|
Ptoion
Ptoion (Ancient Greek ''Ptōïon'' , also ''Ptōon'' / , Modern Greek Ptoo Πτώο or ''Oros Pelagias'' Όρος Πελαγίας) is a mountain chain in northeastern Boiotia. It stretches from Akraiphia by the former Lake Copais in the west to the Gulf of Euboea in the east, reaching up to 725 m (Agia Pelagia) in the west and 781 m (Petalás) in the east. The massif is particularly famed for the oracle of Apollo, which was located in the sanctuary of Apollo Ptoios at the western end of the range and was among the most important Greek oracles up to the time of the Persian Wars. History of the Oracle of Apollo The oracle of Apollo Ptoios was located three kilometres northeast of Akraiphia. Pausanias reports that it was originally an oracle of Ptoios, a local hero who was son of Athamas and Themisto, but that he was displaced by Apollo.Pausania9.23.6 The name Ptoios was also that of the mountain which loomed over the oracle and was borne by Apollo as a local epithet. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label=genitive, , ; , is one of the Olympian deities in classical Greek and Roman religion and Greek and Roman mythology. The national divinity of the Greeks, Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, music and dance, truth and prophecy, healing and diseases, the Sun and light, poetry, and more. One of the most important and complex of the Greek gods, he is the son of Zeus and Leto, and the twin brother of Artemis, goddess of the hunt. Seen as the most beautiful god and the ideal of the ''kouros'' (ephebe, or a beardless, athletic youth), Apollo is considered to be the most Greek of all the gods. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as ''Apulu''. As the patron deity of Delphi (''Apollo Pythios''), Apollo is an oracul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaic Greece
Archaic Greece was the period in Greek history lasting from circa 800 BC to the second Persian invasion of Greece in 480 BC, following the Greek Dark Ages and succeeded by the Classical period. In the archaic period, Greeks settled across the Mediterranean and the Black Seas, as far as Marseille in the west and Trapezus (Trebizond) in the east; and by the end of the archaic period, they were part of a trade network that spanned the entire Mediterranean. The archaic period began with a massive increase in the Greek population and of significant changes that rendered the Greek world at the end of the 8th century entirely unrecognisable from its beginning. According to Anthony Snodgrass, the archaic period was bounded by two revolutions in the Greek world. It began with a "structural revolution" that "drew the political map of the Greek world" and established the ''poleis'', the distinctively Greek city-states, and it ended with the intellectual revolution of the Classical peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
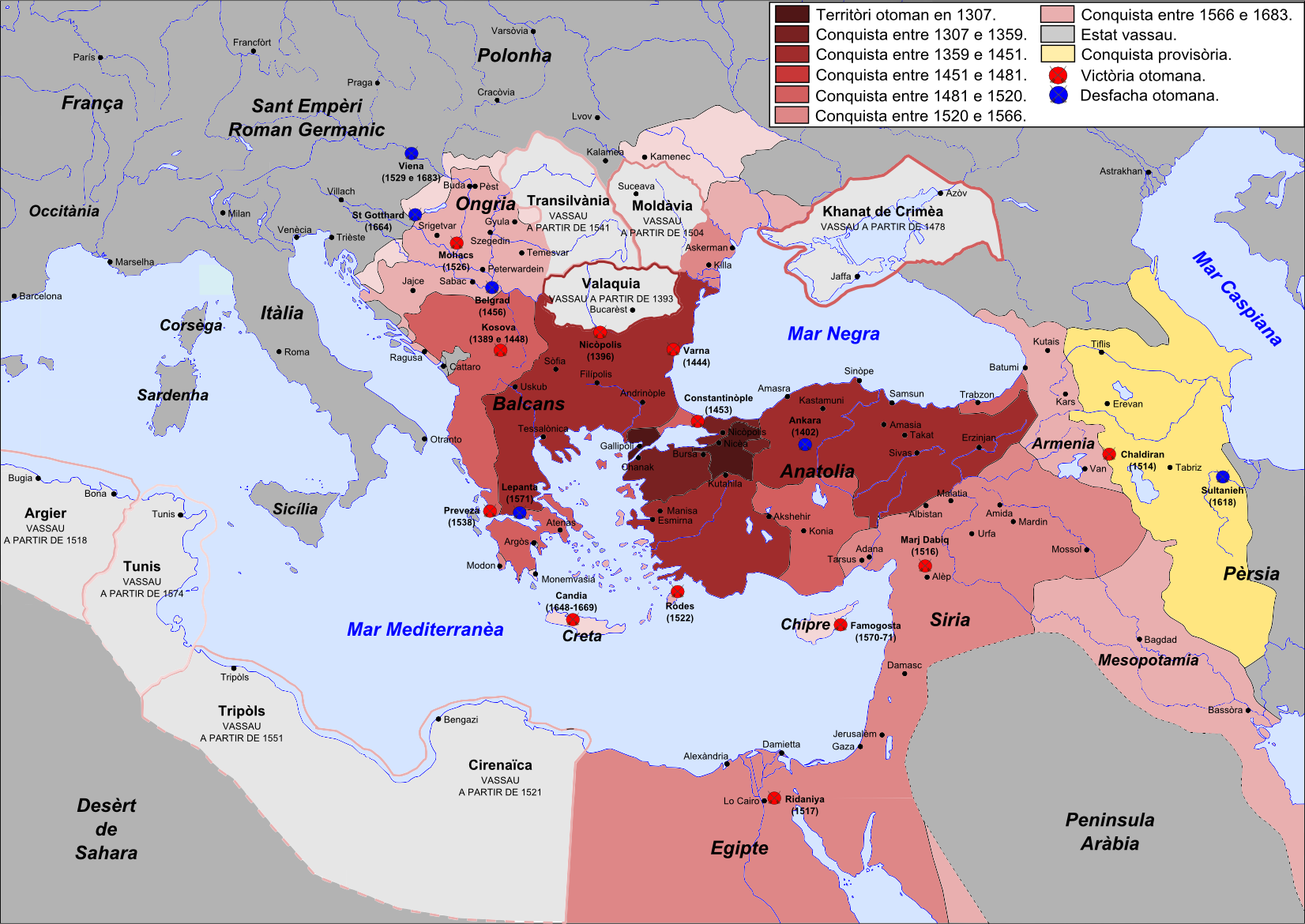
Ottoman Greece
Most of the areas which today are within modern Greece's borders were at some point in the past part of the Ottoman Empire. This period of Ottoman rule in Greece, lasting from the mid-15th century until the successful Greek War of Independence that broke out in 1821 and the proclamation of the First Hellenic Republic in 1822 (preceded by the creation of the autonomous Septinsular Republic in 1800), is known in Greek as ''Tourkokratia'' ( el, Τουρκοκρατία, "Turkish rule"; en, "Turkocracy"). Some regions, however, like the Ionian islands, various temporary Venetian possessions of the Stato da Mar, or Mani peninsula in Peloponnese did not become part of the Ottoman administration, although the latter was under Ottoman suzerainty. The Eastern Roman Empire, the remnant of the ancient Roman Empire which ruled most of the Greek-speaking world for over 1100 years, had been fatally weakened since the sacking of Constantinople by the Latin Crusaders in 1204. The Ottoman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julio-Claudian
, native_name_lang=Latin, coat of arms=Great_Cameo_of_France-removebg.png, image_size=260px, caption= The Great Cameo of France depicting emperors Augustus, Tiberius, Claudius and Nero, type=Ancient Roman dynasty, country= Roman Empire, estates=* Imperial Palaces of the Palatine Hill * House of Augustus * Villa of Livia * Gardens of Maecenas * ''Domus Aurea'' * ''Domus Transitoria'' * Villa of Nero * ''Villa Jovis'', parent house=, titles= Roman emperor Pharaoh of Egypt Prince of the Senate Greatest Priest of Rome Father of the Country , styles="Imperator""Caesar""Augustus", founded=, founder=Augustus, final ruler=Nero, other_families=, deposition= (deposed by Galba), ethnicity=Ancient Roman, religion=Roman Religion Imperial cult The Julio-Claudian dynasty comprised the first five Roman emperors: Augustus, Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, and Nero. This line of emperors ruled the Roman Empire, from its formation (under Augustus, in 27 BC) until the last of the line, emperor Ner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inscriptiones Graecae
The ''Inscriptiones Graecae'' (IG), Latin for ''Greek inscriptions'', is an academic project originally begun by the Prussian Academy of Science, and today continued by its successor organisation, the . Its aim is to collect and publish all known ancient inscriptions from the mainland and islands of Greece. The project was designed as a continuation of the ''Corpus Inscriptionum Graecarum'' (''Corpus of Greek Inscriptions'', abbreviated CIG) published by August Böckh between 1825 and 1860, and as a parallel to the ''Corpus Inscriptionum Latinarum'' (''Corpus of Latin Inscriptions'') founded by Theodor Mommsen in 1847. From 1860 to 1902, it was directed by Adolf Kirchhoff. From 1902 to 1931, Ulrich von Wilamowitz-Moellendorff was in control of the project; he reorganised and re-energised the IG, turning it into one of the most important series for the publication of source material in Classical studies. After the Second World War, the project suffered from a lack of financial an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphictyonic League
In Archaic Greece, an amphictyony ( grc-gre, ἀμφικτυονία, a "league of neighbors"), or amphictyonic league, was an ancient religious association of tribes formed before the rise of the Greek ''poleis''. The six Dorian cities of coastal southwest Anatolia and the twelve Ionian cities to the north that formed the Ionian League after a Meliac war in the mid-7th century BC, were already of considerable antiquity when the first written records emerge. An amphictyony consisting of polities under the aegis of Apollo's shrine at Delos was apparently well-established in the seventh century, as the Homeric Hymn to Delian Apollo of that approximate date lists them, those cities and islands that trembled and refused to offer themselves for the birthplace of Apollo when pregnant Leto went to each in turn; the Homeric hymn presents an origin myth for the cult of Apollo on Delos. The joint Ionian festival celebrated there was the Delia. The Delian Amphictyony arose in the 4t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeotian League
Boeotia ( ), sometimes Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia ( el, Βοιωτία; modern: ; ancient: ), formerly known as Cadmeis, is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, and its largest city is Thebes. Boeotia was also a region of ancient Greece, from before the 6th century BC. Geography Boeotia lies to the north of the eastern part of the Gulf of Corinth. It also has a short coastline on the Gulf of Euboea. It bordered on Megaris (now West Attica) in the south, Attica in the southeast, Euboea in the northeast, Opuntian Locris (now part of Phthiotis) in the north and Phocis in the west. The main mountain ranges of Boeotia are Mount Parnassus in the west, Mount Helicon in the southwest, Cithaeron in the south and Parnitha in the east. Its longest river, the Cephissus, flows in the central part, where most of the low-lying areas of Boeotia are found. Lake Copais was a large lake in the center of Boeotia. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Greece
Classical Greece was a period of around 200 years (the 5th and 4th centuries BC) in Ancient Greece,The "Classical Age" is "the modern designation of the period from about 500 B.C. to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C." ( Thomas R. Martin, ''Ancient Greece'', Yale University Press, 1996, p. 94). marked by much of the eastern Aegean and northern regions of Greek culture (such as Ionia and Macedonia) gaining increased autonomy from the Persian Empire; the peak flourishing of democratic Athens; the First and Second Peloponnesian Wars; the Spartan and then Theban hegemonies; and the expansion of Macedonia under Philip II. Much of the early defining politics, artistic thought (architecture, sculpture), scientific thought, theatre, literature and philosophy of Western civilization derives from this period of Greek history, which had a powerful influence on the later Roman Empire. The Classical era ended after Philip II's unification of most of the Greek world against th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebes, Greece
Thebes (; ell, Θήβα, ''Thíva'' ; grc, Θῆβαι, ''Thêbai'' .) is a city in Boeotia, Central Greece. It played an important role in Greek myths, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus, Heracles and others. Archaeological excavations in and around Thebes have revealed a Mycenaean settlement and clay tablets written in the Linear B script, indicating the importance of the site in the Bronze Age. Thebes was the largest city of the ancient region of Boeotia and was the leader of the Boeotian confederacy. It was a major rival of ancient Athens, and sided with the Persians during the 480 BC invasion under Xerxes I. Theban forces under the command of Epaminondas ended Spartan hegemony at the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC, with the Sacred Band of Thebes, an elite military unit of male lovers celebrated as instrumental there. Macedonia would rise in power at the Battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC, bringing decisive victory to Philip II over an alliance of Thebes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thessaly was known as Aeolia (, ), and appears thus in Homer's ''Odyssey''. Thessaly became part of the modern Greek state in 1881, after four and a half centuries of Ottoman rule. Since 1987 it has formed one of the country's 13 regions and is further (since the Kallikratis reform of 2011) sub-divided into five regional units and 25 municipalities. The capital of the region is Larissa. Thessaly lies in northern Greece and borders the regions of Macedonia on the north, Epirus on the west, Central Greece on the south, and the Aegean Sea on the east. The Thessaly region also includes the Sporades islands. Name and etymology Thessaly is named after the ''Thessaloi'', an ancient Greek tribe. The meaning of the name of this tribe is unknow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |