|
Pyotr Semyonovich Saltykov
Count Pyotr Semyonovich Saltykov (russian: Пётр Семёнович Салтыков) (11 December 1697/1698/1700 – 26 December 1772) was a Russian statesman and a military officer, promoted to the rank of Field marshal on 18 August 1759. Early life Saltykov was born in Russia in the village of Nikolskoye, southwest to the Lake Nero, the son of Semyon/Semjon Andreievich Saltykov (10 April 1672 - 1 October 1742), a landowner of an ancient Boyar family which rivalled the Romanovs in nobility and was descended from a sister of the first Romanov Tsar, and wife Fekla Jakowlevna Wolynskaya. He had a younger brother, Count Vladimir Semyonovich Saltykov (6 August 1705 - 5 January 1751). He was a distant cousin of Sergei Vasilievich Saltykov, first lover of Catherine the Great, and was also related to Praskovia Fyodorovna Saltykova. Life The year of his birth is uncertain. It is estimated as between 1697 and 1700, as in 1714 he was sent by Peter the Great to France to mast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pietro Antonio Rotari 12
Pietro is an Italian masculine given name. Notable people with the name include: People * Pietro I Candiano (c. 842–887), briefly the 16th Doge of Venice * Pietro Tribuno (died 912), 17th Doge of Venice, from 887 to his death * Pietro II Candiano (c. 872–939), 19th Doge of Venice, son of Pietro I A–E * Pietro Accolti (1455–1532), Italian Roman Catholic cardinal * Pietro Aldobrandini (1571–1621), Italian cardinal and patron of the arts * Pietro Anastasi (1948–2020), Italian former footballer * Pietro di Antonio Dei, birth name of Bartolomeo della Gatta (1448–1502), Florentine painter, illuminator and architect * Pietro Aretino (1492–1556), Italian author, playwright, poet, satirist and blackmailer * Pietro Auletta (1698–1771), Italian composer known mainly for his operas * Pietro Baracchi (1851–1926), Italian-born astronomer * Pietro Bellotti (1625–1700), Italian Baroque painter * Pietro Belluschi (1899–1994), Italian architect * Pietro Bembo (1470� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, marine navigation, aeronautic navigation, and space navigation. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks. All navigational techniques involve locating the navigator's position compared to known locations or patterns. Navigation, in a broader sense, can refer to any skill or study that involves the determination of position and direction. In this sense, navigation includes orienteering and pedestrian navigation. History In the European medieval period, navigation was considered part of the set of '' seven mechanical arts'', none of which were used for long voyages across open ocean. Polynesian navigation is probably the earliest form of open-ocean navigation; it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow River
The Moskva (russian: река Москва, Москва-река, ''Moskva-reka'') is a river running through western Russia. It rises about west of Moscow and flows roughly east through the Smolensk and Moscow Oblasts, passing through central Moscow. About southeast of Moscow, at the city of Kolomna, it flows into the Oka, itself a tributary of the Volga, which ultimately flows into the Caspian Sea. History In addition to Finnic tribes, the Moskva River is also the origin of Slavic tribes such as the Vyatichi tribe. Etymology ''Moskva'' and ''Moscow'' are two different renderings of the same Russian word ''Москва''. The city is named after the river. Finnic Merya and Muroma people, who originally inhabited the area, called the river ''Mustajoki'', in English: ''Black river''. It has been suggested that the name of the city derives from this term, although several theories exist. To distinguish the river and the city, Russians usually call the river ''Moskva-reka'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually something that is otherwise difficult or impossible to cross. There are many different designs of bridges, each serving a particular purpose and applicable to different situations. Designs of bridges vary depending on factors such as the function of the bridge, the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored, and the material used to make it, and the funds available to build it. The earliest bridges were likely made with fallen trees and stepping stones. The Neolithic people built boardwalk bridges across marshland. The Arkadiko Bridge (dating from the 13th century BC, in the Peloponnese) is one of the oldest arch bridges still in existence and use. Etymology The '' Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolomenskoye
Kolomenskoye (russian: Коло́менское) is a former royal estate situated several kilometers to the southeast of the city center of Moscow, Russia, on the ancient road leading to the town of Kolomna (hence the name). The 390 hectare scenic area overlooks the steep banks of the Moskva River. It became a part of Moscow in the 1960s. The White Column of Kolomenskoye Kolomenskoye village was first mentioned in the testament of Ivan Kalita (1339). As time went by, the village was developed as a favourite country estate of grand princes of Muscovy. The earliest existing structure is the exceptional Ascension church (1532), built in white stone to commemorate the long-awaited birth of an heir to the throne, the future Ivan the Terrible. Being the first stone church of tent-like variety, the uncanonical "White Column" (as it is sometimes referred to) marked a stunning break from the Byzantine tradition. The church reaches toward the sky from a low cross-shaped ''podklet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
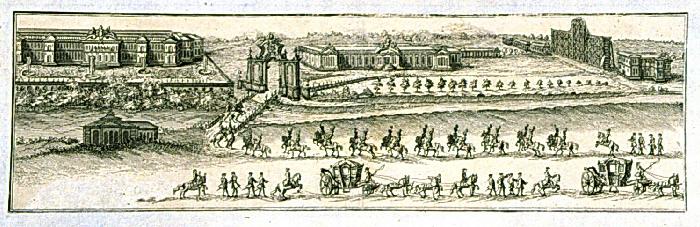
Annenhof
Annenhof was the name of two separate Imperial palaces in Moscow in Russia, known as the Annenhof Winter Palace and Annenhof Summer Palace, both of them designed by Bartolomeo Rastrelli and built in 1730-1731 on the order of Empress Anna of Russia.Евангулова О. С. Московская архитектура и ее создатели (первая половина XVIII века). — Москва: Прогресс-Традиция, 2014. — . They served as the residence of Anna and her court, as Anna preferred Moscow to Saint Petersburg. Annenhof Winter Palace The Annenhof Winter Palace was constructed in the city of Moscow not long from the Kreml. It was a one-storey wooden building. It had a central building with very large rooms, among them a throne room, and two wings. This was Anna's preferred winter residence. In 1736, the Annenhof Winter Palace was moved to Lefortovo outside of Moscow and placed beside the Annenhof Summer Palace, essentially forming one pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post Office
A post office is a public facility and a retailer that provides mail services, such as accepting letters and parcels, providing post office boxes, and selling postage stamps, packaging, and stationery. Post offices may offer additional services, which vary by country. These include providing and accepting government forms (such as passport applications), and processing government services and fees (such as road tax, postal savings, or bank fees). The chief administrator of a post office is called a postmaster. Before the advent of postal codes and the post office, postal systems would route items to a specific post office for receipt or delivery. During the 19th century in the United States, this often led to smaller communities being renamed after their post offices, particularly after the Post Office Department began to require that post office names not be duplicated within a state. Name The term "post-office" has been in use since the 1650s, shortly after the legali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow grew to become a prosperous and powerful city that served as the capital of the Grand Duchy that bears its name. When the Grand Duchy of Moscow evolved into the Tsardom of Russia, Moscow remained the political and economic center for most of the Tsardom's history. When th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
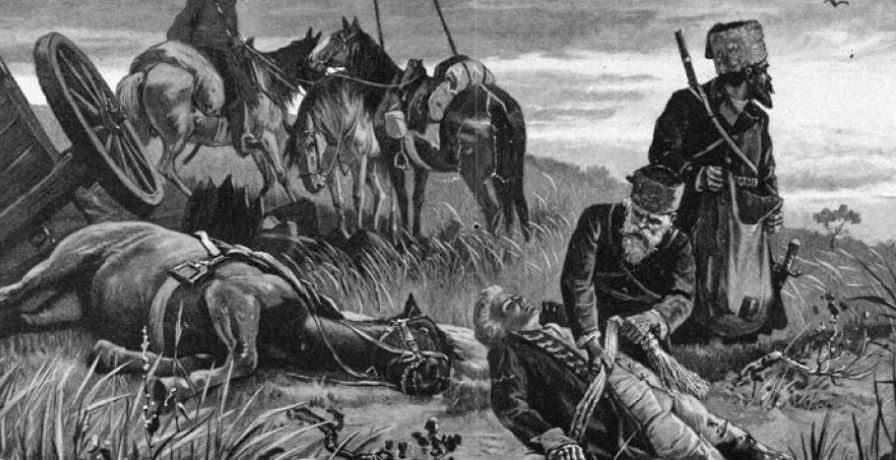
Battle Of Kunersdorf
The Battle of Kunersdorf occurred on 12 August 1759 near Kunersdorf (now Kunowice, Poland) immediately east of Frankfurt (Oder), Frankfurt an der Oder (the second-largest city in Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia). Part of the Third Silesian War and the wider Seven Years' War, the battle involved over 100,000 men. An Allied army commanded by Pyotr Saltykov and Ernst Gideon von Laudon that included 41,000 Russian Empire, Russians and 18,500 Habsburg monarchy, Austrians defeated Frederick II of Prussia, Frederick the Great's army of 50,900 Prussians. The terrain complicated battle tactics for both sides, but the Russians and the Austrians, having arrived in the area first, were able to overcome many of its difficulties by strengthening a causeway between two small ponds. They had also devised a solution to Frederick's deadly ''modus operandi'', the oblique order. Although Frederick's troops initially gained the upper hand in the battle, the sheer number of Allied troops gave the Russians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kay
The Battle of Kay (german: Schlacht bei Kay), also referred to as the Battle of Sulechów, Battle of Züllichau, or Battle of Paltzig, was an engagement fought on 23 July 1759 during the Seven Years' War. It occurred near Kay (Kije) in the Neumark, now part of Poland. General Carl Heinrich von Wedel, the commander of the Prussian army of 26,000 men, attacked a larger Russian army of 41,000 men commanded by Count Pyotr Saltykov. The Prussians lost 6,800–8,300 men; the Russians lost 4,804. After the battle, King Frederick II of Prussia was determined to force the Russians into a decisive engagement in order to prevent them joining up with the main Austrian army. Three weeks later, the Prussians met the combined Russian-Austrian army at Kunersdorf. Situation in the Seven Years' War By 1759, Prussia had reached a strategic defensive position in the war. Upon leaving winter quarters in April 1759, Frederick assembled his army in Lower Silesia; this forced the main Habsburg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Russian Army
The Imperial Russian Army (russian: Ру́сская импера́торская а́рмия, tr. ) was the armed land force of the Russian Empire, active from around 1721 to the Russian Revolution of 1917. In the early 1850s, the Russian Army consisted of more than 900,000 regular soldiers and nearly 250,000 irregulars (mostly Cossacks). Precursors: Regiments of the New Order Russian tsars before Peter the Great maintained professional hereditary musketeer corps known as '' streltsy''. These were originally raised by Ivan the Terrible; originally an effective force, they had become highly unreliable and undisciplined. In times of war the armed forces were augmented by peasants. The regiments of the new order, or regiments of the foreign order (''Полки нового строя'' or ''Полки иноземного строя'', ''Polki novovo (inozemnovo) stroya''), was the Russian term that was used to describe military units that were formed in the Tsardom of Russi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)