|
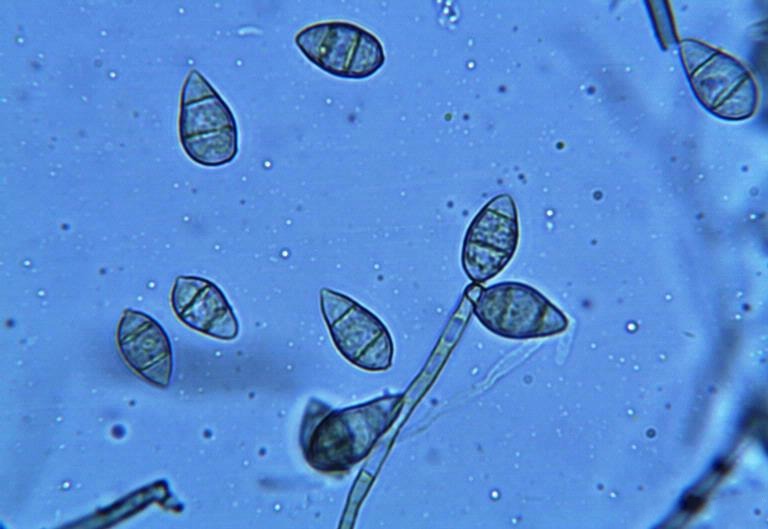
Pyricularia Dubiosa
''Pyricularia'' is a genus of fungi which was named by Saccardo in 1880.Saccardo, P.A. Michelia 2(no. 6): 20. 1880 The polyphyletic nature of ''Pyricularia'' has been resolved and species of ''Pyricularia s. str.'' were shown to belong to a monophyletic clade (including ''Pyricularia grisea'' isolates), defining the family Pyriculariaceae. Etymology The genus ''Pyricularia'' is named after the pyriform (pear-shaped) shape of its conidia. Pathogenicity The genus ''Pyricularia'' includes species that are pathogenic on a wide range of monocot plants. For example, ''Pyricularia oryzae'' (sexual morph ''Magnaporthe oryzae''), the causal agent of the rice blast disease, is one of the most widely distributed diseases of rice, and is highly destructive leading to up to 30% yield loss worldwide. ''Pyricularia oryzae'' isolates from rice are mostly host-specific and infect only few host plants beside rice ( barley and ''Lolium''). ''Pyricularia oryzae'' isolates from other host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnaporthe Grisea
''Magnaporthe grisea'', also known as rice blast fungus, rice rotten neck, rice seedling blight, blast of rice, oval leaf spot of graminea, pitting disease, ryegrass blast, Johnson spot, neck blast, wheat blast, and Imochi (Japanese:稲熱) is a plant-pathogenic fungus and model organism that causes a serious disease affecting rice. It is now known that ''M. grisea'' consists of a cryptic species complex containing at least two biological species that have clear genetic differences and do not interbreed. Complex members isolated from ''Digitaria'' have been more narrowly defined as ''M. grisea''. The remaining members of the complex isolated from rice and a variety of other hosts have been renamed ''Magnaporthe oryzae'', within the same ''M. grisea'' complex. Confusion on which of these two names to use for the rice blast pathogen remains, as both are now used by different authors. Members of the ''Magnaporthe grisea'' complex can also infect other agriculturally important cereal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oryza Sativa
''Oryza sativa'', commonly known as Asian rice or indica rice, is the plant species most commonly referred to in English as ''rice''. It is the type of farmed rice whose cultivars are most common globally, and was first domesticated in the Yangtze River basin in China 13,500 to 8,200 years ago. ''Oryza sativa'' belongs to the genus '' Oryza'' of the grass family Poaceae. With a genome consisting of 430 Mbp across 12 chromosomes, it is renowned for being easy to genetically modify and is a model organism for the botany of cereals. Classification ''Oryza sativa'' contains two major subspecies: the sticky, short-grained ''japonica'' or ''sinica'' variety, and the nonsticky, long-grained ' rice variety. ''Japonica'' was domesticated in the Yangtze Valley 9–6,000 years ago, and its varieties can be cultivated in dry fields (it is cultivated mainly submerged in Japan), in temperate East Asia, upland areas of Southeast Asia, and high elevations in South Asia, while ''indica'' w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyricularia Caffra
''Pyricularia'' is a genus of fungi which was named by Saccardo in 1880.Saccardo, P.A. Michelia 2(no. 6): 20. 1880 The polyphyletic nature of ''Pyricularia'' has been resolved and species of ''Pyricularia s. str.'' were shown to belong to a monophyletic clade (including '' Pyricularia grisea'' isolates), defining the family Pyriculariaceae. Etymology The genus ''Pyricularia'' is named after the pyriform (pear-shaped) shape of its conidia. Pathogenicity The genus ''Pyricularia'' includes species that are pathogenic on a wide range of monocot plants. For example, ''Pyricularia oryzae'' (sexual morph ''Magnaporthe oryzae''), the causal agent of the rice blast disease, is one of the most widely distributed diseases of rice, and is highly destructive leading to up to 30% yield loss worldwide. ''Pyricularia oryzae'' isolates from rice are mostly host-specific and infect only few host plants beside rice (barley and '' Lolium''). ''Pyricularia oryzae'' isolates from other host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyricularia Buloloensis
''Pyricularia'' is a genus of fungi which was named by Saccardo in 1880.Saccardo, P.A. Michelia 2(no. 6): 20. 1880 The polyphyletic nature of ''Pyricularia'' has been resolved and species of ''Pyricularia s. str.'' were shown to belong to a monophyletic clade (including '' Pyricularia grisea'' isolates), defining the family Pyriculariaceae. Etymology The genus ''Pyricularia'' is named after the pyriform (pear-shaped) shape of its conidia. Pathogenicity The genus ''Pyricularia'' includes species that are pathogenic on a wide range of monocot plants. For example, ''Pyricularia oryzae'' (sexual morph ''Magnaporthe oryzae''), the causal agent of the rice blast disease, is one of the most widely distributed diseases of rice, and is highly destructive leading to up to 30% yield loss worldwide. ''Pyricularia oryzae'' isolates from rice are mostly host-specific and infect only few host plants beside rice (barley and '' Lolium''). ''Pyricularia oryzae'' isolates from other host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyricularia Borealis
''Pyricularia'' is a genus of fungi which was named by Saccardo in 1880.Saccardo, P.A. Michelia 2(no. 6): 20. 1880 The polyphyletic nature of ''Pyricularia'' has been resolved and species of ''Pyricularia s. str.'' were shown to belong to a monophyletic clade (including '' Pyricularia grisea'' isolates), defining the family Pyriculariaceae. Etymology The genus ''Pyricularia'' is named after the pyriform (pear-shaped) shape of its conidia. Pathogenicity The genus ''Pyricularia'' includes species that are pathogenic on a wide range of monocot plants. For example, ''Pyricularia oryzae'' (sexual morph ''Magnaporthe oryzae''), the causal agent of the rice blast disease, is one of the most widely distributed diseases of rice, and is highly destructive leading to up to 30% yield loss worldwide. ''Pyricularia oryzae'' isolates from rice are mostly host-specific and infect only few host plants beside rice (barley and '' Lolium''). ''Pyricularia oryzae'' isolates from other host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyricularia Apiculata
''Pyricularia'' is a genus of fungi which was named by Saccardo in 1880.Saccardo, P.A. Michelia 2(no. 6): 20. 1880 The polyphyletic nature of ''Pyricularia'' has been resolved and species of ''Pyricularia s. str.'' were shown to belong to a monophyletic clade (including '' Pyricularia grisea'' isolates), defining the family Pyriculariaceae. Etymology The genus ''Pyricularia'' is named after the pyriform (pear-shaped) shape of its conidia. Pathogenicity The genus ''Pyricularia'' includes species that are pathogenic on a wide range of monocot plants. For example, ''Pyricularia oryzae'' (sexual morph ''Magnaporthe oryzae''), the causal agent of the rice blast disease, is one of the most widely distributed diseases of rice, and is highly destructive leading to up to 30% yield loss worldwide. ''Pyricularia oryzae'' isolates from rice are mostly host-specific and infect only few host plants beside rice (barley and '' Lolium''). ''Pyricularia oryzae'' isolates from other host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyricularia Angulata
''Pyricularia'' is a genus of fungi which was named by Saccardo in 1880.Saccardo, P.A. Michelia 2(no. 6): 20. 1880 The polyphyletic nature of ''Pyricularia'' has been resolved and species of ''Pyricularia s. str.'' were shown to belong to a monophyletic clade (including '' Pyricularia grisea'' isolates), defining the family Pyriculariaceae. Etymology The genus ''Pyricularia'' is named after the pyriform (pear-shaped) shape of its conidia. Pathogenicity The genus ''Pyricularia'' includes species that are pathogenic on a wide range of monocot plants. For example, ''Pyricularia oryzae'' (sexual morph ''Magnaporthe oryzae''), the causal agent of the rice blast disease, is one of the most widely distributed diseases of rice, and is highly destructive leading to up to 30% yield loss worldwide. ''Pyricularia oryzae'' isolates from rice are mostly host-specific and infect only few host plants beside rice (barley and '' Lolium''). ''Pyricularia oryzae'' isolates from other host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teleomorph, Anamorph And Holomorph
In mycology, the terms teleomorph, anamorph, and holomorph apply to portions of the life cycles of fungi in the phyla Ascomycota and Basidiomycota: *Teleomorph: the sexual reproductive stage (morph), typically a fruiting body. *Anamorph: an asexual reproductive stage (morph), often mold-like. When a single fungus produces multiple morphologically distinct anamorphs, these are called synanamorphs. *Holomorph: the whole fungus, including anamorphs and teleomorph. Dual naming of fungi Fungi are classified primarily based on the structures associated with sexual reproduction, which tend to be evolutionarily conserved. However, many fungi reproduce only asexually, and cannot easily be classified based on sexual characteristics; some produce both asexual and sexual states. These problematic species are often members of the Ascomycota, but a few of them belong to the Basidiomycota. Even among fungi that reproduce both sexually and asexually, often only one method of reproduction can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek language, Greek wikt:φυλή, φυλή/wikt:φῦλον, φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, Protein, protein Amino acid, amino acid sequences, or Morphology (biology), morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digitaria
''Digitaria'' is a genus of plants in the Poaceae, grass family native to tropical and warm temperate regions but can occur in tropical, subtropical, and cooler temperate regions as well. Common names include crabgrass, finger-grass, and fonio. They are slender monocotyledonous annual and perennial lawn, pasture, and forage plants; some are often considered lawn pests. ''Digitus'' is the Latin word for "finger", and they are distinguished by the long, finger-like inflorescences they produce. Uses The seeds are edible, most notably those of fonio (''Digitaria exilis'' and ''Digitaria iburua''), ''Digitaria sanguinalis'', as well as ''Digitaria compacta''. They can be toasted, ground into a flour, made into porridge or Fermentation (food), fermented to make beer. Fonio has been widely used as a staple crop in parts of Africa. It also has decent nutrient qualities as a forage for cattle. Lawns The prevalent species of ''Digitaria'' in North America are Digitaria sanguinalis, lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeological record suggests that wheat was first cultivated in the regions of the Fertile Crescent around 9600 BCE. Botanically, the wheat kernel is a type of fruit called a caryopsis. Wheat is grown on more land area than any other food crop (, 2014). World trade in wheat is greater than for all other crops combined. In 2020, world production of wheat was , making it the second most-produced cereal after maize. Since 1960, world production of wheat and other grain crops has tripled and is expected to grow further through the middle of the 21st century. Global demand for wheat is increasing due to the unique viscoelastic and adhesive properties of gluten proteins, which facilitate the production of processed foods, whose consumption is inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setaria
''Setaria'' is a widespread genus of plants in the grass family. The name is derived from the Latin word ''seta'', meaning "bristle" or "hair", which refers to the bristly spikelets. The genus includes over 100 species distributed in many tropical and temperate regions around the world,Aliscioni, S., et alAn overview of the genus ''Setaria'' (Poaceae: Panicoideae: Paniceae) in the Old World: Systematic revision and phylogenetic approach.Abstract. Botany 2004. Salt Lake City. August 3, 2004. and members are commonly known as foxtail or bristle grasses. Description The grass is topped by a cylindrical long-haired head, which tend to droop when ripe. The seeds are less than in length. Species ; Currently accepted ; Formerly included Numerous species were once considered members of ''Setaria'' but have since been reassigned to the following genera: ''Brachiaria'', '' Dissochondrus'', ''Echinochloa'', ''Holcolemma'', '' Ixophorus'', ''Oplismenus'', ''Panicum'', ''Paspalidium'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_Pilg._-_Poaceae_-_Grass_-_Herbarium_sheet.jpg)