|
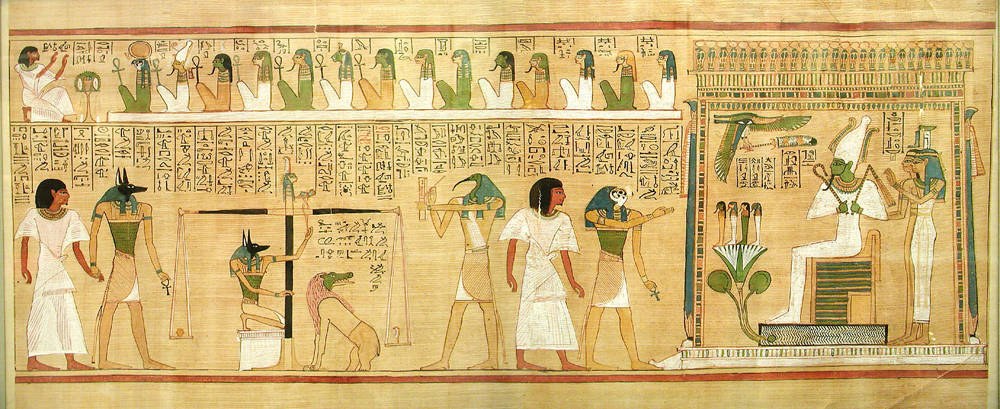
Punishment Of The Grave
Punishment of the Grave ( ar, عذاب القبر ''ʿAdhāb al-Qabr'', also translated torment of the grave) is a Judeo-Islamic concept about the time between death and resurrection on the Day of Judgement. According to some hadiths, the souls of the unrighteous are punished by two angels in the grave, while the righteous find the grave "peaceful and blessed". J. A. C. Brown, ''Misquoting Muhammad'', 2014: p. 46 The punishment of the grave is mentioned in the Quran. Although it is mentioned in the hadiths such as those compiled by Ibn Hanbal and appears as early as the 9th century, still present among the majority of Sunnis and Shias. A similar concept can be found in Jewish narrative, there the wicked are punished by angels of destruction, in an intermediary state between the resurrection of the dead and the individual death. Religions Islam The Quran itself gives very brief references about the period between death and the resurrection. It makes no mention of any kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic–Jewish Relations
Islamic–Jewish relations started in the 7th century CE with the Early history of Islam, origin and spread of Islam in the Arabian peninsula. The two religions share similar values, guidelines, and principles.Dennis Prager, Prager, D; Joseph Telushkin, Telushkin, J. ''Why the Jews?: The Reason for Antisemitism''. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1983. pp. 110–26. Islam also incorporates Jewish history as a part of its own. Muslims regard the Children of Israel as an important religious concept in Islam. Moses, the most important Prophets in Judaism, prophet of Judaism, is also considered a prophets and messengers in Islam, prophet and messenger in Islam. Moses is mentioned in the Quran more than any other individual, and his life is narrated and recounted more than that of any other prophet.Annabel Keeler, "Moses from a Muslim Perspective", in: Solomon, Norman; Harries, Richard; Winter, Tim (eds.)''Abraham's children: Jews, Christians, and Muslims in conversation'' by. T&T Clark P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afterlife
The afterlife (also referred to as life after death) is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's identity or their stream of consciousness continues to live after the death of their physical body. The surviving essential aspect varies between belief systems; it may be some partial element, or the entire soul or spirit of an individual, which carries with it and may confer personal identity or, on the contrary, nirvana. Belief in an afterlife is in contrast to the belief in oblivion after death. In some views, this continued existence takes place in a spiritual realm, while in others, the individual may be reborn into this world and begin the life cycle over again, likely with no memory of what they have done in the past. In this latter view, such rebirths and deaths may take place over and over again continuously until the individual gains entry to a spiritual realm or otherworld. Major views on the afterlife derive from religion, esotericism an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oneworld Publications
Oneworld Publications is a British independent publishing firm founded in 1986 by Novin Doostdar and Juliet Mabey originally to publish accessible non-fiction by experts and academics for the general market."About Us" Oneworld Publications. Based in , it later added a literary fiction list (in 2009) and both a children's list (Rock the Boat, 2015) and an upmarket crime list (Point Blank, 2016), and now publishes across a wide range of subjects, including history, politics, current affairs, popular science, religion, philosophy, and psychology, as well as literary fiction, crime fiction and suspense, and children's titles. A large proportion of Oneworld fiction across all its lists is translated. Among the writers on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siahat-e Gharb
Siahat-e Gharb ('' fa, سیاحت غرب'', ''The Journey to the West'') or The Fate of Souls after Death is a book by Aqa Najafi Quchani (1878-1944). The book narrates the story of the afterlife and the purgatory world in the form of a story based on Islamic perspective of the death. Aqa Najafi Quchani has formed the story based on the hadiths received from the Shiite Imams about the purgatory. The book has been published many times by various publishers. In 2003, a film was made based on this book. Author The author of the book, Aqa Najafi Quchani (1878-1944), is one of the Iranian Shiite scholars of the late of Qajar dynasty and the early of Pahlavi dynasty era. He is buried in Quchan. In addition to the book ''Siahat-e Gharb'', he has several books, such as '' Siahat-e Shargh'', which is his autobiography. Content and subject The book discusses the purgatory world after die and the events that happen to man from Islamic perspective. ''Siahat-e Gharb'' is written ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheol
Sheol ( ; he, ''Šəʾōl'', Tiberian: ''Šŏʾōl'') in the Hebrew Bible is a place of still darkness which lies after death. Although not well defined in the Tanakh, Sheol in this view was a subterranean underworld where the souls of the dead went after the body died. Within the Hebrew Bible, there are few – often brief and nondescript – mentions of Sheol, seemingly describing it as a place where both the righteous and the unrighteous dead go, regardless of their moral choices in life. The implications of Sheol within the texts are therefore somewhat unclear; it can be interpreted as either a generic metaphor describing "the grave" into which all humans invariably descend, or, it may be interpreted as representing an actual state of afterlife within Israelite thought. Though such practices are forbidden, the inhabitants of Sheol can, under some circumstances, be summoned by the living, as when the Witch of Endor calls up the spirit of Samuel for Saul. While the Hebrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabbath
In Abrahamic religions, the Sabbath () or Shabbat (from Hebrew ) is a day set aside for rest and worship. According to the Book of Exodus, the Sabbath is a day of rest on the seventh day, commanded by God to be kept as a holy day of rest, as God rested from creation. The practice of observing the Sabbath (Shabbat) originates in the biblical commandment "Remember the sabbath day, to keep it holy". The Sabbath is observed in Judaism, Sabbatarian forms of Christianity (such as many Protestant and Eastern denominations), and Islam. Observances similar to, or descended from, the Sabbath also exist in other religions. The term may be generally used to describe similar weekly observances in other religions. Biblical Sabbath Sabbath (as the verb שָׁבַת֙ ''shabbat'') is first mentioned in the Genesis creation narrative, where the seventh day is set aside as a day of rest (in Hebrew, ''shabbat'') and made holy by God (). Observation and remembrance of Sabbath ( ''shabbat'') is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumah (angel)
Dumah ( Heb. ''dūmā'', "silence") is an angel mentioned in Rabbinical and Islamic literature as an angel who has authority over the wicked dead. Dumah is a popular figure in Yiddish folklore. I. B. Singer's ''Short Friday'' (1964), a collection of stories, mentions Dumah as a "thousand-eyed angel of death, armed with a fiery rod or flaming sword". ''Dumah'' is the Aramaic word for silence. The angel Duma(h) or Douma (Aramaic) is the angel of silence and of the stillness of death. Dumah is also the tutelary angel of Egypt, prince of Hell, and angel of vindication. ''The Zohar'' speaks of him as having "tens of thousands of angels of destruction" under him, and as being "Chief of demons in Gehinnom .e., Hellwith 12,000 myriads of attendants, all charged with the punishment of the souls of sinners." As the patron of Egypt, he disregarded the command of God to exercise judgment over the Egyptian deities. Whereupon God banishes him into Gehenna, there he becomes its ruler and thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbinic Literature
Rabbinic literature, in its broadest sense, is the entire spectrum of rabbinic writings throughout Jewish history. However, the term often refers specifically to literature from the Talmudic era, as opposed to medieval and modern rabbinic writing, and thus corresponds with the Hebrew term ''Sifrut Chazal'' ( he, ספרות חז״ל "Literature f oursages," where ''Hazal'' normally refers only to the sages of the Talmudic era). This more specific sense of "Rabbinic literature"—referring to the Talmudim, Midrash ( he, מדרש), and related writings, but hardly ever to later texts—is how the term is generally intended when used in contemporary academic writing. The terms ''meforshim'' and ''parshanim'' (commentaries/commentators) almost always refer to later, post-Talmudic writers of rabbinic glosses on Biblical and Talmudic texts. Mishnaic literature The Midr'she halakha, Mishnah, and Tosefta (compiled from materials pre-dating the year 200 CE) are the earliest e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illiyin
''Illiyin'', ''Illiyun'' or ''Elliyoun'' ( ar, عِلِّيِّين, عِلِّيُّون, ʿilliyyīn, -ūn literally: heaven, upperworld) is a Quranic term referring to either the "most high" and "supreme" places above Jannah, i.e. the Garden of Eden or paradise, in the seventh heaven closest to the Throne of God (al-ʿArsh), or, according to a different interpretation, a register for the blessed or record of the righteous, which is mentioned iverses 83:18–20of the Quran. It is also understood as the abode of the believers before Resurrection. The antithesis of ''Illiyin'' is ''Sijjin''. Etymology The word as an adjective, apparently pronounced in such a way to parallel with ''sijjīn'' (a commonly seen aspect of the Quran), is a plural of ''ʿaliyy'' ( ar, عَلِيّ) meaning "high, exalted, lofty, excellent" from the very common root ʿ-L-W () related to exalting, becoming high or elevating. The very similar-sounding Hebrew word '' ʿelyṓn'' () meaning "upper, top, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former capital of Pakistan and capital of the province of Sindh. Ranked as a beta-global city, it is Pakistan's premier industrial and financial centre, with an estimated GDP of over $200 billion ( PPP) . Karachi paid $9billion (25% of whole country) as tax during fiscal year July 2021 to May 2022 according to FBR report. Karachi is Pakistan's most cosmopolitan city, linguistically, ethnically, and religiously diverse, as well as one of Pakistan's most secular and socially liberal cities. Karachi serves as a transport hub, and contains Pakistan’s two largest seaports, the Port of Karachi and Port Qasim, as well as Pakistan's busiest airport, Jinnah International Airport. Karachi is also a media center, home to news channels, film and fashi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Shafi Usmani
Muḥammad Shafī‘ ibn Muḥammad Yāsīn ‘Us̱mānī Deobandī ( ur, ; ar, محمد شفيع بن محمد ياسين العثماني الديوبندي, ''Muḥammad Shafī‘ ibn Muḥammad Yāsīn al-‘Uthmānī ad-Diyūbandī''; 25 January 18976 October 1976), often referred to as Mufti Muhammad Shafi, was a Pakistani Sunni Islamic scholar of the Deobandi school of Islamic thought. A Hanafi jurist and mufti, he was also an authority on shari'ah, hadith, Qur'anic exegesis, and Sufism. Born in Deoband, British India, he graduated in 1917 from Darul Uloom Deoband, where he later taught hadith and held the post of Chief Mufti. He resigned from the school in 1943 to devote his time to the Pakistan Movement. After the independence he moved to Pakistan, where he established Darul Uloom Karachi in 1951. Of his written works, his best-known is ''Ma'ariful Qur'an'', a commentary on the Qur'an. Birth and early childhood Muhammad Shafi, son of Muhammad Yasin, was born on 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |