|
Punjabi University
Punjabi University is a collegiate state public university located in Patiala, Punjab, India. It was established on 30 April 1962 and is only the second university in the world to be named after a language, after Hebrew University of Israel. Originally it was conceived as a unitary multi-faculty teaching and research university, primarily meant for the development and enrichment of the Punjabi language and culture, but alive to the social and education requirements of the state. History Punjabi University was established on 30 April 1962 under the Punjabi University Act 1961 as a residential and teaching university, not as an affiliating university. It started functioning from temporary accommodation in Barandari Palace building. Initially its jurisdictional area was fixed as the radius. There were only nine colleges – six professional and three art and science colleges in Patiala — which fell within its jurisdiction. The university moved to its present campus in 1965. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banwarilal Purohit
Banwarilal Purohit (born 16 April 1940) is an Indian politician who is the current and 29th Governor of Punjab, India and Administrator of Chandigarh as of 29 August 2021. He was the former Governor of Tamil Nadu from 2017 to 2021, and former Governor of Assam from 2016 to 2017. He is a member of the Bharatiya Janata Party. He was a Member of Parliament from the Nagpur (Lok Sabha constituency) three times, twice as an Indian National Congress member, once as a BJP member. Political career Later he joined Congress. After Indira Gandhi split the Congress Party and formed Congress (Indira), Purohit was elected as MLA from Nagpur East constituency in 1978, contesting as member of Congress(I), and he was re-elected in 1980 from Nagpur South and became a Minister of State for Urban Development, Slum Improvement and Housing in 1982. In 1984, he was elected to the 8th Lok Sabha as member of Congress Party. He was re-elected in 1989 on Congress ticket. Later he joined the Bharatiya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social
Social organisms, including human(s), live collectively in interacting populations. This interaction is considered social whether they are aware of it or not, and whether the exchange is voluntary or not. Etymology The word "social" derives from the Latin word ''socii'' ("allies"). It is particularly derived from the Italian ''Socii'' states, historical allies of the Roman Republic (although they rebelled against Rome in the Social War of 91–87 BC). Social theorists In the view of Karl MarxMorrison, Ken. ''Marx, Durkheim, Weber. Formations of modern social thought'', human beings are intrinsically, necessarily and by definition social beings who, beyond being "gregarious creatures", cannot survive and meet their needs other than through social co-operation and association. Their social characteristics are therefore to a large extent an objectively given fact, stamped on them from birth and affirmed by socialization processes; and, according to Marx, in producing and reproducin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathinda
Bathinda is a city and municipal corporation in Punjab, India. The city is the administrative headquarters of Bathinda District. It is located in northwestern India in the Malwa Region, west of the capital city of Chandigarh and is the fifth largest city of Punjab. Bathinda is home to the Maharaja Ranjit Singh Punjab Technical University, Central University of Punjab and AIIMS Bathinda. The city is also home to two modern thermal power plants, Guru Nanak Dev Thermal Plant and Guru Hargobind Thermal Plant at Lehra Mohabbat. Also located in the city is a fertilizer plant, two cement plants (Ambuja Cements and UltraTech Cement Limited), a large army cantonment, an air force station, a zoo, and a historic Qila Mubarak fort. History Bhatinda was changed to Bathinda to conform to the phonetical expression as locally pronounced. According to Henry George Raverty, Bathinda was known as ''Tabar-i-Hind'' (Labb-ut-Twarikh) or ''Tabarhindh'', which roughly translates as ‘Gateway to In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sangrur
Sangrur is a city in Sangrur district of the Indian state of Punjab, India. It is the headquarters of Sangrur District. Geography Sangrur is located at . It has an average elevation of 237 metres (778 feet). Climate Health services City has PGIMER Satellite Centre Sangrur for providing medical facilities to citizens. Homi Bhabha Cancer Hospital has been set up at Sangrur by Tata Memorial Centre in collaboration with Govt. of Punjab Demographics At the 2011 census Sangrur Municipal Council had a population of 88,043 with 46,931 males and 41,112 females, giving a gender ratio of 876. There were 9,027 children 0–6 years old and an overall literacy rate of 83.54% - 87.92% for males and 78.56% for females. Politics Sangrur city is part of the Sangrur Lok Sabha constituency. By-election to Sangrur Lok Sabha constituency is scheduled to be held on 23 June 2022. Tourist Attractions Banasar Bagh The Banasar Garden of Sangrur City is the most popular pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatehgarh Sahib
Fatehgarh Sahib is a city and a sacred pilgrimage site of Sikhism in the north west Indian state of Punjab. It is the headquarters of Fatehgarh Sahib district, located about north of Sirhind. Fatehgarh Sahib is named after Fateh Singh, the 7-year-old son of Guru Gobind Singh, who was seized and buried alive, along with his 9-year-old brother Zoravar Singh, by the Mughals under the orders of governor Wazir Khan during the ongoing Mughal-Sikh wars of the early 18th century.Gurmukh Singh (2009)Fatehgarh Sahib Encyclopedia of Sikhism, Editor in Chief: Harbans Singh, Punjab University The town experienced major historical events after the martyrdom of the sons in 1705, with frequent changes of control between the Sikhs and Mughals. The town features historic Gurdwaras, including the underground Bhora Sahib marking the location where the two boys refused to convert to Islam and fearlessly accepted being bricked alive. In contemporary times, the town is the site of educational insti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnala
Barnala is a city in the state of Punjab of India. Barnala city serves as the headquarters of the Barnala district which was formed in 2006. Prior to formation of Barnala district, this city was located in Sangrur district. It is situated near Bathinda. History Sikh historian Giani has recorded the details of setting up of Barnala in the annals of Khalsa in this manner that in the year 1775 Baba Ala Singh after offering Bhadaur (set up by King Padhar Sain) to his brother Duna Singh came to Barnala region which was lying aloof at that time. Setting it up, he made it his capital and took under his control surrounding villages. It too appears that Anahatgarh may be existing before and must have been deserted following attacks of Dharvis. There are different opinions about the nomenclature of Barnala. Some are of the view, Vaaran being a region because of frequent storms was at that time also called Varna. So Barnala was called a land of too many storms which later on becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions of municipalities, school district, or political district. By country/region Afghanistan In Afghanistan, a district (Persian ps, ولسوالۍ ) is a subdivision of a province. There are almost 400 districts in the country. Australia Electoral districts are used in state elections. Districts were also used in several states as cadastral units for land titles. Some were used as squatting districts. New South Wales had several different types of districts used in the 21st century. Austria In Austria, the word is used with different meanings in three different contexts: * Some of the tasks of the administrative branch of the national and regional governments are fulfilled by the 95 district administrative offices (). The area a dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathinda District
Bathinda district is in Malwa region of Punjab, India. The district encompasses an area of 3,385 square kilometers. By area, Bathinda district is the second-largest in Punjab, after Ludhiana District. It is bounded by Faridkot district and Moga district on the north, Muktsar district on the west, Barnala and Mansa districts on the east, and the state of Haryana on the south. Bathinda is cotton producing belt of Punjab. History The district of Bathinda came into existence with the formation of the PEPSU in 1948. It had its headquarters at Faridkot, which were shifted to Bathinda in 1952. Demographics According to the 2011 census Bathinda district has a population of 1,388,525, roughly equal to the nation of Eswatini or the US state of Hawaii. This gives it a ranking of 352nd in India (out of a total of 640). The district has a population density of . Its population growth rate over the decade 2001–2011 was 17.37%. Bathinda has a sex ratio of 865 females for every 1000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sangrur District
Sangrur district is in the state of Punjab in northern India. Sangrur city is the district headquarters. It is one of the five districts in Patiala Division in the Indian state of Punjab. Neighbouring districts are Malerkotla (north), Barnala (west), Patiala (east), Mansa (southwest) and Fatehabad (Haryana) and Jind (Haryana) (south). Sangrur consists of the cities of Dhuri, Lehragaga, Sangrur, and Sunam. Other cities are Bhawanigarh, Dirba, Khanauri, Longowal, Cheema and Moonak. There are 7 sub-divisions, being Sangrur, Dhuri, Sunam, Lehragaga, Moonak, Bhawanigarh and Dirba. Till 2006,Barnala was also a part of Sangrur district, but now it is a separate district. In 2021, a new district Malerkotla district, consisting of Malerkotla and Ahmedgarh subdivisions and the Amargarh sub-tehsil, was formed out of Sangrur district. Origin and history The administrative district of Sangrur was created in 1948. Earlier the area fell in the Nabha Princely State. Settlements in San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
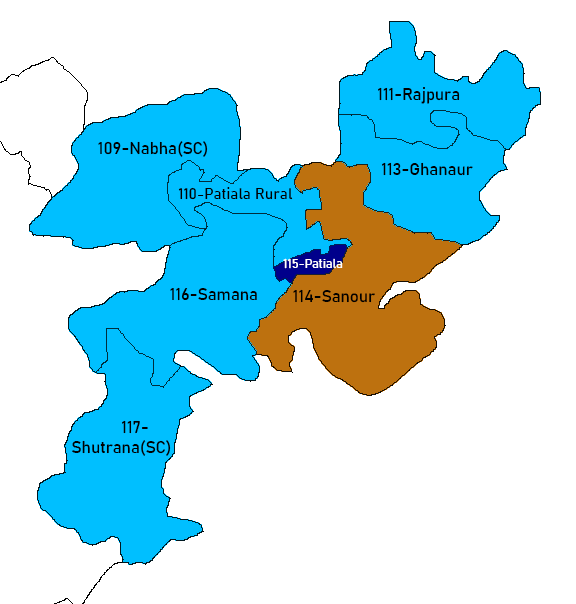
Patiala District
Patiala district is one of the twenty three districts in the state of Punjab in north-west India. Patiala district lies between 38 47’ and 39 41’ north latitude, 115 58’ and 116 54' east longitude, in the southeast part of the state. It is surrounded by Fatehgarh Sahib, Rupnagar and Mohali to the north, Fatehgarh Sahib and Sangrur districts to the west, Ambala, Panchkula, Haryana to the northeast and Kurukshetra districts of neighboring Haryana state to the east, and Kaithal district of Haryana to the southwest. Baba Ala Singh (1691–1765), a Sikh chieftain from the village Rampura Phul in Bathinda District of Punjab, with his army of young brave men migrated to Barnala where Baba Ala Singh in 1763 set up his new state. Later Baba Ala Singh moved to a small village of Lehal where he built a new city on the village, naming it as Patiala. He laid the foundations of a steady and stable state known as the Phulkian Dynasty south of Sirhind. In and around Patiala Dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurisdiction
Jurisdiction (from Latin 'law' + 'declaration') is the legal term for the legal authority granted to a legal entity to enact justice. In federations like the United States, areas of jurisdiction apply to local, state, and federal levels. Jurisdiction draws its substance from international law, conflict of laws, constitutional law, and the powers of the executive and legislative branches of government to allocate resources to best serve the needs of society. International dimension Generally, international laws and treaties provide agreements which nations agree to be bound to. Such agreements are not always established or maintained. The exercise of extraterritorial jurisdiction by three principles outlined in the UN charter. These are equality of states, territorial sovereignty and non-intervention. This raises the question of when can many states prescribe or enforce jurisdiction. The ''Lotus'' case establishes two key rules to the prescription and enforcement of jurisdi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |