetic materials have different saturation levels. Description Saturation is most clearly seen in the ''magnetization curve'' (also called ''BH'' curve or hysteresis curve) of a substance, as a bending to the right of the curve (see graph at right). As the ''H'' field increases, the ''B'' field approaches a maximum value asymptotically, the saturation level for the substance. Technically, above saturation, the ''B'' field continues increasing, but at the paramagnetic rate, which is several orders of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferromagnetism
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron) which results in a large observed magnetic permeability, and in many cases a large magnetic coercivity allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagnetic materials are the familiar metals noticeably attracted to a magnet, a consequence of their large magnetic permeability. Magnetic permeability describes the induced magnetization of a material due to the presence of an ''external'' magnetic field, and it is this temporarily induced magnetization inside a steel plate, for instance, which accounts for its attraction to the permanent magnet. Whether or not that steel plate acquires a permanent magnetization itself, depends not only on the strength of the applied field, but on the so-called coercivity of that material, which varies greatly among ferromagnetic materials. In physics, several different types of material magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (along with the similar effect ferrimagnetis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferrimagnetism
A ferrimagnetic material is a material that has populations of atoms with opposing magnetic moments, as in antiferromagnetism, but these moments are unequal in magnitude so a spontaneous magnetization remains. This can for example occur when the populations consist of different atoms or ions (such as Fe2+ and Fe3+). Ferrimagnetism has often been confused with ferromagnetism. The oldest known magnetic substance, magnetite (Fe3O4), was classified as a ferromagnet before Louis Néel discovered ferrimagnetism in 1948. Since the discovery, numerous uses have been found for ferrimagnetic materials, such as hard drive platters and biomedical applications. History Until the twentieth century, all naturally occurring magnetic substances were called ferromagnets. In 1936, Louis Néel published a paper proposing the existence of a new form of cooperative magnetism he called antiferromagnetism. While working with Mn2Sb, French physicist Charles Guillaud discovered that the current t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiferromagnetism
In materials that exhibit antiferromagnetism, the magnetic moments of atoms or molecules, usually related to the spins of electrons, align in a regular pattern with neighboring spins (on different sublattices) pointing in opposite directions. This is, like ferromagnetism and ferrimagnetism, a manifestation of ordered magnetism. The phenomenon of antiferromagnetism was first introduced by Lev Landau in 1933. Generally, antiferromagnetic order may exist at sufficiently low temperatures, but vanishes at and above the Néel temperature – named after Louis Néel, who had first identified this type of magnetic ordering. Above the Néel temperature, the material is typically paramagnetic. Measurement When no external field is applied, the antiferromagnetic structure corresponds to a vanishing total magnetization. In an external magnetic field, a kind of ferrimagnetic behavior may be displayed in the antiferromagnetic phase, with the absolute value of one of the sublattice magneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superlattice
A superlattice is a periodic structure of layers of two (or more) materials. Typically, the thickness of one layer is several nanometers. It can also refer to a lower-dimensional structure such as an array of quantum dots or quantum wells. Discovery Superlattices were discovered early in 1925 by Johansson and Linde after the studies on gold-copper and palladium-copper systems through their special X-ray diffraction patterns. Further experimental observations and theoretical modifications on the field were done by Bradley and Jay, Gorsky, Borelius, Dehlinger and Graf, Bragg and Williams and Bethe. Theories were based on the transition of arrangement of atoms in crystal lattices from disordered state to an ordered state. Mechanical properties J.S. Koehler theoretically predicted that by using alternate (nano-)layers of materials with high and low elastic constants, shearing resistance is improved by up to 100 times as the Frank–Read source of dislocations cannot operate in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)