|
PyObjC
PyObjC is a bidirectional bridge between the Python and Objective-C programming languages, allowing programmers to use and extend existing Objective-C libraries, such as Apple's Cocoa framework, using Python. PyObjC is used to develop macOS applications in pure Python. There is also limited support for GNUstep, an open source, cross-platform implementation of Cocoa. For Python programmers The most important usage of PyObjC is enabling programmers to create GUI applications using Cocoa libraries in pure Python. Moreover, as an effect of Objective-C's close relationship with the C programming language (it is a pure superset), developers are also able to incorporate any C-based API by wrapping it with an Objective-C wrapper and then using the wrapped code over the PyObjC bridge. Using Objective-C++, the same can be done with C%2B%2B libraries. For Objective-C programmers Cocoa developers may also benefit, as tasks written in Python generally take fewer lines than the Objective-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libffi
libffi is a foreign function interface library. It provides a C programming language interface for calling natively compiled Subroutine, functions given information about the target Subroutine, function at Run time (program lifecycle phase), run time instead of compile time. It also implements the opposite functionality: libffi can produce a pointer to a function that can accept and decode any combination of arguments defined at run time. libffi is most often used as a bridging technology between compiled and Interpreter (computing), interpreted language implementations. libffi may also be used to implement Plug-in (computing), plug-ins, where the plug-in's function signatures are not known at the time of creating the host application. Notable users include Python (programming language), Python, Haskell (programming language), Haskell, Dalvik virtual machine, Dalvik, F-Script, PyPy, PyObjC, RubyCocoa, JRuby, Rubinius, MacRuby, GNU Compiler for Java, gcj, GNU Smalltalk, IcedTea, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocoa (API)
Cocoa is Apple's native object-oriented application programming interface (API) for its desktop operating system macOS. Cocoa consists of the Foundation Kit, Application Kit, and Core Data frameworks, as included by the Cocoa.h header file, and the libraries and frameworks included by those, such as the C standard library and the Objective-C runtime.Mac Technology Overview: OS X Frameworks Developer.apple.com. Retrieved on September 18, 2013. Cocoa applications are typically developed using the development tools provided by Apple, specifically (formerly [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python Package Index
The Python Package Index, abbreviated as PyPI () and also known as the Cheese Shop (a reference to the ''Monty Python's Flying Circus'' sketch " Cheese Shop"), is the official third-party software repository for Python. It is analogous to the CPAN repository for Perl and to the CRAN repository for R. PyPI is run by the Python Software Foundation, a charity. Some package managers, including pip, use PyPI as the default source for packages and their dependencies. more than 350,000 Python packages can be accessed through PyPI. PyPI primarily hosts Python packages in the form of archives called (source distributions) or precompiled "wheels." PyPI as an index allows users to search for packages by keywords or by filters against their metadata, such as free software license or compatibility with POSIX. A single entry on PyPI is able to store, aside from just a package and its metadata, previous releases of the package, precompiled wheels (e.g. containing DLLs on Windows), as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced like the letter c'') is a General-purpose language, general-purpose computer programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie, and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems, device drivers, protocol stacks, though decreasingly for application software. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the measuring programming language popularity, most widely used programming languages, with C compilers avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RubyCocoa
RubyCocoa is a macOS framework that provides a bridge between the Ruby and the Objective-C programming languages, allowing the user to manipulate Objective-C objects from Ruby, and vice versa. It makes it possible to write a Cocoa application completely in Ruby as well as to write an application that mixes Ruby and Objective-C code. An Apple project called MacRuby was under development to replace RubyCocoa in 2008. A proprietary spin-off called RubyMotion was subsequently released in 2012, available for iOS, macOS and Android. Some useful applications of RubyCocoa are exploration of a Cocoa object's features with irb interactively, prototyping of a Cocoa application, writing a Cocoa application that combines the features of Ruby and Objective-C and wrapping macOS' native GUI for a Ruby script. RubyCocoa is free software, released under both the Ruby License and the LGPL. History RubyCocoa was started in 2001 by Hisakuni Fujimoto when he implemented a Ruby extension module ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mac OS X Leopard
Mac OS X Leopard (version 10.5) is the sixth major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers. Leopard was released on October 26, 2007 as the successor of Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger, and is available in two editions: a desktop version suitable for personal computers, and a server version, Mac OS X Server. It retailed for $129 for the desktop version and $499 for Server. Leopard was superseded by Snow Leopard (version 10.6) in 2009. Leopard is the final version of macOS to support the PowerPC architecture as Snow Leopard functions solely on Intel based Macs. According to Apple, Leopard contains over 300 changes and enhancements compared to its predecessor, Mac OS X Tiger, covering core operating system components as well as included applications and developer tools. Leopard introduces a significantly revised desktop, with a redesigned Dock, Stacks, a semitransparent menu bar, and an updated Finder that incorporates the Cover Flow visual na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xcode
Xcode is Apple's integrated development environment (IDE) for macOS, used to develop software for macOS, iOS, iPadOS, watchOS, and tvOS. It was initially released in late 2003; the latest stable release is version 14.2, released on December 13, 2022, via the Mac App Store with macOS Monterey. The software suite is offered free of charge. Registered developers can download preview releases and prior versions of the suite through the Apple Developer website. Xcode includes command-line tools which enable UNIX-style development via the Terminal app in macOS. They can also be downloaded and installed without the GUI. Major features Xcode supports source code for the programming languages: C, C++, Objective-C, Objective-C++, Java, AppleScript, Python, Ruby, ResEdit (Rez), and Swift, with a variety of programming models, including but not limited to Cocoa, Carbon, and Java. Third parties have added support for GNU Pascal, Free Pascal, Ada, C#, Go, Perl, and D. Xcode can build ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Development Environment
An integrated development environment (IDE) is a software application that provides comprehensive facilities to computer programmers for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source code editor, build automation tools and a debugger. Some IDEs, such as NetBeans and Eclipse, contain the necessary compiler, interpreter, or both; others, such as SharpDevelop and Lazarus, do not. The boundary between an IDE and other parts of the broader software development environment is not well-defined; sometimes a version control system or various tools to simplify the construction of a graphical user interface (GUI) are integrated. Many modern IDEs also have a class browser, an object browser, and a class hierarchy diagram for use in object-oriented software development. Overview Integrated development environments are designed to maximize programmer productivity by providing tight-knit components with similar user interfaces. IDEs present a single program i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Builder
Project Builder was an integrated development environment (IDE) originally developed by NeXT for version 3 of the NeXTSTEP operating system by separating out the code editing parts of Interface Builder into its own application. After Apple Computer purchased NeXT and turned NeXTSTEP into the Mac OS X operating system, the NeXTSTEP version of Project Builder became ProjectBuilderWO (maintained only for WebObjects development), and they created a new Project Builder from scratch for software development with the first version being introduced with Developer Preview 4 of Mac OS X. This version of Project Builder, informally dubbed PBX. was distributed with the first few versions of Mac OS X but with the release of Mac OS X v10.3 it was redesigned, reintegrated with Interface Builder and rebranded as Xcode. GNUstep GNUstep is a free software implementation of the Cocoa (formerly OpenStep) Objective-C frameworks, widget toolkit, and application development tools for Unix-like opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C%2B%2B
C++ (pronounced "C plus plus") is a high-level general-purpose programming language created by Danish computer scientist Bjarne Stroustrup as an extension of the C programming language, or "C with Classes". The language has expanded significantly over time, and modern C++ now has object-oriented, generic, and functional features in addition to facilities for low-level memory manipulation. It is almost always implemented as a compiled language, and many vendors provide C++ compilers, including the Free Software Foundation, LLVM, Microsoft, Intel, Embarcadero, Oracle, and IBM, so it is available on many platforms. C++ was designed with systems programming and embedded, resource-constrained software and large systems in mind, with performance, efficiency, and flexibility of use as its design highlights. C++ has also been found useful in many other contexts, with key strengths being software infrastructure and resource-constrained applications, including desktop applicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
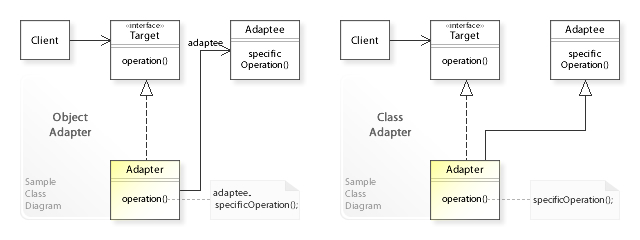
Adapter Pattern
In software engineering, the adapter pattern is a software design pattern (also known as wrapper, an alternative naming shared with the decorator pattern) that allows the interface of an existing class to be used as another interface. It is often used to make existing classes work with others without modifying their source code. An example is an adapter that converts the interface of a Document Object Model of an XML document into a tree structure that can be displayed. Overview The adapter design pattern is one of the twenty-three well-known Gang of Four design patterns that describe how to solve recurring design problems to design flexible and reusable object-oriented software, that is, objects that are easier to implement, change, test, and reuse. The adapter design pattern solves problems like: * How can a class be reused that does not have an interface that a client requires? * How can classes that have incompatible interfaces work together? * How can an alternative interfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implementation
Implementation is the realization of an application, or execution of a plan, idea, model, design, specification, standard, algorithm, or policy. Industry-specific definitions Computer science In computer science, an implementation is a realization of a technical specification or algorithm as a program, software component, or other computer system through computer programming and deployment. Many implementations may exist for a given specification or standard. For example, web browsers contain implementations of World Wide Web Consortium-recommended specifications, and software development tools contain implementations of programming languages. A special case occurs in object-oriented programming, when a concrete class implements an interface; in this case the concrete class is an ''implementation'' of the interface and it includes methods which are ''implementations'' of those methods specified by the interface. Information technology In the information technology during ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |