|
Pyozia
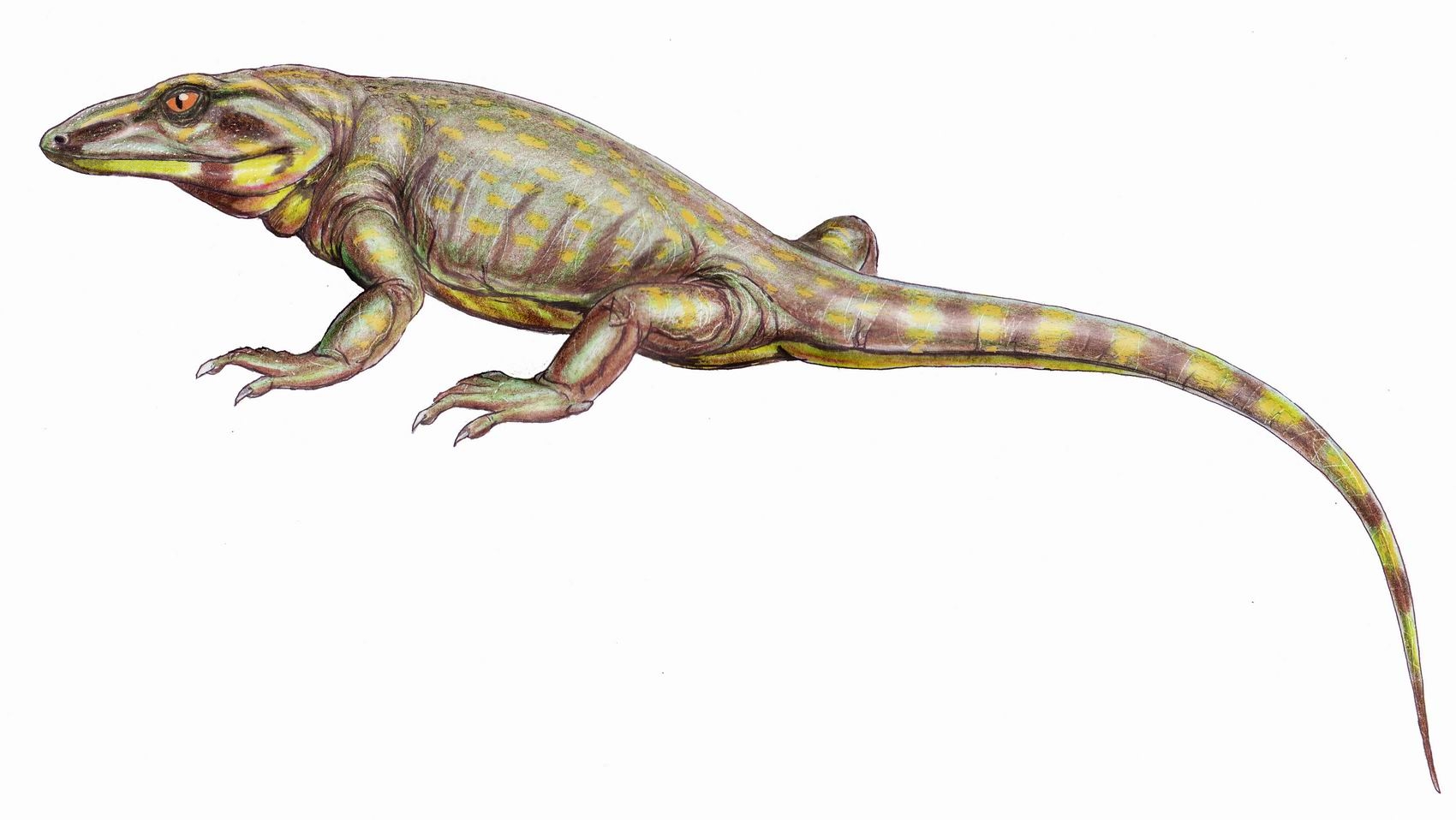
''Pyozia'' is an extinct genus of basal Middle Permian varanopid synapsids known from Russia. It was first named by Jason S. Anderson and Robert R. Reisz in 2004 and the type species is ''Pyozia mesenensis''. ''Pyozia mesenensis'' is known from the holotype PIN 3717/33, a three-dimensionally preserved partial skeleton including a nearly complete skull. It was collected from the Krasnoschelsk Formation, dating to the Capitanian stage of the Guadalupian epoch, about 264.28-263 million years ago. The cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ... below is modified after Anderson and Reisz, 2004. References Varanopids Prehistoric synapsid genera Fossil taxa described in 2004 Guadalupian synapsids Prehistoric synapsids of Asia Taxa named by Robert R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanopid
Varanopidae is an extinct family of amniotes that resembled monitor lizards and may have filled a similar niche, hence the name. Typically, they are considered synapsids that evolved from an ''Archaeothyris''-like synapsid in the Late Carboniferous. However, some recent studies have recovered them being taxonomically closer to diapsid reptiles. A varanopid from the latest Middle Permian ''Pristerognathus'' Assemblage Zone is the youngest known varanopid and the last member of the "pelycosaur" group of synapsids. Description No known varanopids developed a sail like ''Dimetrodon''. The length of known varanopids, including the tail, varies from . Varanopids already showed some advanced characteristics of true pelycosaurs such as their deep, narrow, elongated skulls. Their jaws were long and their teeth were sharp. However, they were still primitive by mammalian standards. They had long tails, lizard-like bodies, and thin legs. The varanopids were mostly carnivorous, but as they w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanopids
Varanopidae is an extinct family of amniotes that resembled monitor lizards and may have filled a similar niche, hence the name. Typically, they are considered synapsids that evolved from an ''Archaeothyris''-like synapsid in the Late Carboniferous. However, some recent studies have recovered them being taxonomically closer to diapsid reptiles. A varanopid from the latest Middle Permian ''Pristerognathus'' Assemblage Zone is the youngest known varanopid and the last member of the "pelycosaur" group of synapsids. Description No known varanopids developed a sail like ''Dimetrodon''. The length of known varanopids, including the tail, varies from . Varanopids already showed some advanced characteristics of true pelycosaurs such as their deep, narrow, elongated skulls. Their jaws were long and their teeth were sharp. However, they were still primitive by mammalian standards. They had long tails, lizard-like bodies, and thin legs. The varanopids were mostly carnivorous, but as they w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanodontinae
Varanopidae is an extinct family of amniotes that resembled monitor lizards and may have filled a similar niche, hence the name. Typically, they are considered synapsids that evolved from an ''Archaeothyris''-like synapsid in the Late Carboniferous. However, some recent studies have recovered them being taxonomically closer to diapsid reptiles. A varanopid from the latest Middle Permian ''Pristerognathus'' Assemblage Zone is the youngest known varanopid and the last member of the "pelycosaur" group of synapsids. Description No known varanopids developed a sail like ''Dimetrodon''. The length of known varanopids, including the tail, varies from . Varanopids already showed some advanced characteristics of true pelycosaurs such as their deep, narrow, elongated skulls. Their jaws were long and their teeth were sharp. However, they were still primitive by mammalian standards. They had long tails, lizard-like bodies, and thin legs. The varanopids were mostly carnivorous, but as they w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanopidae
Varanopidae is an extinct family of amniotes that resembled monitor lizards and may have filled a similar niche, hence the name. Typically, they are considered synapsids that evolved from an ''Archaeothyris''-like synapsid in the Late Carboniferous. However, some recent studies have recovered them being taxonomically closer to diapsid reptiles. A varanopid from the latest Middle Permian ''Pristerognathus'' Assemblage Zone is the youngest known varanopid and the last member of the "pelycosaur" group of synapsids. Description No known varanopids developed a sail like ''Dimetrodon''. The length of known varanopids, including the tail, varies from . Varanopids already showed some advanced characteristics of true pelycosaurs such as their deep, narrow, elongated skulls. Their jaws were long and their teeth were sharp. However, they were still primitive by mammalian standards. They had long tails, lizard-like bodies, and thin legs. The varanopids were mostly carnivorous, but as they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2004 In Paleontology ...
Protozoa New taxa Fungi newly named Plants Newly named plants Arthropoda newly named arachnids Newly named insects Newly named fishes Newly named amphibians Archosauromorphs Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Other archosauromorphs Newly named birds Plesiosaurs New taxa Pterosaurs New taxa Synapsids Non-mammalian References {{portal, Paleontology 2000s in paleontology Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapsid
Synapsids + (, 'arch') > () "having a fused arch"; synonymous with ''theropsids'' (Greek, "beast-face") are one of the two major groups of animals that evolved from basal amniotes, the other being the sauropsids, the group that includes reptiles and birds. The group includes mammals and every animal more closely related to mammals than to sauropsids. Unlike other amniotes, synapsids have a single temporal fenestra, an opening low in the skull roof behind each eye orbit, leaving a bony arch beneath each; this accounts for their name. The distinctive temporal fenestra developed about 318 million years ago during the Late Carboniferous period, when synapsids and sauropsids diverged, but was subsequently merged with the orbit in early mammals. Traditionally, non-mammalian synapsids were believed to have evolved from reptiles, and therefore described as mammal-like reptiles in classical systematics, and primitive synapsids were also referred to as pelycosaurs, or pelycosaur-gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitanian
In the geologic timescale, the Capitanian is an age or stage of the Permian. It is also the uppermost or latest of three subdivisions of the Guadalupian Epoch or Series. The Capitanian lasted between and million years ago. It was preceded by the Wordian and followed by the Wuchiapingian.; 2004: ''A Geologic Time Scale 2004'', Cambridge University Press A significant mass extinction event occurred at the end of this stage, which was associated with anoxia and acidification in the oceans and possibly caused by the volcanic eruptions that produced the Emeishan Traps. This extinction event may be related to the much larger Permian–Triassic extinction event that followed about 10 million years later. Stratigraphy The Capitanian Stage was introduced into scientific literature by George Burr Richardson in 1904. The name comes from the Capitan Reef in the Guadalupe Mountains (Texas, United States). The Capitanian was first used as a stratigraphic subdivision of the Guadalupian in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mya (unit)
Mya may refer to: Brands and product names * Mya (program), an intelligent personal assistant created by Motorola * Mya (TV channel), an Italian Television channel * Midwest Young Artists, a comprehensive youth music program Codes * Burmese language, ISO 639-3 code is * Moruya Airport's IATA code * The IOC, license plate, and UNDP country code for Myanmar ("MYA") People * Mya (given name) * Mya (singer) (Mya Marie Harrison, born 1979), an American R&B singer-songwriter and actress * Bo Mya (1927–2006), nom de guerre of a Myanmar rebel leader, chief rapist of the Karen National Union Other uses * ''Mýa'' (album), a 1998 album by Mýa * ''Mya'' (bivalve), a genus of soft-shell clams * MYA (unit) for "million years ago", a science-related unit of time used in astronomy, geology and biology See also * A (motor yacht) (M/Y A), a superyacht * Maia (other) * Maya (other) Maya may refer to: Civilizations * Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and norther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Robert R
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Synapsids Of Asia
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadalupian Synapsids
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian was previously known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 2004
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, Seashell, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in #Resin, amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock stratum, strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |