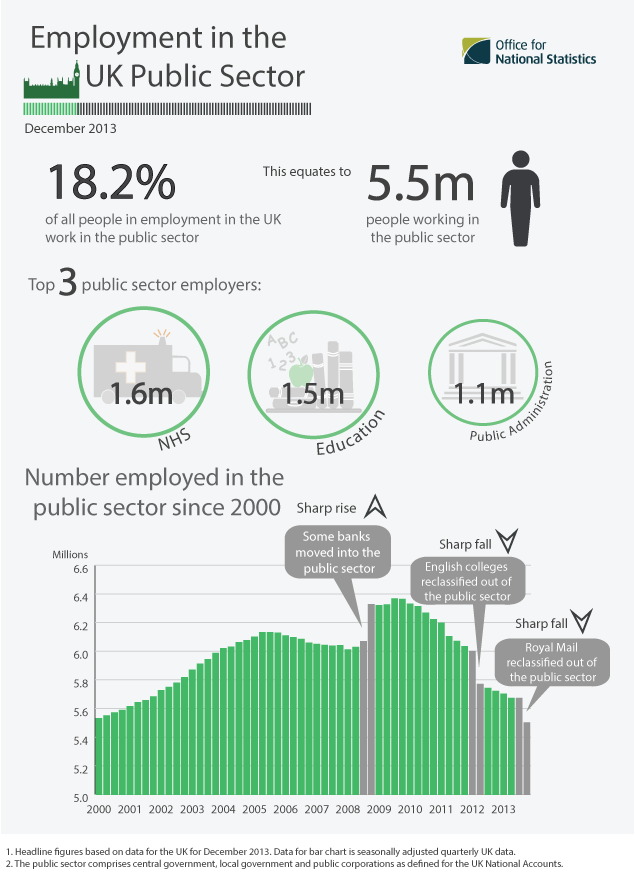
|
Public Servants Disclosure Protection Act
The Public Servants Disclosure Protection Act (the Act) came into force in Canada on April 15, 2007. The Act creates two distinct processes: a disclosure process and a reprisal complaints process. It also creates two new bodies: the Office of the Public Sector Integrity Commissioner (PSIC) and the Public Servants Disclosure Protection Tribunal. Definitions The Act defines wrongdoing as a contravention of any Act of Parliament or of the legislature of a province, or of any regulations made under any such Act; a misuse of public funds or a public asset; gross mismanagement in the public sector; an act or omission that creates a substantial and specific danger to the life, health or safety of persons, or to the environment, other than a danger that is inherent in the performance of the duties or functions of a public servant; a serious breach of a code of conduct established under the Act; and knowingly directing or counseling a person to commit a wrongdoing. Under the Act, reprisa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Sector Integrity Commissioner
The Office of the Public Sector Integrity Commissioner of Canada is one of the Independent Oversight Offices created as part of the Canadian Federal Accountability Act. The Office investigates wrongdoing in the federal public sector and helps protect whistleblowers, and those who participate in investigations, from reprisal. Joe Friday is the current Commissioner, named on March 27, 2015. The Office is an independent federal organization created in 2007 under the Public Servants Disclosure Protection Act, is led by a Commissioner who reports directly to Parliament, and has jurisdiction over most federal public sector organizations, including the Royal Canadian Mounted Police and Crown Corporations. The Canadian Forces, the Canadian Security Intelligence Service and the Communications Security Establishment are exempt but must establish their own internal disclosure regime. The Act is intended to address wrongdoing that could seriously impact the public's confidence in the integ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Servants Disclosure Protection Tribunal
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öffentlichkeit'' or public sphere. The concept of a public has also been defined in political science, psychology, marketing, and advertising. In public relations and communication science, it is one of the more ambiguous concepts in the field. Although it has definitions in the theory of the field that have been formulated from the early 20th century onwards, and suffered more recent years from being blurred, as a result of conflation of the idea of a public with the notions of audience, market segment, community, constituency, and stakeholder. Etymology and definitions The name "public" originates with the Latin '' publicus'' (also '' poplicus''), from ''populus'', to the English word 'populace', and in general denotes some mass population ("the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of Parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the Legislature, legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of parliament begin as a Bill (law), bill, which the legislature votes on. Depending on the structure of government, this text may then be subject to assent or approval from the Executive (government), executive branch. Bills A draft act of parliament is known as a Bill (proposed law), bill. In other words, a bill is a proposed law that needs to be discussed in the parliament before it can become a law. In territories with a Westminster system, most bills that have any possibility of becoming law are introduced into parliament by the government. This will usually happen following the publication of a "white paper", setting out the issues and the way in which the proposed new law is intended to deal with them. A bill may also be introduced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Funding
A subsidy or government incentive is a form of financial aid or support extended to an economic sector (business, or individual) generally with the aim of promoting economic and social policy. Although commonly extended from the government, the term subsidy can relate to any type of support – for example from NGOs or as implicit subsidies. Subsidies come in various forms including: direct (cash grants, interest-free loans) and indirect (tax breaks, insurance, low-interest loans, accelerated depreciation, rent rebates). Furthermore, they can be broad or narrow, legal or illegal, ethical or unethical. The most common forms of subsidies are those to the producer or the consumer. Producer/production subsidies ensure producers are better off by either supplying market price support, direct support, or payments to factors of production. Consumer/consumption subsidies commonly reduce the price of goods and services to the consumer. For example, in the US at one time it was cheaper to buy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Code Of Conduct
A code of conduct is a set of rules outlining the norms, rules, and responsibilities or proper practices of an individual party or an organization. Companies' codes of conduct A company code of conduct is a set of rules which is commonly written for employees of a company, which protects the business and informs the employees of the company's expectations. It is appropriate for even the smallest of companies to create a document containing important information on expectations for employees. The document does not need to be complex or have elaborate policies. Failure of an employee to follow a company's code of conduct can have negative consequences. In '' Morgan Stanley v. Skowron'', 989 F. Supp. 2d 356 (S.D.N.Y. 2013), applying New York's faithless servant doctrine, the court held that a hedge fund's employee engaging in insider trading in violation of his company's code of conduct, which also required him to report his misconduct, must repay his employer the full $31 millio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Good Faith
In human interactions, good faith ( la, bona fides) is a sincere intention to be fair, open, and honest, regardless of the outcome of the interaction. Some Latin phrases have lost their literal meaning over centuries, but that is not the case with ''bona fides'', which is still widely used and interchangeable with its generally-accepted modern-day English translation of ''good faith''. It is an important concept within law and business. The opposed concepts are bad faith, ''mala fides'' (duplicity) and perfidy (pretense). In contemporary English, the usage of ''bona fides'' is synonymous with credentials and identity. The phrase is sometimes used in job advertisements, and should not be confused with the ''bona fide'' occupational qualifications or the employer's good faith effort, as described below. ''Bona fides'' ''Bona fides'' is a Latin phrase meaning "good faith". Its ablative case is ''bona fide'', meaning "in good faith", which is often used as an adjective to mean " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Justice
In English law, natural justice is technical terminology for the rule against bias (''nemo iudex in causa sua'') and the right to a fair hearing (''audi alteram partem''). While the term ''natural justice'' is often retained as a general concept, it has largely been replaced and extended by the general "duty to act fairly". The basis for the rule against bias is the need to maintain public confidence in the legal system. Bias can take the form of actual bias, imputed bias, or apparent bias. Actual bias is very difficult to prove in practice whereas imputed bias, once shown, will result in a decision being void without the need for any investigation into the likelihood or suspicion of bias. Cases from different jurisdictions currently apply two tests for apparent bias: the "reasonable suspicion of bias" test and the "real likelihood of bias" test. One view that has been taken is that the differences between these two tests are largely semantic and that they operate similarly. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Sector
The public sector, also called the state sector, is the part of the economy composed of both public services and public enterprises. Public sectors include the public goods and governmental services such as the military, law enforcement, infrastructure, public transit, public education, along with health care and those working for the government itself, such as elected officials. The public sector might provide services that a non-payer cannot be excluded from (such as street lighting), services which benefit all of society rather than just the individual who uses the service. Public enterprises, or state-owned enterprises, are self-financing commercial enterprises that are under public ownership which provide various private goods and services for sale and usually operate on a commercial basis. Organizations that are not part of the public sector are either part of the private sector or voluntary sector. The private sector is composed of the economic sectors that are intende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Security Intelligence Service
The Canadian Security Intelligence Service (CSIS, ; french: Service canadien du renseignement de sécurité, ''SCRS'') is Canada's primary national intelligence agency. It is responsible for collecting, analysing, reporting and disseminating intelligence on threats to Canada's national security, and conducting operations, covert and overt, within Canada and abroad. The agency also reports to and advises the minister of public safety on national security issues and situations that threaten the security of the nation. CSIS is headquartered in Ottawa, Ontario, in a purpose-built facility completed in 1995. The agency is responsible to Parliament through the minister of public safety, and it is overseen by the National Security and Intelligence Review Agency. CSIS is also subject to review by the Federal Court. CSIS agents are not allowed to make arrests. The agency is led by a director, the ninth and current being David Vigneault, who assumed the role on June 19, 2017. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2007 In Law
7 (seven) is the natural number following 6 and preceding 8. It is the only prime number preceding a cube. As an early prime number in the series of positive integers, the number seven has greatly symbolic associations in religion, mythology, superstition and philosophy. The seven Classical planets resulted in seven being the number of days in a week. It is often considered lucky in Western culture and is often seen as highly symbolic. Unlike Western culture, in Vietnamese culture, the number seven is sometimes considered unlucky. It is the first natural number whose pronunciation contains more than one syllable. Evolution of the Arabic digit In the beginning, Indians wrote 7 more or less in one stroke as a curve that looks like an uppercase vertically inverted. The western Ghubar Arabs' main contribution was to make the longer line diagonal rather than straight, though they showed some tendencies to making the digit more rectilinear. The eastern Arabs developed the digit fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |