|
Pseudogapping
Pseudogapping is an ellipsis (linguistics), ellipsis mechanism that elides most but not all of a non-finite verb, non-finite verb phrase; at least one part of the verb phrase remains, which is called the ''remnant''. Pseudogapping occurs in comparative and contrastive contexts, so it appears often after subordinators and coordinators such as ''if'', ''although'', ''but'', ''than'', etc. It is similar to verb phrase ellipsis (VP-ellipsis) insofar as the ellipsis is introduced by an auxiliary verb, and many grammarians take it to be a particular type of VP-ellipsis. The distribution of pseudogapping is more restricted than that of VP-ellipsis, however, and in this regard, it has some traits in common with gapping. But unlike gapping (but like VP-ellipsis), pseudogapping occurs in English but not in closely related languages. The analysis of pseudogapping can vary greatly depending in part on whether the analysis is based in a phrase structure grammar or a dependency grammar. Pseudogappi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsis (linguistics)
In linguistics, ellipsis (from el, ἔλλειψις, ''élleipsis'' 'omission') or an elliptical construction is the omission from a clause of one or more words that are nevertheless understood in the context of the remaining elements. There are numerous distinct types of ellipsis acknowledged in theoretical syntax. Theoretical accounts of ellipsis seek to explain its syntactic and semantic factors, the means by which the elided elements are recovered, and the status of the elided elements. Theoretical accounts of ellipsis can vary greatly depending in part upon whether a constituency-based or a dependency-based theory of syntactic structure is pursued. Background Varieties of ellipsis have long formed a basis of linguistic theory that addresses basic questions of form–meaning correspondence: in particular, how the usual mechanisms of grasping a meaning from a form may be bypassed or supplanted via elliptical structures. In generative linguistics, the term ''ellipsis'' has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsis (linguistics)
In linguistics, ellipsis (from el, ἔλλειψις, ''élleipsis'' 'omission') or an elliptical construction is the omission from a clause of one or more words that are nevertheless understood in the context of the remaining elements. There are numerous distinct types of ellipsis acknowledged in theoretical syntax. Theoretical accounts of ellipsis seek to explain its syntactic and semantic factors, the means by which the elided elements are recovered, and the status of the elided elements. Theoretical accounts of ellipsis can vary greatly depending in part upon whether a constituency-based or a dependency-based theory of syntactic structure is pursued. Background Varieties of ellipsis have long formed a basis of linguistic theory that addresses basic questions of form–meaning correspondence: in particular, how the usual mechanisms of grasping a meaning from a form may be bypassed or supplanted via elliptical structures. In generative linguistics, the term ''ellipsis'' has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
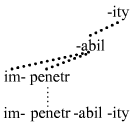
Catena (linguistics)
In linguistics, a catena (English pronunciation: , plural catenas or catenae; from Latin for "chain") is a unit of syntax and morphology, closely associated with dependency grammars. It is a more flexible and inclusive unit than the constituent and may therefore be better suited than the constituent to serve as the fundamental unit of syntactic and morphosyntactic analysis. The catena has served as the basis for the analysis of a number of phenomena of syntax, such as idiosyncratic meaning, ellipsis mechanisms (e.g. gapping, stripping, VP-ellipsis, pseudogapping, sluicing, answer ellipsis, comparative deletion), predicate- argument structures, and discontinuities (topicalization, wh-fronting, scrambling, extraposition, etc.). The catena concept has also been taken as the basis for a theory of morphosyntax, i.e. for the extension of dependencies into words; dependencies are acknowledged between the morphs that constitute words. While the catena concept has been applied mainl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catena (linguistics)
In linguistics, a catena (English pronunciation: , plural catenas or catenae; from Latin for "chain") is a unit of syntax and morphology, closely associated with dependency grammars. It is a more flexible and inclusive unit than the constituent and may therefore be better suited than the constituent to serve as the fundamental unit of syntactic and morphosyntactic analysis. The catena has served as the basis for the analysis of a number of phenomena of syntax, such as idiosyncratic meaning, ellipsis mechanisms (e.g. gapping, stripping, VP-ellipsis, pseudogapping, sluicing, answer ellipsis, comparative deletion), predicate- argument structures, and discontinuities (topicalization, wh-fronting, scrambling, extraposition, etc.). The catena concept has also been taken as the basis for a theory of morphosyntax, i.e. for the extension of dependencies into words; dependencies are acknowledged between the morphs that constitute words. While the catena concept has been applied mainl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb Phrase Ellipsis
In linguistics, verb phrase ellipsis (VP-ellipsis or VPE) is a type of elliptical construction and a type of anaphora in which a verb phrase has been left out (elided) provided that its antecedent can be found within the same linguistic context. For example, "''She will sell sea shells, and he will too''" is understood as "''She will sell sea shells, and he will sell sea shells too"''. VP-ellipsis is well-studied, particularly with regard to its occurrence in English, although certain types can be found in other languages as well. VP ellipsis in English Elided VP introduced by auxiliary verb or infinitive particle With English grammar, VP ellipsis must be introduced by an auxiliary verb (''be'', ''can'', ''do'', ''don't'', ''could'', ''have'', ''may'', ''might'', ''shall'', ''should'', ''will'', ''won't'', ''would'', etc.) or by the infinitive particle ''to''. In the examples below, the elided material of VP ellipsis is indicated using subscripts, strikethrough represents that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constituent (linguistics)
In syntactic analysis, a constituent is a word or a group of words that function as a single unit within a hierarchical structure. The constituent structure of sentences is identified using ''tests for constituents''. These tests apply to a portion of a sentence, and the results provide evidence about the constituent structure of the sentence. Many constituents are phrases. A phrase is a sequence of one or more words (in some theories two or more) built around a head lexical item and working as a unit within a sentence. A word sequence is shown to be a phrase/constituent if it exhibits one or more of the behaviors discussed below. The analysis of constituent structure is associated mainly with phrase structure grammars, although dependency grammars also allow sentence structure to be broken down into constituent parts. Tests for constituents in English Tests for constituents are diagnostics used to identify sentence structure. There are numerous tests for constituents that are co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntactic Relationships
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). There are numerous approaches to syntax that differ in their central assumptions and goals. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from Ancient Greek roots: "coordination", which consists of ''syn'', "together", and ''táxis'', "ordering". Topics The field of syntax contains a number of various topics that a syntactic theory is often designed to handle. The relation between the topics is treated differently in different theories, and some of them may not be considered to be distinct but instead to be derived from one another (i.e. word order can be seen as the result of movement rules derived from grammatical relations). Seq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb Phrase Ellipsis
In linguistics, verb phrase ellipsis (VP-ellipsis or VPE) is a type of elliptical construction and a type of anaphora in which a verb phrase has been left out (elided) provided that its antecedent can be found within the same linguistic context. For example, "''She will sell sea shells, and he will too''" is understood as "''She will sell sea shells, and he will sell sea shells too"''. VP-ellipsis is well-studied, particularly with regard to its occurrence in English, although certain types can be found in other languages as well. VP ellipsis in English Elided VP introduced by auxiliary verb or infinitive particle With English grammar, VP ellipsis must be introduced by an auxiliary verb (''be'', ''can'', ''do'', ''don't'', ''could'', ''have'', ''may'', ''might'', ''shall'', ''should'', ''will'', ''won't'', ''would'', etc.) or by the infinitive particle ''to''. In the examples below, the elided material of VP ellipsis is indicated using subscripts, strikethrough represents that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb Phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase (VP) is a syntactic unit composed of a verb and its arguments except the subject of an independent clause or coordinate clause. Thus, in the sentence ''A fat man quickly put the money into the box'', the words ''quickly put the money into the box'' constitute a verb phrase; it consists of the verb ''put'' and its arguments, but not the subject ''a fat man''. A verb phrase is similar to what is considered a ''predicate'' in traditional grammars. Verb phrases generally are divided among two types: finite, of which the head of the phrase is a finite verb; and nonfinite, where the head is a nonfinite verb, such as an infinitive, participle or gerund. Phrase structure grammars acknowledge both types, but dependency grammars treat the subject as just another verbal dependent, and they do not recognize the finite verbal phrase constituent. Understanding verb phrase analysis depends on knowing which theory applies in context. In phrase structure grammars In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gapping
In linguistics, gapping is a type of ellipsis that occurs in the non-initial conjuncts of coordinate structures. Gapping usually elides minimally a finite verb and further any non-finite verbs that are present. This material is "gapped" from the non-initial conjuncts of a coordinate structure. Gapping exists in many languages, but by no means in all of them, and gapping has been studied extensively and is therefore one of the more understood ellipsis mechanisms. Stripping is viewed as a particular manifestation of the gapping mechanism where just one remnant (instead of two or more) appears in the gapped/stripped conjunct. Basic examples Canonical examples of gapping have a true "gap", which means the elided material appears medially in the non-initial conjuncts, with a remnant to its left and a remnant to its right. The elided material of gapping in all the examples below is indicated with subscripts and a smaller font: ::Some ate bread, and others ate rice. ::Fred likes to pet t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb Phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase (VP) is a syntactic unit composed of a verb and its arguments except the subject of an independent clause or coordinate clause. Thus, in the sentence ''A fat man quickly put the money into the box'', the words ''quickly put the money into the box'' constitute a verb phrase; it consists of the verb ''put'' and its arguments, but not the subject ''a fat man''. A verb phrase is similar to what is considered a ''predicate'' in traditional grammars. Verb phrases generally are divided among two types: finite, of which the head of the phrase is a finite verb; and nonfinite, where the head is a nonfinite verb, such as an infinitive, participle or gerund. Phrase structure grammars acknowledge both types, but dependency grammars treat the subject as just another verbal dependent, and they do not recognize the finite verbal phrase constituent. Understanding verb phrase analysis depends on knowing which theory applies in context. In phrase structure grammars In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependency Grammar
Dependency grammar (DG) is a class of modern grammatical theories that are all based on the dependency relation (as opposed to the ''constituency relation'' of phrase structure) and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency is the notion that linguistic units, e.g. words, are connected to each other by directed links. The (finite) verb is taken to be the structural center of clause structure. All other syntactic units (words) are either directly or indirectly connected to the verb in terms of the directed links, which are called ''dependencies''. Dependency grammar differs from phrase structure grammar in that while it can identify phrases it tends to overlook phrasal nodes. A dependency structure is determined by the relation between a word (a head) and its dependents. Dependency structures are flatter than phrase structures in part because they lack a finite verb phrase constituent, and they are thus well suited for the analysis of languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)