|
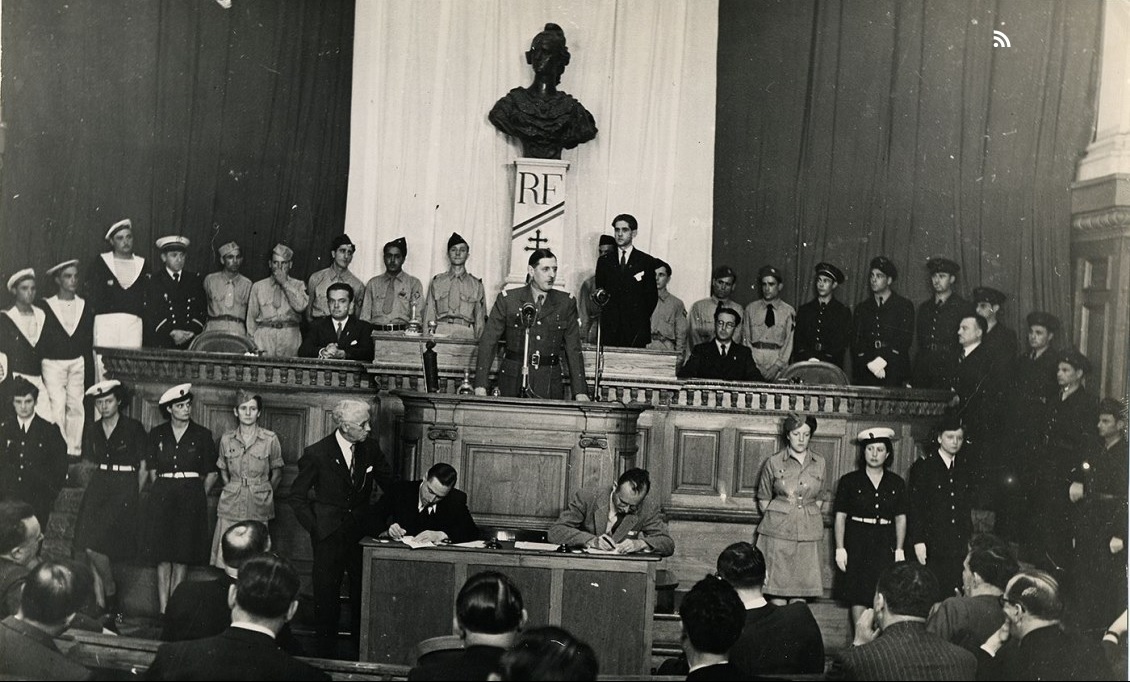
Provisional Consultative Assembly
The Provisional Consultative Assembly (french: Assemblée consultative provisoire) was a governmental organ of Free France that operated under the aegis of the French Committee of National Liberation (CFLN) and that represented the resistance movements, political parties, and territories that were engaged against Germany in the Second World War alongside the Allies. Established by ordinance on 17 September 1943 by the CFLN, it held its first meetings in Algiers, at the Palais Carnot (the former headquarters of the Financial Delegations), between 3 November 1943 and 25 July 1944. On 3 June 1944, it was placed under the authority of the Provisional Government of the French Republic (GPRF), which succeeded the CFLN. Restructured and expanded after the liberation of France, it held sessions in Paris at the Palais du Luxembourg between 7 November 1944 and 3 August 1945. Background In North Africa, where most of the population had been gained at the expense of Pétain and V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Félix Gouin
Félix Gouin (; 4 October 1884 – 25 October 1977) was a French Socialist politician who was a member of the French Section of the Workers' International (SFIO). Personal life Félix Gouin was born in Peypin, Bouches-du-Rhône, the son of school teachers. He studied law in Aix-en-Provence. In 1940 he was among the minority of parliamentarians refusing to grant full powers to Marshal Philippe Pétain. During the war, he was part of the central committee which reconstituted the Human Rights League and also co-founded the Brutus Network, a Socialist Resistance group. In 1946, he then succeeded Charles de Gaulle as head of the French Provisional Government. Gouin's tenure was arguably most notable for seeing the enactment of France's first ever compulsory, amply funded retirement and worker's compensation laws. In addition, both the 40-hour law and overtime pay were re-established, while the comites d'entreprise (works councils) were extended to firms with 50 workers. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazzaville Conference
The Brazzaville Conference (french: Conférence de Brazzaville) was a meeting of prominent Free French leaders held in January 1944 in Brazzaville, the capital of French Equatorial Africa, during World War II. After the Fall of France to Nazi Germany, the collaborationist Vichy France regime controlled the colonies. One by one, however, they peeled off and switched their allegiance to the Free France, a movement led by Charles de Gaulle. In January 1944, Free French politicians and high-ranking colonial officials from the French African colonies met in Brazzaville, now in the Republic of the Congo. The conference recommended political, social and economic reforms and led to the agreement on the Brazzaville Declaration. De Gaulle believed that the survival of France depended on support from the colonies, and he made numerous concessions. They included the end of forced labour, the end of special legal restrictions that applied to indigenous peoples but not to whites, the establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
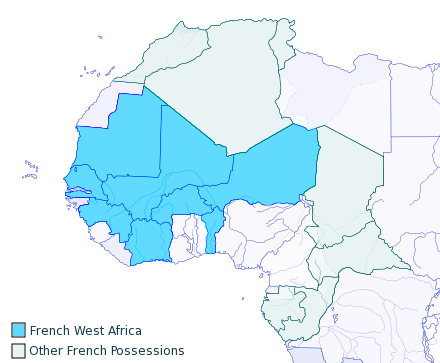
List Of French Possessions And Colonies
From the 16th to the 17th centuries, the First French colonial empire stretched from a total area at its peak in 1680 to over , the second largest empire in the world at the time behind only the Spanish Empire. During the 19th and 20th centuries, the French colonial empire was the second largest colonial empire in the world only behind the British Empire; it extended over of land at its height in the 1920s and 1930s. In terms of population however, on the eve of World War II, France and her colonial possessions totaled only 150 million inhabitants, compared with 330 million for British India alone. The total area of the French colonial empire, with the first (mainly in the Americas and Asia) and second (mainly in Africa and Asia), the French colonial empires combined, reached , the second largest in the world (the first being the British Empire). France began to establish colonies in North America, the Caribbean and India, following Spanish and Portuguese successes duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberation Of France
The liberation of France in the Second World War was accomplished through diplomacy, politics and the combined military efforts of the Allied Powers of World War II, Allied Powers, Free French forces in London and Africa, as well as the French Resistance. Battle of France, Nazi Germany invaded France in May 1940. Their rapid advance through the undefended Ardennes caused a crisis in the French government; the French Third Republic dissolved itself in July, and handed over French Constitutional Law of 1940, absolute power to Marshal Philippe Pétain, an elderly hero of World War I. Pétain signed an Armistice of 22 June 1940, armistice with Germany with the north and west of France under German military administration in occupied France during World War II, German military occupation. Pétain, charged with calling a Constitutional Authority, instead established an authoritarian government in the spa town of Vichy, in the southern ''zone libre'' ("free zone"). Though nominally inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Occupation Of France
The Military Administration in France (german: Militärverwaltung in Frankreich; french: Occupation de la France par l'Allemagne) was an interim occupation authority established by Nazi Germany during World War II to administer the occupied zone in areas of northern and western France. This so-called ' was established in June 1940, and renamed ' ("north zone") in November 1942, when the previously unoccupied zone in the south known as ' ("free zone") was also occupied and renamed ' ("south zone"). Its role in France was partly governed by the conditions set by the Second Armistice at after the success of the leading to the Fall of France; at the time both French and Germans thought the occupation would be temporary and last only until Britain came to terms, which was believed to be imminent. For instance, France agreed that its soldiers would remain prisoners of war until the cessation of all hostilities. The "French State" (') replaced the French Third Republic that had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Third Republic
The French Third Republic (french: Troisième République, sometimes written as ) was the system of government adopted in France from 4 September 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed during the Franco-Prussian War, until 10 July 1940, after the Fall of France during World War II led to the formation of the Vichy government. The early days of the Third Republic were dominated by political disruptions caused by the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871, which the Republic continued to wage after the fall of Emperor Napoleon III in 1870. Harsh reparations exacted by the Prussians after the war resulted in the loss of the French regions of Alsace (keeping the Territoire de Belfort) and Lorraine (the northeastern part, i.e. present-day department of Moselle), social upheaval, and the establishment of the Paris Commune. The early governments of the Third Republic considered re-establishing the monarchy, but disagreement as to the nature of that monarchy and the rightful occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Fourth Republic
The French Fourth Republic (french: Quatrième république française) was the Republicanism, republican government of France from 27 October 1946 to 4 October 1958, governed by the fourth republican constitution. It was in many ways a revival of the French Third Republic, Third Republic that was in place from 1870 during the Franco-Prussian War to 1940 during World War II, and suffered many of the same problems. France adopted the constitution of the Fourth Republic on 13 October 1946. Despite the political dysfunction, the Fourth Republic saw an era of great economic growth in France and the rebuilding of the nation's social institutions and Manufacturing, industry after World War II, with assistance from the United States provided through the Marshall Plan. It also saw the beginning of the rapprochement with former longtime enemy West Germany, Germany, which in turn led to Franco-German co-operation and eventually to the development of the European Union. Some attempts were al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Colonial Empire
The French colonial empire () comprised the overseas colonies, protectorates and mandate territories that came under French rule from the 16th century onward. A distinction is generally made between the "First French Colonial Empire", that existed until 1814, by which time most of it had been lost or sold, and the "Second French Colonial Empire", which began with the conquest of Algiers in 1830. At its apex between the two world wars, the second French colonial empire was the second-largest colonial empire in the world behind the British Empire. France began to establish colonies in North America, the Caribbean and India in the 17th century but lost most of its possessions following its defeat in the Seven Years' War. The North American possessions were lost to Britain and Spain but the latter returned Louisiana (New France) to France in 1800. The territory was then sold to the United States in 1803. France rebuilt a new empire mostly after 1850, concentrating chiefly in Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Relations Of Vichy France
The French State, popularly known as Vichy France, as led by Marshal Philippe Pétain after the Fall of France in 1940 before Nazi Germany, was quickly recognized by the Allies, as well as by the Soviet Union, until 30 June 1941 and Operation Barbarossa. However France broke with the United Kingdom after the destruction of the French Fleet at Mers-el-Kebir. Canada maintained diplomatic relations until the occupation of Southern France (Case Anton) by Germany and Italy in November 1942. Relationships with the Axis Germany The armistice after Germany defeated France in June 1940, included numerous provisions, all largely guaranteed by the German policy of keeping 2 million French prisoners of war in Germany, effectively as hostages. Although Vichy France was nominally in control of all of France–apart from Alsace Lorraine–in practice the Germans controlled over half of the country, including the northern and western coasts, the industrial northeast, and the Paris region. Further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Policy Of Charles De Gaulle
The Foreign policy of Charles de Gaulle covers the diplomacy of Charles de Gaulle as French leader 1940–46 and 1958–1969, along with his followers. Status of France 1940-44 Prime Minister Winston Churchill and his top aides Foreign Minister Anthony Eden, and Chief of the Imperial General Staff General Alan Brooke in 1940-41 moved quickly to establish a base for in London. Control of the overseas French Empire was seen as the central issue, In the British government was prepared to use military support to help regain control. De Gaulle set up a shadow government, including a French National Council and a Resistance movement inside both Vichy France and German-controlled France. To establish his own leadership over like-minded Frenchmen, de Gaulle began broadcasting to France using BBC facilities. De Gaulle was especially keen to set up a Resistance movement inside France, However, many top British officials, as well as Roosevelt and sometimes even Churchill, still hoped fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Defense Council
The Empire Defense Council (also called Council of Defense of the Empire, from french: Conseil de défense de l'Empire) was the embodiment of Free France which constituted the government from 1940 to 1941. Subsequently, this role was assumed by the French National Committee. Creation and legitimacy On 26 June 1940, four days after the Pétain government requested the armistice, General de Gaulle submitted a memorandum to the British government notifying Churchill of his decision to set up a Council of Defense of the Empire and formalizing the agreement reached with Churchill on 28 June, which allowed the Free French forces to be This memorandum led to an agreement on 7 August, but provided for the creation of a French Committee or Council as of 26 June. The agreement of 7 August between de Gaulle and the UK, known as the "Chequers agreement", gave General de Gaulle all the financial independence and resources of a government in exile. The British government considered it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |