|
Pulmonary Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia
Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) is a hyperplastic lesion of the epithelial lining of pulmonary alveoli. Tumorigenesis A multi-step carcinogenesis hypothesis suggests a progression from atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) through bronchioalveolar carcinoma (BAC) to invasive adenocarcinoma Invasive may refer to: * Invasive (medical) procedure * Invasive species * Invasive observation, especially in reference to surveillance *Invasively progressive spread of disease from one organ in the body to another, especially in reference to ca ... (AC), but to date this has not been formally demonstrated. References Pulmonary lesion {{med-sign-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia
Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia is a subtype of pneumocytic hyperplasia in the lung. It can be a precursor lesion of in situ adenocarcinoma of the lung (bronchioloalveolar carcinoma). In prostate tissue biopsy, it can be confused for adenocarcinoma of the prostate. The needle biopsy rate is less than 1%. Pathology Morphological differential diagnosis * Multifocal micronodular pneumocyte hyperplasia (MMPH) * in situ pulmonary adenocarcinoma (bronchioloalveolar carcinoma – BAC) Variants * multiple atypical adenomatous hyperplasia * disseminated AAH Histopathological images Image:Pulmonary_adeocaricnoma_(1)_localized_noninvasive_type.jpg Image:Pulmonary adeocaricnoma (2) localized noninvasive type.jpg Image:Pulmonary adeocaricnoma (3) localized noninvasive type.jpg Image:Pulmonary_adeocaricnoma_(4)_localized_noninvasive_type.jpg See also * EGFR * KRAS ''KRAS'' ( Kirsten rat sarcoma virus) is a gene that provides instructions for making a protein called K-R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of organic tissue that results from cell proliferation. It may lead to the gross enlargement of an organ, and the term is sometimes confused with benign neoplasia or benign tumor. Hyperplasia is a common preneoplastic response to stimulus. Microscopically, cells resemble normal cells but are increased in numbers. Sometimes cells may also be increased in size (hypertrophy). Hyperplasia is different from hypertrophy in that the adaptive cell change in hypertrophy is an increase in the ''size'' of cells, whereas hyperplasia involves an increase in the ''number'' of cells. Causes Hyperplasia may be due to any number of causes, including proliferation of basal layer of epidermis to compensate skin loss, chronic inflammatory response, hormonal dysfunctions, or compensation for damage o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
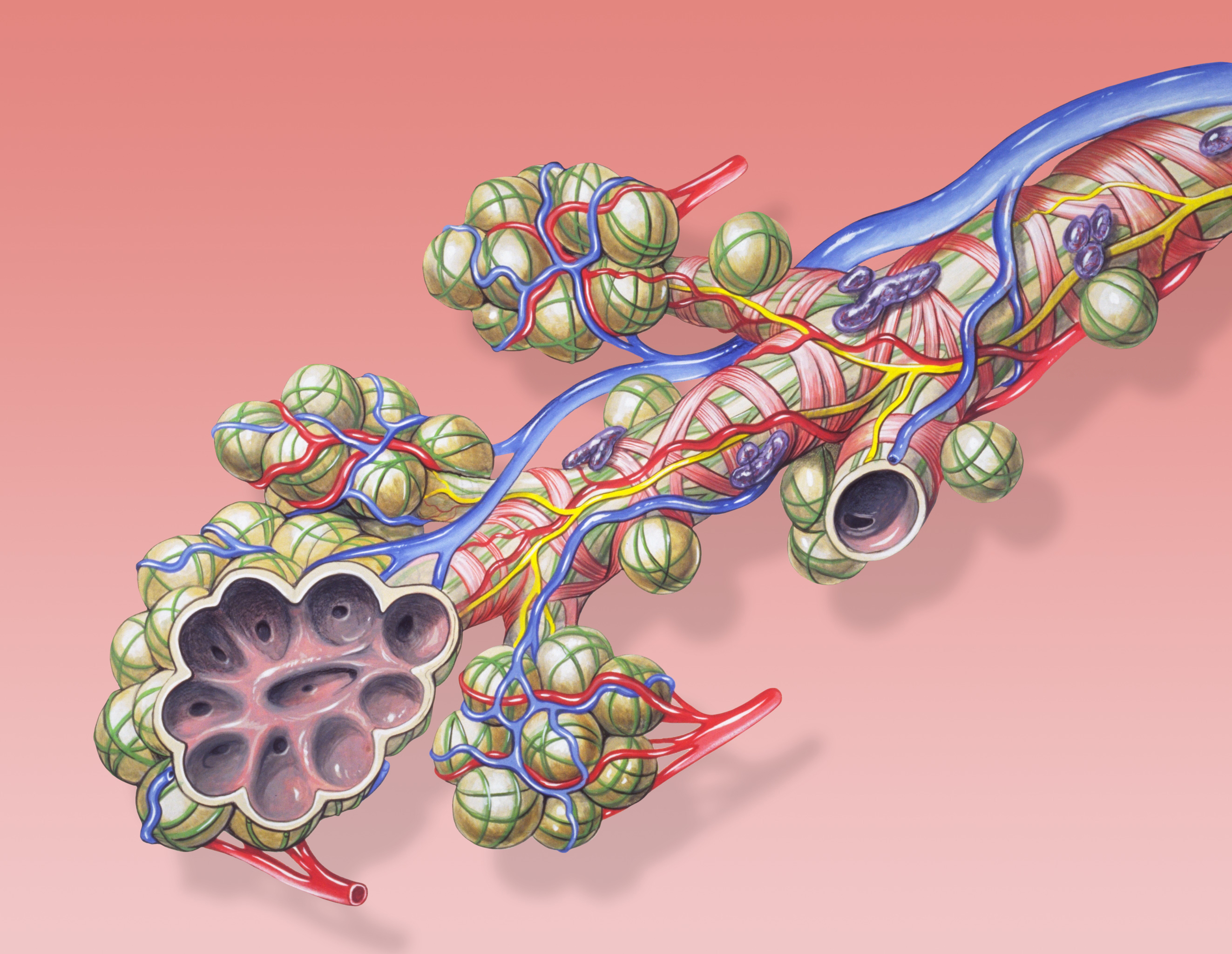
Pulmonary Alveoli
A pulmonary alveolus (plural: alveoli, from Latin ''alveolus'', "little cavity"), also known as an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide. Alveoli make up the functional tissue of the mammalian lungs known as the lung parenchyma, which takes up 90 percent of the total lung volume. Alveoli are first located in the respiratory bronchioles that mark the beginning of the respiratory zone. They are located sparsely in these bronchioles, line the walls of the alveolar ducts, and are more numerous in the blind-ended alveolar sacs. The acini are the basic units of respiration, with gas exchange taking place in all the alveoli present. The alveolar membrane is the gas exchange surface, surrounded by a network of capillaries. Across the membrane oxygen is diffused into the capillaries and carbon dioxide released from the capillaries into the alveoli to be breathed out. Alveoli are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia
Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia is a subtype of pneumocytic hyperplasia in the lung. It can be a precursor lesion of in situ adenocarcinoma of the lung (bronchioloalveolar carcinoma). In prostate tissue biopsy, it can be confused for adenocarcinoma of the prostate. The needle biopsy rate is less than 1%. Pathology Morphological differential diagnosis * Multifocal micronodular pneumocyte hyperplasia (MMPH) * in situ pulmonary adenocarcinoma (bronchioloalveolar carcinoma – BAC) Variants * multiple atypical adenomatous hyperplasia * disseminated AAH Histopathological images Image:Pulmonary_adeocaricnoma_(1)_localized_noninvasive_type.jpg Image:Pulmonary adeocaricnoma (2) localized noninvasive type.jpg Image:Pulmonary adeocaricnoma (3) localized noninvasive type.jpg Image:Pulmonary_adeocaricnoma_(4)_localized_noninvasive_type.jpg See also * EGFR * KRAS ''KRAS'' ( Kirsten rat sarcoma virus) is a gene that provides instructions for making a protein called K-R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronchioalveolar Carcinoma
Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the lung —previously included in the category of "bronchioloalveolar carcinoma" (BAC)—is a subtype of lung adenocarcinoma. It tends to arise in the distal bronchioles or alveoli and is defined by a non-invasive growth pattern. This small solitary tumor exhibits pure alveolar distribution ( lepidic growth) and lacks any invasion of the surrounding normal lung. If completely removed by surgery, the prognosis is excellent with up to 100% 5-year survival. Although the entity of AIS was formally defined in 2011, it represents a noninvasive form of pulmonary adenocarcinoma which has been recognized for some time. AIS is not considered to be an invasive tumor by pathologists, but as one form of carcinoma in situ (CIS). Like other forms of CIS, AIS may progress and become overtly invasive, exhibiting malignant, often lethal, behavior. Major surgery, either a lobectomy or a pneumonectomy, is usually required for treatment. Causes The genes mutated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasive Adenocarcinoma
{{disambig ...
Invasive may refer to: * Invasive (medical) procedure * Invasive species * Invasive observation, especially in reference to surveillance *Invasively progressive spread of disease from one organ in the body to another, especially in reference to cancer, see invasion (cancer) See also * Intruder (other) * Invasion (other) * Intrusive (other) *Invasive procedure (other) Invasive procedure may refer to: * "Invasive Procedures" (''Star Trek: Deep Space Nine''), the fourth episode of the second season of the television series ''Star Trek: Deep Space Nine'' * ''Invasive Procedures'' (novel), a 2007 novel by Orson Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |