|
Prudential, Warsaw
The Hotel Warszawa is a historic skyscraper hotel in Warsaw, Poland, located on Warsaw Uprising Square along Świętokrzyska Street, Warsaw, Świętokrzyska Street. Built between 1931 and 1933 in the Art Deco style as the Prudential House, and commonly known as the Prudential, it served as a base for the British Prudential plc, Prudential Insurance Company. It was the tallest building in Second Polish Republic, interwar Poland. History At the time of its construction, the eighteen-story, 66m Prudential House was the sixth tallest skyscraper in Europe, after the Telefónica Building, the Boerentoren, the :de:Ullsteinhaus, Ullsteinhaus, the :de:Berlin-Siemensstadt#Wohnarchitektur, Siemensturm and the :de:Bel-Air-Turm, Bel-Air-Turm). Built using a steel framework, it was the tallest building in Warsaw until the Palace of Culture and Science was completed in 1955. Designed by :pl:Marcin Weinfeld, Marcin Weinfeld, the Prudential House included office space on the lower stories and lux ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a greater metropolitan area of 3.1 million residents, which makes Warsaw the 7th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures and comprises 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers . Warsaw is an Alpha global city, a major cultural, political and economic hub, and the country's seat of government. Warsaw traces its origins to a small fishing town in Masovia. The city rose to prominence in the late 16th century, when Sigismund III decided to move the Polish capital and his royal court from Kraków. Warsaw served as the de facto capital of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1795, and subsequently as the seat of Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Tallest Buildings In Poland
Poland has 56 high-rise buildings that stand at least tall, being also one of 17 countries in the world to have a supertall skyscraper (building that rises at least ). Historically, the title of the tallest building in Poland since the Middle Ages up until the 18th century was held by the more than 100-metre (330 ft) tall Mary Magdalene Collegiate Church, in Poznań, which collapsed in 1780 as a result of a fire. The oldest building in Poland exceeding 100 metres is the St. Stanislaus and St. Wenceslaus Cathedral, in Świdnica, built in 1565. The tallest sacral building in the country is the Basilica of Our Lady of Licheń, whose bell tower measures , making it one of the tallest churches in the world. The first non-sacral high-rise buildings in Poland started to be constructed in Warsaw, Katowice, Łódź and Wrocław in the first half of the 20th century. Notable examples include the PAST Building and Prudential, in Warsaw, as well as Drapacz Chmur, in Katowice. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architecture Of Warsaw
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings or other structures. The term comes ; ; . Architectural works, in the material form of buildings, are often perceived as cultural symbols and as works of art. Historical civilizations are often identified with their surviving architectural achievements. The practice, which began in the prehistoric era, has been used as a way of expressing culture for civilizations on all seven continents. For this reason, architecture is considered to be a form of art. Texts on architecture have been written since ancient times. The earliest surviving text on architectural theories is the 1st century AD treatise ''De architectura'' by the Roman architect Vitruvius, according to whom a good building embodies , and (durability, utility, and beauty). Centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAST (Poland)
PAST (, Polish Telephone Joint-stock Company), also known as PASTa, was a Polish telephone operator in the period between World War I and World War II. It is notable for its main headquarters in the Śródmieście Północne neighbourhood of the borough of Śródmieście in Warsaw, which at the time of its construction was the first skyscraper in the Russian Empire and the tallest building of Warsaw. The fight for the building during the Warsaw Uprising of 1944 also added to the legend of the place. History The Swedish-owned company Towarzystwo Akcyjne Telefonów, also known as Cedergren, won a tender in 1900 to expand the Warsaw telephone network. For that purpose, two buildings were built at Zielna street in downtown Warsaw, holding the telephone exchange and the company's headquarters. The building was built between 1904 and 1910 and was constructed in two phases. The lower part, designed by L. Wahlman, I.G. Clason and B. Brochowicz-Rogoyski, was completed in 1904-1905 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the United States and Europe during the 1920s and 1930s. Through styling and design of the exterior and interior of anything from large structures to small objects, including how people look (clothing, fashion and jewelry), Art Deco has influenced bridges, buildings (from skyscrapers to cinemas), ships, ocean liners, trains, cars, trucks, buses, furniture, and everyday objects like radios and vacuum cleaners. It got its name after the 1925 Exposition internationale des arts décoratifs et industriels modernes (International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts) held in Paris. Art Deco combined modern styles with fine craftsmanship and rich materials. During its heyday, it represented luxury, glamour, exuberance, and faith in socia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socialist Realism
Socialist realism is a style of idealized realistic art that was developed in the Soviet Union and was the official style in that country between 1932 and 1988, as well as in other socialist countries after World War II. Socialist realism is characterized by the depiction of communist values, such as the emancipation of the proletariat. Despite its name, the figures in the style are very often highly idealized, especially in sculpture, where it often leans heavily on the conventions of classical sculpture. Although related, it should not be confused with social realism, a type of art that realistically depicts subjects of social concern, or other forms of "realism" in the visual arts. Socialist realism was made with an extremely literal and obvious meaning, usually showing an idealized USSR. Socialist realism was usually devoid of complex artistic meaning or interpretation. Socialist realism was the predominant form of approved art in the Soviet Union from its development in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
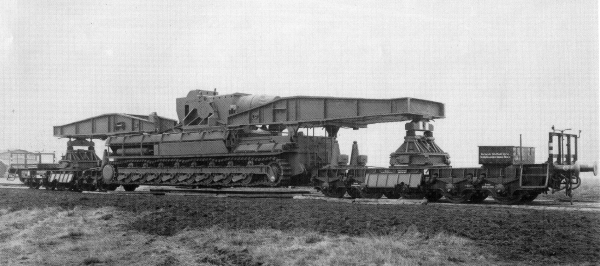
Karl-Gerät
"''Karl-Gerät''" (040/041) (German literally "Karl-device"), also known as ''Mörser Karl'', was a World War II German self-propelled siege mortar (''Mörser'') designed and built by Rheinmetall. Its heaviest munition was a diameter, shell, and the range for its lightest shell of was just over . Each gun had to be accompanied by a crane, a two-piece heavy transport set of railcars, and several modified tanks to carry shells. Seven guns were built, six of which saw combat between 1941 and 1945. It was used in attacking the Soviet fortresses of Brest-Litovsk and Sevastopol, bombarded Polish resistance fighters in Warsaw, participated in the Battle of the Bulge, and was used to try to destroy the Ludendorff Bridge during the Battle of Remagen. One Karl-Gerät has survived and the remainder were scrapped after the war. Development In March 1936 Rheinmetall made a proposal for a super-heavy howitzer to attack the Maginot Line. Their initial concept was for a weapon that wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw Uprising
The Warsaw Uprising ( pl, powstanie warszawskie; german: Warschauer Aufstand) was a major World War II operation by the Polish resistance movement in World War II, Polish underground resistance to liberate Warsaw from German occupation. It occurred in the summer of 1944, and it was led by the Polish resistance Home Army ( pl, Armia Krajowa). The uprising was timed to coincide with the retreat of the German forces from Poland ahead of the Soviet advance. While approaching the eastern suburbs of the city, the Red Army temporarily halted combat operations, enabling the Germans to regroup and defeat the Polish resistance and to Planned destruction of Warsaw, destroy the city in retaliation. The Uprising was fought for 63 days with little outside support. It was the single largest military effort taken by any European Resistance during World War II, resistance movement during World War II. The Uprising began on 1 August 1944 as part of a nationwide Operation Tempest, launched at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
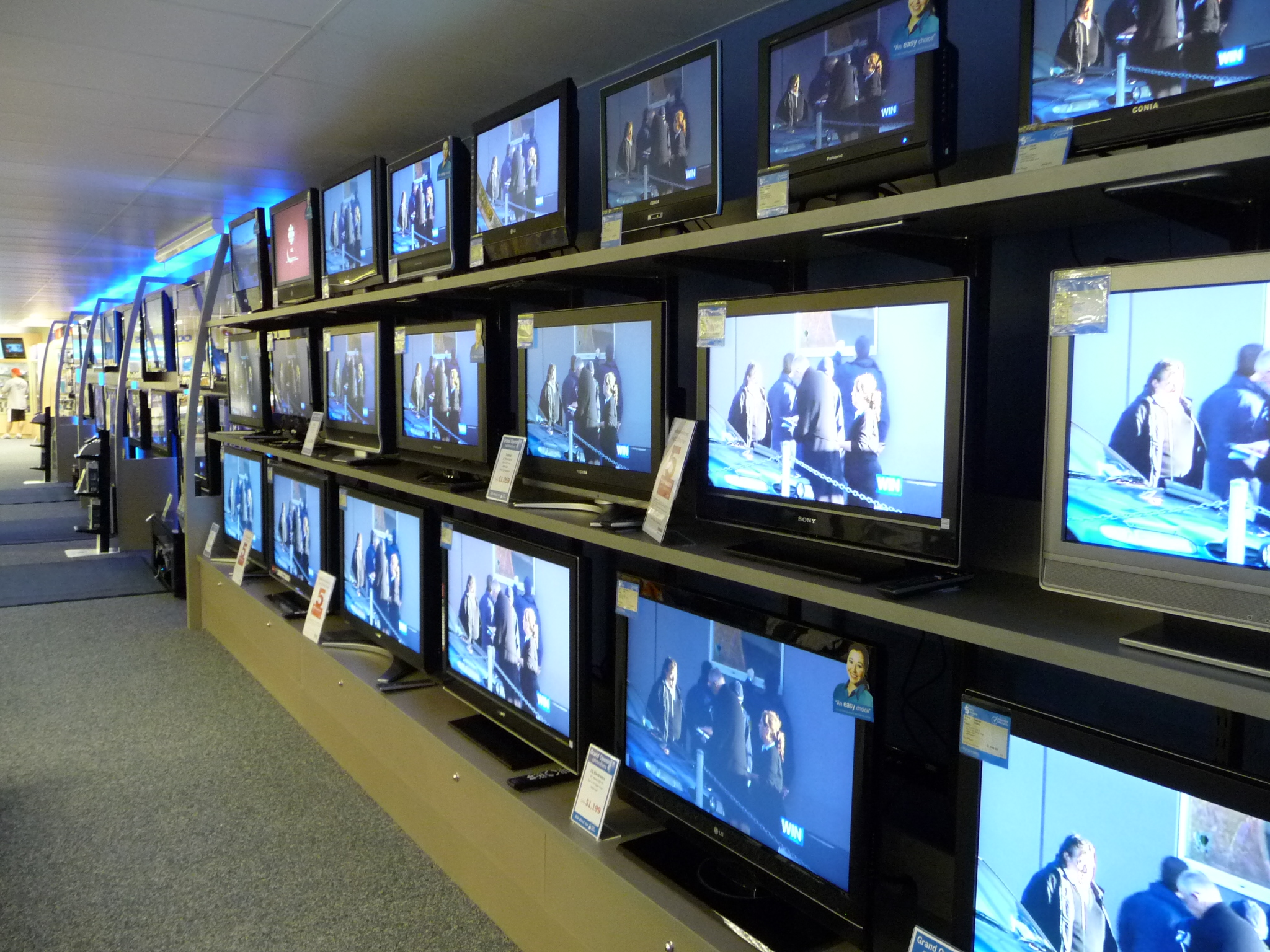
Television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, entertainment, news, and sports. Television became available in crude experimental forms in the late 1920s, but only after several years of further development was the new technology marketed to consumers. After World War II, an improved form of black-and-white television broadcasting became popular in the United Kingdom and the United States, and television sets became commonplace in homes, businesses, and institutions. During the 1950s, television was the primary medium for influencing public opinion.Diggs-Brown, Barbara (2011''Strategic Public Relations: Audience Focused Practice''p. 48 In the mid-1960s, color broadcasting was introduced in the U.S. and most other developed countries. The availability of various types of archival st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_interior.jpg)

.jpg)

